(Press-News.org) About The Study: The modified vaccinia Ankara–Bavarian Nordic (MVA-BN) vaccination generated mpox antibodies that waned by 6 to 12 months. In participants who received 2 doses of MVA-BN vaccine, mpox antibody responses at 12 months were comparable to or lower than peak antibody responses in people receiving 1 dose, which provided limited protection.
Quote from corresponding author Dan H. Barouch, MD, PhD:
“In this observational study, we show that mpox antibody responses decline 6-12 months following Jynneos (MVA-BN) vaccination. Our data suggest that protective immunity may be waning in individuals who were vaccinated with this vaccine in 2022.”
Contact information for Dan H. Barouch, MD, PhD: email dbarouch@bidmc.harvard.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.20951)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/10.1001/jama.2024.20951?guestAccessKey=bb14d353-976b-4703-883f-1d2cdabf8ec1&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=100324
END
Decline of mpox antibody responses after modified vaccinia Ankara–Bavarian Nordic vaccination
JAMA
2024-10-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Wider use of convalescent plasma might have saved thousands more lives during pandemic
2024-10-03
A new study led by researchers at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health estimates that thousands of lives could have been saved during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic if convalescent plasma had been used more broadly, particularly in outpatients at high risk for severe disease and in hospitalized patients during their first few days of admission.
Convalescent plasma from patients who had recovered from COVID was used starting in the early months of the pandemic at the urging of a group of physicians who cited the blood ...
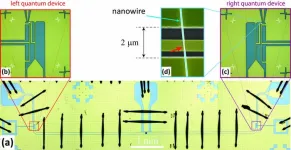
Strong coupling between Andreev qubits mediated by a microwave resonator
2024-10-03
Quantum communication and quantum computing operate based on quantum bits (qubits) as the smallest unit of information — related to bits in a classical computer. Of the many different approaches currently being investigated around the world, one promising option is to use Andreev pair qubits.
These qubits are formed at interfaces between a metal and a superconductor in a process known as Andreev reflection. Here, an electron from the metal enters the superconductor, where it becomes part of an electron pair (a Cooper pair) — while a hole, ...
UNF biological sciences professor receives NIH grant to study muscle atrophy
2024-10-03
Jacksonville, Fla. – A University of North Florida biology professor has been awarded a prestigious four-year National Institutes of Health (NIH) grant totaling over $720K to study the functional role of an enzyme called dual-specificity phosphatase 4 (Dusp4) in skeletal muscle atrophy.
Dr. David Waddell’s NIH-funded research project will help contribute to knowledge about skeletal muscle atrophy associated with neuromuscular disorders, neurodegenerative diseases and aging. Skeletal muscle atrophy is a decrease in muscle mass that occurs when protein degradation exceeds protein ...
Child Health Day 2024: influenza vaccine protects children from infection and hospitalization for the disease, Spanish study shows
2024-10-03
A study published on Eurosurveillance has demonstrated that Spain's influenza vaccination campaign for children aged 6-59 months during the 2023/24 season was effective in preventing acute respiratory infections (ARI) and hospitalisation, as vaccination was recommended for this age group at the national level for the first time.
In the context of Child Health Day 2024, this research emphasises that continued efforts should be made to increase vaccination coverage among children for future seasons.
Context and methods
Influenza A was dominant in the 2023/2024 season, ...
Announcing the 2024 Glenn Foundation Discovery Awards: Jeffrey Friedman, MD, Ph.D/ (the Rockefeller University) and Myriam Heiman, Ph.D. (MIT)
2024-10-03
Santa Barbara, CA and New York, NY -- The Glenn Foundation for Medical Research (GFMR) and the American Federation for Aging Research (AFAR) are pleased to announce the 2024 recipients of the Glenn Foundation Discovery Awards: Jeffrey Friedman, MD, PhD (Professor, The Rockefeller University and Investigator, Howard Hughes Medical Institute) and Myriam Heiman, PhD (Associate Professor of Neuroscience, Massachusetts Institute of Technology).
The Glenn Foundation Discovery Award supports research projects with strong potential to develop pioneering discoveries to understand ...
Stem cell transplants close macular holes in monkeys
2024-10-03
Human stem cell transplants successfully repaired macular holes in a monkey model, researchers report October 3rd in the journal Stem Cell Reports. After transplantation, the macular holes were closed by continuous filling of the space with retinal tissue.
