(Press-News.org) University of Copenhagen mathematicians have developed a recipe for upgrading quantum computers to simulate complex quantum systems, such as molecules. Their discovery brings us closer to being able to predict how new drugs will behave within our bodies and has the potential to revolutionize pharmaceutical development.
Developing a new drug can take more than a decade and cost anywhere from hundreds of millions to billions of euro — with multiple failed attempts along the way. But what if we could predict how a drug worked in the body before its laboratory trials, and in doing so, speed up the entire process from years to months?
Drugs are composed of molecules, which in turn consist of atoms. And since atoms behave in a quantum mechanical manner, a quantum computer is needed to mimic their behavior. Herein lies the challenge. A traditional computer — no matter how big — could never manage the vast amount of information required by the task with the same precision.
At the University of Copenhagen’s Quantum for Life Centre, a team of physicists, computer scientists, and mathematicians has dedicated years of their careers to understanding how so-called quantum simulators, a type of specialized quantum computer, can be deployed for this task: to simulate, and in doing so predict, the behaviour of molecules.
It’s all about size, or is it?
One fundamental problem that all quantum computer researchers struggle with is size. Today’s quantum computers are simply too small. In practice, this means that they can only simulate a few atoms, which is problematic, because the complex molecules in medicinal drugs often contain millions of atoms.
Now, the Quantum for Life team has taken a significant step toward solving this problem by coming up with a mathematical recipe for making it easier to program quantum simulators, and in doing so, extract more computing power from a simulator of the same size.
“Quantum simulators consist not only of quantum hardware, but of quantum software too — essentially, the recipe for using the quantum simulator. With these new results, we are making a major leap on the software side, presenting a much better method than we’ve had before to scale up the existing hardware and solve more complex tasks,” says Dylan Harley, the research paper’s first author and a doctoral student at the Quantum for Life Centre.
The conventional wisdom about how to scale up a quantum simulator has been that it would need to be built from the ground up. The new quantum algorithm addresses this obstacle and is at the core of the quantum software. The algorithm introduces a controlled amount of noise among the particles being simulated, so as to ensure that the simulation does not stall, but carries on as desired. The idea is of a general nature and can be applied to any type of quantum hardware, regardless of whether it is based on atoms, ions, or even artificial atoms like superconducting qubits.
Could revolutionize pharmaceutical development
“Quantum technology is seen as the key to creating the new and improved medicines of the future. But without the ability to scale quantum simulators effectively, their practical use is very limited. That is why it’s essential to find out how our quantum software can support this scaling. And now we have a recipe to do just that,” says Matthias Christandl, professor of quantum theory and centre leader at the Quantum for Life Centre.
According to Christandl, the prospects will be revolutionary if the researchers succeed in developing an effective quantum simulator:
“If we can use a computer to simulate how a new drug will behave in a human body before conducting any experiments, it could fundamentally change the way we develop and test pharmaceuticals, which will significantly accelerate the amount of time from lab to patient.”
The next step will be to test the mathematical recipe on quantum hardware.
QUANTUM FOR LIFE CENTRE
The Quantum for Life Centre at the University of Copenhagen conducts research to develop quantum algorithms for simulating biomolecules that can then be used to study complex biochemical processes and contribute to accelerating pharmaceutical development.
The Centre is working on building a so-called quantum simulator, a type of computer that contains a controlled system of particles that can accurately mimic various quantum systems, including molecules and atoms. The Centre combines quantum physics, mathematics, chemistry, and computer science research and is funded by the Novo Nordisk Foundation.
ABOUT THE STUDY
The researchers behind the study are Dylan Harley, Frederik Ravn Klausen, Albert H. Werner, and Matthias Christandl from the Quantum for Life Centre, Department of Mathematical Sciences at the University of Copenhagen; Ishaun Datta from Stanford University; Andreas Bluhm from Université Grenoble Alpes, France; and Daniel Stilck França from Université de Lyon, France.
The scientific article about the study has been published in the journal Nature Communications. END
A new publication in Nature Reviews Methods Primers provides essential guidance for conducting rigorous systematic reviews on studies with animals and cells. It also highlights the benefits of these reviews, such as improving reproducibility and reducing animal use, and addresses potential pitfalls and recent advancements like review automation.
Systematic reviews synthesize existing evidence in a scientific field to answer specific research questions in a structured and unbiased way. With over 100 million animals used in scientific ...
Oysters once formed extensive reefs along much of Europe's coastline – but these complex ecosystems were destroyed over a century ago, new research shows.
Based on documents from the 18th and 19th Centuries, the study reveals that European flat oysters formed large reefs of both living and dead shells, providing a habitat supporting rich biodiversity.
