(Press-News.org) About The Study: In this retrospective cohort study of women undergoing screening mammography, mean absolute artificial intelligence (AI) scores were higher for breasts developing vs not developing cancer 4 to 6 years before their eventual detection. These findings suggest that commercial AI algorithms developed for breast cancer detection may identify women at high risk of a future breast cancer, offering a pathway for personalized screening approaches that can lead to earlier cancer diagnosis.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Solveig Hofvind, PhD, email sshh@kreftregisteret.no.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.37402)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.37402?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=100324
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
AI algorithm for subclinical breast cancer detection
JAMA Network Open
2024-10-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study identifies potential novel drug to treat tuberculosis
2024-10-03
Highlights:
Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which causes tuberculosis (TB), is a threat to public health.
A new study identified that a semi-synthetic compound can be derived from natural compounds and shows potent activity against M. tuberculosis, including multi-drug resistant strains.
This is a promising step toward new potent treatment for TB.
Washington, D.C.—A new study published in the American Society for Microbiology journal Microbiology Spectrum demonstrates that a novel semi-synthetic compound can be derived from ...
UTEP study: Zooplankton go “Eew!” to cleaning feces contaminated water
2024-10-03
EL PASO, Texas (Oct. 3, 2024) – Scientists at The University of Texas at El Paso and Stanford University were recently surprised to find that the natural community of zooplankton — tiny, aquatic animals known to graze on bacteria — present in freshwater and saltwater do not clean water that is contaminated with fecal microorganisms.
The research, published today in the biology journal mSphere, reveals important insights about the limitations of zooplankton in treating bodies of water that have been contaminated with fecal organisms, the team said. A 2017 U.S. water quality inventory ...
FAU awarded $10M to train people with disabilities for in-demand tech jobs
2024-10-03
The rising demand for tech jobs presents an outstanding opportunity for growth and inclusivity in the industry. Developing accessible training programs tailored for individuals with disabilities can foster a more diverse workforce. Florida Atlantic University’s College of Education and the College of Engineering and Computer Science have received a $9,961,460 grant from the United States Department of Education’s Office of Special Education and Rehabilitative Services to increase the capacity and participation of transition-age youths and working-age adults with disabilities in high demand technology jobs locally and nationally. ...
Plants have a backup plan
2024-10-03
Tending a garden is hard work. Imagine it from the plants’ perspective. Each relies on fine-tuned genetic processes to pass down accurate copies of chromosomes to future generations. These processes sometimes involve billions of moving parts. Even the tiniest disruption can have a cascading effect. So, for plants like Arabidopsis thaliana, it’s good to have a backup plan.
“Chromosomes have to be accurately partitioned every time a cell divides,” explains Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Professor and HHMI Investigator Rob Martienssen. “For that to happen, each chromosome has ...
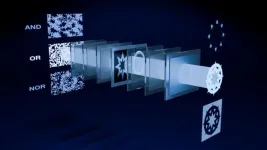
Logic with light
2024-10-03
Increasingly complex applications such as artificial intelligence require ever more powerful and power-hungry computers to run. Optical computing is a proposed solution to increase speed and power efficiency but has yet to be realized due to constraints and drawbacks. A new design architecture, called diffraction casting, seeks to address these shortcomings. It introduces some concepts to the field of optical computing that might make it more appealing for implementation in next-generation computing devices.
Whether ...
Wastewater bacteria can breakdown plastic for food
2024-10-03
Researchers have long observed that a common family of environmental bacteria, Comamonadacae, grow on plastics littered throughout urban rivers and wastewater systems. But what, exactly, these Comamonas bacteria are doing has remained a mystery.
Now, Northwestern University-led researchers have discovered how cells of a Comamonas bacterium are breaking down plastic for food. First, they chew the plastic into small pieces, called nanoplastics. Then, they secrete a specialized enzyme that breaks down the plastic even further. Finally, the bacteria use a ring of carbon atoms from the plastic as a ...
Researchers study 3D printing tungsten parts for extreme conditions in nuclear reactors
2024-10-03
10-2-24
Contacts:
Sougata Roy, Mechanical Engineering, 515-294-5001, sroy@iastate.edu
Mike Krapfl, News Service, 515-294-4917, mkrapfl@iastate.edu
Researchers study 3D printing tungsten parts for extreme conditions in nuclear reactors
AMES, Iowa – Sougata Roy, who doesn’t study electrons or grids or wind turbines, has found a way to contribute to a clean-energy future.
“This work in advanced manufacturing, particularly in using additive manufacturing, is about making a difference,” ...
Promising ‘first’ in Alzheimer’s drug development
2024-10-03
EMBARGOED: NOT FOR RELEASE UNTIL THURSDAY 3 OCTOBER AT 07:00 ET (12:00 UK TIME)
An international team of researchers have made a promising breakthrough in the development of drugs to treat Alzheimer’s Disease.
For the first time, scientists have developed a drug that works on both major aggregation-promoting ‘hotspots’ of the Tau protein - addressing a critical gap in current treatments.
The drug, a peptide inhibitor called RI-AG03, was effective at preventing the build-up of Tau proteins - a key driver of neurodegeneration - in both lab and fruit fly studies.
The ...
Quantum researchers come up with a recipe that could accelerate drug development
2024-10-03
University of Copenhagen mathematicians have developed a recipe for upgrading quantum computers to simulate complex quantum systems, such as molecules. Their discovery brings us closer to being able to predict how new drugs will behave within our bodies and has the potential to revolutionize pharmaceutical development.
Developing a new drug can take more than a decade and cost anywhere from hundreds of millions to billions of euro — with multiple failed attempts along the way. But what if we could predict how a drug worked ...
Experts publish the latest guide for systematic reviews of preclinical research
2024-10-03
A new publication in Nature Reviews Methods Primers provides essential guidance for conducting rigorous systematic reviews on studies with animals and cells. It also highlights the benefits of these reviews, such as improving reproducibility and reducing animal use, and addresses potential pitfalls and recent advancements like review automation.
Systematic reviews synthesize existing evidence in a scientific field to answer specific research questions in a structured and unbiased way. With over 100 million animals used in scientific ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] AI algorithm for subclinical breast cancer detectionJAMA Network Open