Experts publish the latest guide for systematic reviews of preclinical research
Widespread application would improve research quality and reduce animal use
2024-10-03
(Press-News.org)
A new publication in Nature Reviews Methods Primers provides essential guidance for conducting rigorous systematic reviews on studies with animals and cells. It also highlights the benefits of these reviews, such as improving reproducibility and reducing animal use, and addresses potential pitfalls and recent advancements like review automation.
Systematic reviews synthesize existing evidence in a scientific field to answer specific research questions in a structured and unbiased way. With over 100 million animals used in scientific research annually and a deluge of publications to keep track of, the need for systematic reviews of animal research is more pressing than ever. Before initiating new studies, it's crucial to review the existing literature to avoid losing valuable time and resources. Regular narrative reviews are prone to biases, but systematic reviews follow a rigorous and transparent methodology, helping researchers make sense of conflicting reports and identify gaps in the field to focus on.
The Cochrane organization popularized systematic reviews and meta-analyses in clinical research. The first Cochrane Reviews Handbook, the gold-standard guide on performing systematic reviews, was published in 1994 and continues to be updated. For the last decade, researcher Kim Wever and colleagues from Radboud university medical center, along with collaborators from Switzerland and the UK, have been adapting this approach for animal studies that require different considerations. The new Nature Primer provides a comprehensive guide for the first time to perform systematic reviews of animal research and in vitro research using cells.
The article guides researchers throughout the whole process: defining the research question, writing and registering the protocol, conducting a literature search, selecting studies, critical assessment of evidence, data synthesis and drawing conclusions, ending up with reporting and publication. This process benefits the research, the researcher, and the animals. According to Wever, 'People realize, while doing the review, what types of animal models exist in their field, how they may refine these models, reduce the number of animals used, or even replace the animal model with an animal-free alternative. Looking at the literature through the lens of a systematic reviewer helps the quality of the research and its reporting'.
A global effort
The authors are part of the international collaboration CAMARADES (Collaborative Approach to Meta-Analysis and Review of Animal Experimental Studies). Wever and colleagues also run the PROSPERO4animals platform, where researchers can register their systematic review protocols and get expert feedback before starting the research. 'We frequently encounter poor methodology and it’s critical to amend it before the research is already done. Still, registration in PROSPERO is not mandatory, so I hope researchers will read the new article before they begin their systematic review', says Wever.
Funding for systematic reviews in the Netherlands
The Netherlands has a pioneering funding scheme to incentivize systematic reviews of animal studies and animal-free alternatives. With this fund from ZonMw (Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development), researchers from Dutch institutions can receive 2 months of salary and up to 80 hours of expert supervision by Kim Wever and colleague Carlijn Hooijmans, also from Radboud university medical center. More information on this can be found on the ZonMw website.
This press release is embargoed and the publication will be out on 3rd of October. For media requests, please contact nieuws@radboudumc.nl / +31-243667338.
About the publication
This article will be published in Nature Reviews Methods Primers: Systematic review and meta-analysis of preclinical studies - Benjamin V. Ineichen, Ulrike Held, Georgia Salanti, Malcolm R. Macleod, Kimberley E. Wever.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-10-03
Oysters once formed extensive reefs along much of Europe's coastline – but these complex ecosystems were destroyed over a century ago, new research shows.
Based on documents from the 18th and 19th Centuries, the study reveals that European flat oysters formed large reefs of both living and dead shells, providing a habitat supporting rich biodiversity.
Today these oysters are mostly found as scattered individuals – but the researchers found evidence of reefs almost everywhere, from Norway to the Mediterranean, covering at least 1.7 million hectares, an area larger than Northern Ireland.
The research was ...
2024-10-03
Utilizing one of the longest-running ecosystem experiments in the Arctic, a Colorado State University-led team of researchers have developed a better understanding of the interplay among plants, microbes and soil nutrients — findings that offer new insight into how critical carbon deposits may be released from thawing Arctic permafrost.
Estimates suggest that Arctic soils contain nearly twice the amount of carbon that is currently in the atmosphere. As climate change has caused portions of Earth’s northernmost polar regions to thaw, scientists have long been concerned about significant amounts of carbon being released in the ...
2024-10-03
The legacy of the Soviet Union’s collapse plays a greater role in the foreign policies of Georgia and Ukraine than previous studies have suggested. Conducting foreign policy in former Soviet countries can be a major challenge as the Russian state does not accept the new order. These are the findings outlined in the thesis of political scientist Per Ekman from Uppsala University.