Today these oysters are mostly found as scattered individuals – but the researchers found evidence of reefs almost everywhere, from Norway to the Mediterranean, covering at least 1.7 million hectares, an area larger than Northern Ireland.
The research was ...
Utilizing one of the longest-running ecosystem experiments in the Arctic, a Colorado State University-led team of researchers have developed a better understanding of the interplay among plants, microbes and soil nutrients — findings that offer new insight into how critical carbon deposits may be released from thawing Arctic permafrost.
Estimates suggest that Arctic soils contain nearly twice the amount of carbon that is currently in the atmosphere. As climate change has caused portions of Earth’s northernmost polar regions to thaw, scientists have long been concerned about significant amounts of carbon being released in the ...
The legacy of the Soviet Union’s collapse plays a greater role in the foreign policies of Georgia and Ukraine than previous studies have suggested. Conducting foreign policy in former Soviet countries can be a major challenge as the Russian state does not accept the new order. These are the findings outlined in the thesis of political scientist Per Ekman from Uppsala University.
“To understand Russia’s war in Ukraine, for example, it is important to see the war as part of a longer historical event. Since their first day of independence, Georgia and Ukraine have had to deal with Russian ambitions to control the region. For many in the West, it took a ...
Oxford, UK – Genomic Press has released a captivating interview with Professor Robin Dunbar, the eminent evolutionary psychologist and anthropologist whose work has fundamentally altered our understanding of human social networks. Published in the Innovators and Ideas section of Genomic Psychiatry, this in-depth conversation offers unique insights into Professor Dunbar's scientific journey and the far-reaching implications of his research.
Professor Dunbar, best known for conceptualizing "Dunbar's number" - the cognitive limit to the number of stable social relationships ...
Hepatocellular carcinoma, a type of liver cancer associated with hepatitis infections, is known to have a high recurrence rate after cancer removal. Recent advances in antiviral therapy have reduced the number of patients affected, but obesity and diabetes are factors in hepatocellular carcinoma prevalence. However, these factors’ effects on patient survival and cancer recurrence have been unclear.
To gain insights, Dr. Hiroji Shinkawa’s research team at Osaka Metropolitan University’s Graduate School of Medicine analyzed the relationship between diabetes mellitus, obesity, and postoperative outcomes in 1,644 patients with hepatocellular carcinoma ...
Duke-NUS introduces 35 innovative pictograms to make medication instructions clearer, especially for seniors.
These visual aids are designed to ensure patients take their medications correctly and safely, with the aim of improving overall health outcomes.
The team looks to collaborate with healthcare institutions and pharmacies to standardise pictograms portraying medication instructions across Singapore.
SINGAPORE, 3 OCTOBER 2024 – Transforming patient care through clarity and simplicity, Duke-NUS Medical School has introduced visual aids or pictograms designed to make medication instructions clearer. ...
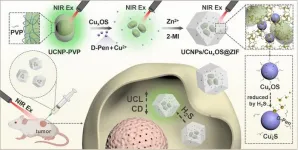
With the continuous development of nanotechnology, more artificial chiral nanomaterials have been constructed. As one of the most representative optical properties of these chiral nanomaterials, CD is a powerful sensing technology. Compared with other analytical methods, CD signal has higher sensitivity, but it cannot achieve in-situ imaging in vivo. Scientists have managed to prepare chiral nanocomposites with more diverse biological functional properties to compensate for this shortcoming. However, some chiral nanocomposites assembled by electrostatic adsorption or other methods are easily dissociated and destroyed in complex physiological environments, resulting in performance ...
FINDINGS
A UCLA research team has created the Comorbid Operative Risk Evaluation (CORE) score to better account for the role chronic illness plays in patient's risk of mortality after operation, allowing surgeons to adjust to patients’ pre-existing conditions and more easily determine mortality risk.
BACKGROUND
For almost 40 years, researchers have used two tools, the Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) and Elixhauser Comorbidity Index (ECI), to measure the impact of existing health conditions on patient outcomes. These tools use ICD codes that are input by medical professionals and billers to account for patient illness. These ...
Mount Sinai Health System today announced that Mount Sinai BioDesign, the medical technology incubator of the Health System, has expanded its reach to become a key, effective partner for the broader MedTech community.
Through synergistic partnerships between clinicians, technologists, and industry partners, Mount Sinai BioDesign is able to offer an array of services, including expert clinical and engineering feedback, preclinical trial development and execution, data gathering and analysis, and pivotal clinical study management. Mount Sinai BioDesign has already established several mature partnerships that have ...