“We confirmed for the first time in a non-human primate model that embryonic stem-derived retinal organoid sheet transplantation facilitates the closure of macular holes,” says senior study author Michiko Mandai of the Kobe City Eye Hospital. “Our results suggest that this method could become a practical, safe, and effective ...
Our brains divide the day into chapters. New psychology research offers details on how.
2024-10-03
The moment a person steps off the street and into a restaurant—to take just one example—the brain mentally starts a new “chapter” of the day, a change that causes a big shift in brain activity. Shifts like this happen all day long, as people encounter new environments, like going out for lunch, attending their kid’s soccer game, or settling in for a night of watching TV.
But what determines how the brain divides the day into individual events that we can understand and remember separately? That’s what a new paper in the journal Current Biology aimed to find ...
Fear of cancer recurrence in adult survivors of childhood cancer
2024-10-03
About The Study: Decades following treatment, one-third of childhood cancer survivors in this study reported elevated fear their cancer will recur or a subsequent malignant neoplasm will develop. Findings suggest that fear of cancer recurrence should be routinely screened, and clinically significant symptoms intervened upon as a part of survivorship care.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Nicole M. Alberts, PhD, email nicole.alberts@concordia.ca.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.36144)
Editor’s ...
AI algorithm for subclinical breast cancer detection
2024-10-03
About The Study: In this retrospective cohort study of women undergoing screening mammography, mean absolute artificial intelligence (AI) scores were higher for breasts developing vs not developing cancer 4 to 6 years before their eventual detection. These findings suggest that commercial AI algorithms developed for breast cancer detection may identify women at high risk of a future breast cancer, offering a pathway for personalized screening approaches that can lead to earlier cancer diagnosis.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Solveig Hofvind, PhD, email sshh@kreftregisteret.no.
To access the embargoed study: ...
Study identifies potential novel drug to treat tuberculosis
2024-10-03
Highlights:
Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which causes tuberculosis (TB), is a threat to public health.
A new study identified that a semi-synthetic compound can be derived from natural compounds and shows potent activity against M. tuberculosis, including multi-drug resistant strains.
This is a promising step toward new potent treatment for TB.
Washington, D.C.—A new study published in the American Society for Microbiology journal Microbiology Spectrum demonstrates that a novel semi-synthetic compound can be derived from ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Breaking through water treatment limits with defect-free, high-efficiency next-generation ceramic filters!
Researchers determine structural motifs of water undecamer cluster
Researchers enhance photocatalytic hydrogen evolution performance of covalent organic frameworks by constitutional isomer strategy
Molecular target drives immunogenicity in cancer immunotherapy
Plant cell structure could hold key to cancer therapies and improved crops
Sustainable hydrogen peroxide production: Breakthroughs in electrocatalyst design for on-site synthesis
Cash rewards for behavior change: A review of financial incentives science in one health contexts and implications
One Health antimicrobial resistance modelling: from science to policy
Artificial feeding platform transforms study of ticks and their diseases
Researchers uncover microscopic mechanism of alkali species dissolution in water clusters
Methionine restriction for cancer therapy: A comprehensive review of mechanisms and clinical applications
White House autism briefing linked to swift shifts in prescribing patterns, study finds
Specialist palliative care can save the NHS up to £8,000 per person and improves quality of life
New research warns charities against ‘AI shortcut’ to empathy
Cannabis compounds show promise in fighting fatty liver disease
Study in mice reveals the brain circuits behind why we help others
Online forum to explore how organic carbon amendments can improve soil health while storing carbon
Turning agricultural plastic waste into valuable chemicals with biochar catalysts
Hidden viral networks in soil microplastics may shape the future of sustainable agriculture
Americans don’t just fear driverless cars will crash — they fear mass job losses
Mayo Clinic researchers find combination therapy reduces effects of ‘zombie cells’ in diabetic kidney disease
Preventing breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors using genomic findings
Carbon nanotube fiber ‘textile’ heaters could help industry electrify high-temperature gas heating
Improving your biological age gap is associated with better brain health
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
Physicists mathematically create the first ‘ideal glass’
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
Rapid population growth helped koala’s recovery from severe genetic bottleneck
[Press-News.org] Decline of mpox antibody responses after modified vaccinia Ankara–Bavarian Nordic vaccinationJAMA