“To understand Russia’s war in Ukraine, for example, it is important to see the war as part of a longer historical event. Since their first day of independence, Georgia and Ukraine have had to deal with Russian ambitions to control the region. For many in the West, it took a ...
2024-10-03
Oxford, UK – Genomic Press has released a captivating interview with Professor Robin Dunbar, the eminent evolutionary psychologist and anthropologist whose work has fundamentally altered our understanding of human social networks. Published in the Innovators and Ideas section of Genomic Psychiatry, this in-depth conversation offers unique insights into Professor Dunbar's scientific journey and the far-reaching implications of his research.
Professor Dunbar, best known for conceptualizing "Dunbar's number" - the cognitive limit to the number of stable social relationships ...
2024-10-03
Hepatocellular carcinoma, a type of liver cancer associated with hepatitis infections, is known to have a high recurrence rate after cancer removal. Recent advances in antiviral therapy have reduced the number of patients affected, but obesity and diabetes are factors in hepatocellular carcinoma prevalence. However, these factors’ effects on patient survival and cancer recurrence have been unclear.
To gain insights, Dr. Hiroji Shinkawa’s research team at Osaka Metropolitan University’s Graduate School of Medicine analyzed the relationship between diabetes mellitus, obesity, and postoperative outcomes in 1,644 patients with hepatocellular carcinoma ...
2024-10-03
Duke-NUS introduces 35 innovative pictograms to make medication instructions clearer, especially for seniors.
These visual aids are designed to ensure patients take their medications correctly and safely, with the aim of improving overall health outcomes.
The team looks to collaborate with healthcare institutions and pharmacies to standardise pictograms portraying medication instructions across Singapore.
SINGAPORE, 3 OCTOBER 2024 – Transforming patient care through clarity and simplicity, Duke-NUS Medical School has introduced visual aids or pictograms designed to make medication instructions clearer. ...
2024-10-03
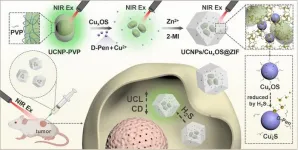
With the continuous development of nanotechnology, more artificial chiral nanomaterials have been constructed. As one of the most representative optical properties of these chiral nanomaterials, CD is a powerful sensing technology. Compared with other analytical methods, CD signal has higher sensitivity, but it cannot achieve in-situ imaging in vivo. Scientists have managed to prepare chiral nanocomposites with more diverse biological functional properties to compensate for this shortcoming. However, some chiral nanocomposites assembled by electrostatic adsorption or other methods are easily dissociated and destroyed in complex physiological environments, resulting in performance ...
2024-10-03
FINDINGS
A UCLA research team has created the Comorbid Operative Risk Evaluation (CORE) score to better account for the role chronic illness plays in patient's risk of mortality after operation, allowing surgeons to adjust to patients’ pre-existing conditions and more easily determine mortality risk.
BACKGROUND
For almost 40 years, researchers have used two tools, the Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) and Elixhauser Comorbidity Index (ECI), to measure the impact of existing health conditions on patient outcomes. These tools use ICD codes that are input by medical professionals and billers to account for patient illness. These ...
2024-10-02
Mount Sinai Health System today announced that Mount Sinai BioDesign, the medical technology incubator of the Health System, has expanded its reach to become a key, effective partner for the broader MedTech community.
Through synergistic partnerships between clinicians, technologists, and industry partners, Mount Sinai BioDesign is able to offer an array of services, including expert clinical and engineering feedback, preclinical trial development and execution, data gathering and analysis, and pivotal clinical study management. Mount Sinai BioDesign has already established several mature partnerships that have ...
2024-10-02
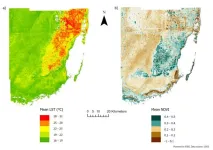
Study Reveals Limits of Using Land Surface Temperature to Explain Heat Hazards in Miami-Dade County
The findings underscore the importance of further research to enhance our understanding of urban heat dynamics in subtropical and tropical regions, ensuring that heat mitigation efforts are informed by the most accurate data available.
A recent study published in the journal PLOS Climate on October 2, 2024, examines the effectiveness of using land surface temperatures (LSTs) as proxies for ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Experts publish the latest guide for systematic reviews of preclinical research
Widespread application would improve research quality and reduce animal use