(Press-News.org) The moment a person steps off the street and into a restaurant—to take just one example—the brain mentally starts a new “chapter” of the day, a change that causes a big shift in brain activity. Shifts like this happen all day long, as people encounter new environments, like going out for lunch, attending their kid’s soccer game, or settling in for a night of watching TV.
But what determines how the brain divides the day into individual events that we can understand and remember separately? That’s what a new paper in the journal Current Biology aimed to find out. The research team, led by Christopher Baldassano, an associate professor of Psychology, and Alexandra De Soares, then a member of his lab, turned up interesting results.
The researchers wanted to better understand what prompts the brain to form a boundary around the events we encounter, effectively registering it as a new “chapter” in the day. One possibility is that new chapters are entirely caused by big changes in a person’s surroundings, like how walking into a restaurant takes them from outdoors to indoors. Another possibility, however, is that the new chapters are prompted by internal scripts that our brain writes based on past experience, and that even big environmental changes might be ignored by our brain if they are not related to our current priorities and goals.
To test their hypothesis, researchers developed a set of 16 audio narratives, each about three to four minutes long. Each narrative took place in one of four locations (a restaurant, an airport, a grocery store, and a lecture hall) and dealt with one of four social situations (a breakup, a proposal, a business deal, and a meet cute).
The researchers found that the way the brain divides up an experience into individual events depends on what a person currently cares about and is paying attention to. When listening to a story about a marriage proposal at a restaurant, for example, subjects’ prefrontal cortex would usually be organizing the story into events related to the proposal, leading up (hopefully) to the final “yes.”
But the researchers found that they could force the prefrontal cortex to organize the story in a different way if they instead asked study participants to focus on the events related to the dinner orders of the couple. For study participants who were told to focus on these details, moments like ordering dishes became critical new chapters in the story.
“We wanted to challenge the theory that the sudden shifts in brain activity when we start a new chapter of our day are only being caused by sudden shifts in the world—that the brain isn’t really ‘doing’ anything interesting when it creates new chapters, it’s just responding passively to a change in sensory inputs,” Baldassano said. “Our research found that isn’t the case: The brain is, in fact, actively organizing our life experiences into chunks that are meaningful to us.”
The researchers measured where the brain created new chapters both by looking at MRI scans of the brain to identify fresh brain activity, and, in a separate group of participants, by asking them to press a button to indicate when they thought a new part of the story had begun.
They found that the brain divided stories into separate chapters depending on the perspective they were told to be attuned to—and it didn’t just apply to the proposal-in-a-restaurant scenario: A person hearing a story about a breakup in an airport could, if prompted to pay attention to details of the airport experience, register new chapters as they went through security and arrived at their gate. Meanwhile, a person who heard a story about a person closing a business deal while grocery shopping could be prompted to register either the new steps of the business deal as new chapters, or to be attuned primarily to the phases of grocery shopping instead. The details that the study participants were prompted to pay attention to influenced what their brain perceived as a new chapter in the story.
Moving forward, the researchers hope to investigate the impact that expectations have on long-term memory. As part of this study, the researchers also asked each participant to tell them everything they remembered about each story. They are still in the process of analyzing the data to understand how the perspective they were asked to adopt while listening to the story changes the way they remember it. More broadly, this study is part of an ongoing effort in the field to build a comprehensive theory about how real-life experiences are divided up into event memories. The results indicate that prior knowledge and expectations are a key ingredient in how this cognitive system works.
Baldassano described the work as a passion project. “Tracking activity patterns in the brain over time is a big challenge that requires using complex analysis tools,” he said: “Using meaningful stories and mathematical models to discover something new about cognition is exactly the kind of unconventional research in my lab that I am most proud of and excited about.”
END
Our brains divide the day into chapters. New psychology research offers details on how.
2024-10-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Fear of cancer recurrence in adult survivors of childhood cancer
2024-10-03
About The Study: Decades following treatment, one-third of childhood cancer survivors in this study reported elevated fear their cancer will recur or a subsequent malignant neoplasm will develop. Findings suggest that fear of cancer recurrence should be routinely screened, and clinically significant symptoms intervened upon as a part of survivorship care.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Nicole M. Alberts, PhD, email nicole.alberts@concordia.ca.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.36144)
Editor’s ...
AI algorithm for subclinical breast cancer detection
2024-10-03
About The Study: In this retrospective cohort study of women undergoing screening mammography, mean absolute artificial intelligence (AI) scores were higher for breasts developing vs not developing cancer 4 to 6 years before their eventual detection. These findings suggest that commercial AI algorithms developed for breast cancer detection may identify women at high risk of a future breast cancer, offering a pathway for personalized screening approaches that can lead to earlier cancer diagnosis.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Solveig Hofvind, PhD, email sshh@kreftregisteret.no.
