Stem cell transplants close macular holes in monkeys
2024-10-03
(Press-News.org) Human stem cell transplants successfully repaired macular holes in a monkey model, researchers report October 3rd in the journal Stem Cell Reports. After transplantation, the macular holes were closed by continuous filling of the space with retinal tissue.
“We confirmed for the first time in a non-human primate model that embryonic stem-derived retinal organoid sheet transplantation facilitates the closure of macular holes,” says senior study author Michiko Mandai of the Kobe City Eye Hospital. “Our results suggest that this method could become a practical, safe, and effective treatment option with minimal invasive risks, particularly for difficult macular hole cases.”
Macular holes are small gaps that form in the macula—the central part of the retina in the eye. They can cause blurred or distorted central vision, making it difficult to read, drive, or see fine details. In the past decade, advances in surgical techniques have achieved closure rates exceeding 90%, but refractory cases are still a problem. Management of recurrent macular holes after surgery is also challenging. For retinal degenerative diseases, cell-based therapy is a promising strategy for restoring visual function. Although retinal transplantation has shown good anatomic success, visual improvement is limited, and peripheral visual field defects are inevitable.
In the new study, Mandai and collaborators evaluated whether they could overcome these hurdles by transplanting human embryonic stem cell-derived retinal organoid sheets. Transplantation of the retinal tissue resulted in graft survival and maturation and the development of light-detecting retinal cells called photoreceptors, including rods and cones. Additional experiments revealed improvements in eye fixation and responses to light.
However, the researchers pointed out a few caveats, including mild transplantation rejection, which they controlled using steroid injections. “The mild rejection may have limited the functional integration of the transplanted tissue,” Mandai says. “Additionally, this was a single-case result for one eye, and the model did not exactly replicate the pathology of human refractory macular holes. However, the findings suggest that the surgical technique is feasible for human macular holes.”
The authors say further studies will be required to validate the advantage of the stem cell-derived retina, including the protective effect for host retinal cells. More research is also needed to understand how cell composition in the graft influences visual function. For their own part, the researchers plan to examine whether some form of synaptic communication can be established between the host and graft over a longer period of observation.
###
This research was supported by the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED), the Japan Science and Technology Agency, and the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Stem Cell Reports, Iwama et al.: “Transplantation of human pluripotent stem cell-derived retinal sheet in a primate model of macular hole.” https://www.cell.com/stem-cell-reports/fulltext/S2213-6711(24)00264-9
Stem Cell Reports (@stemcellreports), published by Cell Press for the International Society for Stem Cell Research (@ISSCR), is a monthly open access peer-reviewed publication communicating basic discoveries across the spectrum of stem cell research and translational and clinical studies. The journal focuses on shorter, single-point manuscripts that report original research with conceptual or practical advances that are of broad interest to scientists and clinicians across the continuum of stem cell science and application. Visit http://www.cell.com/stem-cell-reports. To receive Cell Press media alerts, please contact press@cell.com.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-10-03
The moment a person steps off the street and into a restaurant—to take just one example—the brain mentally starts a new “chapter” of the day, a change that causes a big shift in brain activity. Shifts like this happen all day long, as people encounter new environments, like going out for lunch, attending their kid’s soccer game, or settling in for a night of watching TV.
But what determines how the brain divides the day into individual events that we can understand and remember separately? That’s what a new paper in the journal Current Biology aimed to find ...
2024-10-03
About The Study: Decades following treatment, one-third of childhood cancer survivors in this study reported elevated fear their cancer will recur or a subsequent malignant neoplasm will develop. Findings suggest that fear of cancer recurrence should be routinely screened, and clinically significant symptoms intervened upon as a part of survivorship care.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Nicole M. Alberts, PhD, email nicole.alberts@concordia.ca.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.36144)
Editor’s ...