To access the embargoed study: ...
Study identifies potential novel drug to treat tuberculosis
2024-10-03
Highlights:
Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which causes tuberculosis (TB), is a threat to public health.
A new study identified that a semi-synthetic compound can be derived from natural compounds and shows potent activity against M. tuberculosis, including multi-drug resistant strains.
This is a promising step toward new potent treatment for TB.
Washington, D.C.—A new study published in the American Society for Microbiology journal Microbiology Spectrum demonstrates that a novel semi-synthetic compound can be derived from ...
UTEP study: Zooplankton go “Eew!” to cleaning feces contaminated water
2024-10-03
EL PASO, Texas (Oct. 3, 2024) – Scientists at The University of Texas at El Paso and Stanford University were recently surprised to find that the natural community of zooplankton — tiny, aquatic animals known to graze on bacteria — present in freshwater and saltwater do not clean water that is contaminated with fecal microorganisms.
The research, published today in the biology journal mSphere, reveals important insights about the limitations of zooplankton in treating bodies of water that have been contaminated with fecal organisms, the team said. A 2017 U.S. water quality inventory ...
FAU awarded $10M to train people with disabilities for in-demand tech jobs
2024-10-03
The rising demand for tech jobs presents an outstanding opportunity for growth and inclusivity in the industry. Developing accessible training programs tailored for individuals with disabilities can foster a more diverse workforce. Florida Atlantic University’s College of Education and the College of Engineering and Computer Science have received a $9,961,460 grant from the United States Department of Education’s Office of Special Education and Rehabilitative Services to increase the capacity and participation of transition-age youths and working-age adults with disabilities in high demand technology jobs locally and nationally. ...
Plants have a backup plan
2024-10-03
Tending a garden is hard work. Imagine it from the plants’ perspective. Each relies on fine-tuned genetic processes to pass down accurate copies of chromosomes to future generations. These processes sometimes involve billions of moving parts. Even the tiniest disruption can have a cascading effect. So, for plants like Arabidopsis thaliana, it’s good to have a backup plan.
“Chromosomes have to be accurately partitioned every time a cell divides,” explains Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Professor and HHMI Investigator Rob Martienssen. “For that to happen, each chromosome has ...
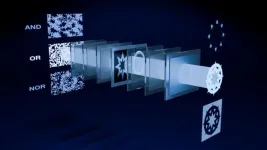
Logic with light
2024-10-03
Increasingly complex applications such as artificial intelligence require ever more powerful and power-hungry computers to run. Optical computing is a proposed solution to increase speed and power efficiency but has yet to be realized due to constraints and drawbacks. A new design architecture, called diffraction casting, seeks to address these shortcomings. It introduces some concepts to the field of optical computing that might make it more appealing for implementation in next-generation computing devices.
Whether ...
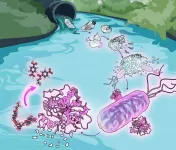
Wastewater bacteria can breakdown plastic for food
2024-10-03
Researchers have long observed that a common family of environmental bacteria, Comamonadacae, grow on plastics littered throughout urban rivers and wastewater systems. But what, exactly, these Comamonas bacteria are doing has remained a mystery.
Now, Northwestern University-led researchers have discovered how cells of a Comamonas bacterium are breaking down plastic for food. First, they chew the plastic into small pieces, called nanoplastics. Then, they secrete a specialized enzyme that breaks down the plastic even further. Finally, the bacteria use a ring of carbon atoms from the plastic as a ...
Researchers study 3D printing tungsten parts for extreme conditions in nuclear reactors
2024-10-03
10-2-24
Contacts:
Sougata Roy, Mechanical Engineering, 515-294-5001, sroy@iastate.edu
Mike Krapfl, News Service, 515-294-4917, mkrapfl@iastate.edu
Researchers study 3D printing tungsten parts for extreme conditions in nuclear reactors
AMES, Iowa – Sougata Roy, who doesn’t study electrons or grids or wind turbines, has found a way to contribute to a clean-energy future.
“This work in advanced manufacturing, particularly in using additive manufacturing, is about making a difference,” ...
Promising ‘first’ in Alzheimer’s drug development
2024-10-03
EMBARGOED: NOT FOR RELEASE UNTIL THURSDAY 3 OCTOBER AT 07:00 ET (12:00 UK TIME)
An international team of researchers have made a promising breakthrough in the development of drugs to treat Alzheimer’s Disease.
For the first time, scientists have developed a drug that works on both major aggregation-promoting ‘hotspots’ of the Tau protein - addressing a critical gap in current treatments.
The drug, a peptide inhibitor called RI-AG03, was effective at preventing the build-up of Tau proteins - a key driver of neurodegeneration - in both lab and fruit fly studies.
The ...