2024-10-03
About The Study: In this retrospective cohort study of women undergoing screening mammography, mean absolute artificial intelligence (AI) scores were higher for breasts developing vs not developing cancer 4 to 6 years before their eventual detection. These findings suggest that commercial AI algorithms developed for breast cancer detection may identify women at high risk of a future breast cancer, offering a pathway for personalized screening approaches that can lead to earlier cancer diagnosis.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Solveig Hofvind, PhD, email sshh@kreftregisteret.no.
To access the embargoed study: ...
2024-10-03
Highlights:
Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which causes tuberculosis (TB), is a threat to public health.
A new study identified that a semi-synthetic compound can be derived from natural compounds and shows potent activity against M. tuberculosis, including multi-drug resistant strains.
This is a promising step toward new potent treatment for TB.
Washington, D.C.—A new study published in the American Society for Microbiology journal Microbiology Spectrum demonstrates that a novel semi-synthetic compound can be derived from ...
2024-10-03
EL PASO, Texas (Oct. 3, 2024) – Scientists at The University of Texas at El Paso and Stanford University were recently surprised to find that the natural community of zooplankton — tiny, aquatic animals known to graze on bacteria — present in freshwater and saltwater do not clean water that is contaminated with fecal microorganisms.
The research, published today in the biology journal mSphere, reveals important insights about the limitations of zooplankton in treating bodies of water that have been contaminated with fecal organisms, the team said. A 2017 U.S. water quality inventory ...
2024-10-03
The rising demand for tech jobs presents an outstanding opportunity for growth and inclusivity in the industry. Developing accessible training programs tailored for individuals with disabilities can foster a more diverse workforce. Florida Atlantic University’s College of Education and the College of Engineering and Computer Science have received a $9,961,460 grant from the United States Department of Education’s Office of Special Education and Rehabilitative Services to increase the capacity and participation of transition-age youths and working-age adults with disabilities in high demand technology jobs locally and nationally. ...
2024-10-03
Tending a garden is hard work. Imagine it from the plants’ perspective. Each relies on fine-tuned genetic processes to pass down accurate copies of chromosomes to future generations. These processes sometimes involve billions of moving parts. Even the tiniest disruption can have a cascading effect. So, for plants like Arabidopsis thaliana, it’s good to have a backup plan.
“Chromosomes have to be accurately partitioned every time a cell divides,” explains Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Professor and HHMI Investigator Rob Martienssen. “For that to happen, each chromosome has ...
2024-10-03
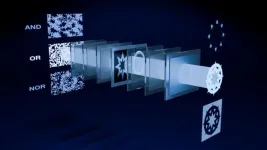
Increasingly complex applications such as artificial intelligence require ever more powerful and power-hungry computers to run. Optical computing is a proposed solution to increase speed and power efficiency but has yet to be realized due to constraints and drawbacks. A new design architecture, called diffraction casting, seeks to address these shortcomings. It introduces some concepts to the field of optical computing that might make it more appealing for implementation in next-generation computing devices.
Whether ...
2024-10-03
Researchers have long observed that a common family of environmental bacteria, Comamonadacae, grow on plastics littered throughout urban rivers and wastewater systems. But what, exactly, these Comamonas bacteria are doing has remained a mystery.
Now, Northwestern University-led researchers have discovered how cells of a Comamonas bacterium are breaking down plastic for food. First, they chew the plastic into small pieces, called nanoplastics. Then, they secrete a specialized enzyme that breaks down the plastic even further. Finally, the bacteria use a ring of carbon atoms from the plastic as a ...
2024-10-03
10-2-24
Contacts:
Sougata Roy, Mechanical Engineering, 515-294-5001, sroy@iastate.edu
Mike Krapfl, News Service, 515-294-4917, mkrapfl@iastate.edu
Researchers study 3D printing tungsten parts for extreme conditions in nuclear reactors
AMES, Iowa – Sougata Roy, who doesn’t study electrons or grids or wind turbines, has found a way to contribute to a clean-energy future.
“This work in advanced manufacturing, particularly in using additive manufacturing, is about making a difference,” ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Stem cell transplants close macular holes in monkeys