(Press-News.org) A PeerJ Life and Environment study has revealed a significant departure of sperm whales (Physeter macrocephalus) from the central portion of the Gulf of California, linked to the collapse of the jumbo squid (Dosidicus gigas) population, their primary prey. The study, led by researchers Msc. Héctor Pérez-Puig and Dr. Alejandro Arias Del Razo, offers insight into the relationship between apex marine predators and their environment, highlighting sperm whales as key indicators of oceanic health.
The research, conducted over a 9-year period in the eastern Midriff Islands Region of the Gulf of California, utilized extensive survey data and photo-identification techniques to track sperm whale populations. Findings indicate a striking correlation between the decline of jumbo squid and the disappearance of sperm whales from the region, with no sightings recorded from 2016 to 2018.
Key Findings:
Population Decline: Between 2009 and 2015, the population of sperm whales in the central Gulf of California ranged between 20 and 167 individuals, with a total "super population" of 354 whales. However, from 2016 to 2018, sperm whale sightings ceased entirely.
Impact of Jumbo Squid Collapse: General additive models show a positive relationship (R² = 0.644) between sperm whale sightings and jumbo squid landings, indicating that as squid populations dwindled, sperm whales left the region.
Environmental Drivers: The decline of both species is attributed to environmental changes, including sustained ocean warming and intensified El Niño events, which have shifted the ecosystem dynamics in the Gulf of California. The jumbo squid population has been particularly affected, showing a shift to smaller phenotypes, which may no longer sustain larger predators like sperm whales.
Ecosystem Implications:
Sperm whales, as apex predators, play a crucial role in controlling energy flow within marine ecosystems. Their departure from the Gulf of California suggests broader ecosystem changes and raises concerns about the long-term health of the region. The study underscores the importance of long-term data collection in understanding population trends and the effects of climate change on marine species.
Lead author Héctor Pérez-Puig emphasized the broader ecological implications of the findings: "The departure of sperm whales from the Gulf of California serves as a sentinel signal, reflecting significant shifts in marine ecosystems. As the environment changes, so too does the delicate balance between predators and prey."
Conclusion:
The study calls for more detailed analysis to fully understand the movements of sperm whales and their prey, particularly in light of the ongoing "tropicalization" of the Gulf of California. Researchers recommend continued monitoring to assess the impact of environmental changes on marine species and the overall health of the ecosystem.
This research offers a vital contribution to the field of marine biology and ecology, with implications for the conservation of both sperm whales and the larger marine environment in the Gulf of California.
END
Sperm whale departure linked to decline in jumbo squid population in Gulf of California: new study unveils long-term impact on ecosystem health
2024-10-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New apps will enable safer indoor navigation for blind people
2024-10-08
Two new apps will enable blind people to navigate indoor buildings with spoken directions from a smartphone app, providing a safe method of wayfinding where GPS doesn’t work.
UC Santa Cruz professor of Computer Science and Engineering Roberto Manduchi has devoted much of his research career to creating accessible technology for the blind and visually impaired. Throughout years of working with these communities, he has learned that there is a particular need for tools to help with indoor navigation of new spaces.
“Moving about independently in a place that you don't know is particularly ...
Scientists from IOCB Prague help to improve medical drugs
2024-10-08
Researchers from IOCB Prague are furthering the understanding of how medicines work and what it takes to develop their most effective variants. In one current study, they have focused on the disease caused by the protozoan parasite Trichomonas vaginalis, especially because of the recent appearance of strains that are resistant to conventional treatment. In an effort to find a new weak spot of this parasite, the research group led by Dr. Evžen Bouřa has succeeded in preparing a key enzyme complex – the proteasome. This has made it possible to gain knowledge that is indispensable for the development of new effective ...
Recreating a hallmark of Parkinson's disease in human neurons
2024-10-08
Lewy bodies are a hallmark of Parkinson's disease (PD) and other related neurological conditions. Understanding why and how they develop is critical to developing better treatments. A study from The Neuro (Montreal Neurological Institute-Hospital) of McGill University, in collaboration with its Early Drug Discovery Unit, has recreated the growth of Lewy bodies in human neurons and followed their formation to gain important insight into why and how they form. Critically, they find that immune challenge is important for this process, identifying a previously unknown link between the immune system and neurological disease.
Lewy ...
Solar-powered desalination system requires no extra batteries
2024-10-08
MIT engineers have built a new desalination system that runs with the rhythms of the sun.
The solar-powered system removes salt from water at a pace that closely follows changes in solar energy. As sunlight increases through the day, the system ramps up its desalting process and automatically adjusts to any sudden variation in sunlight, for example by dialing down in response to a passing cloud or revving up as the skies clear.
Because the system can quickly react to subtle changes in sunlight, it maximizes the utility of solar energy, producing large quantities of clean water despite ...
When it comes to emergency care, ChatGPT overprescribes
2024-10-08
Generative AI still needs to find the right balance between too little and too much care before it can help doctors make decisions in the Emergency Department.
If ChatGPT were cut loose in the Emergency Department, it might suggest unneeded x-rays and antibiotics for some patients and admit others who didn’t require hospital treatment, a new study from UC San Francisco has found.
The researchers said that, while the model could be prompted in ways that make its responses more accurate, it’s still no match for the clinical judgment of a human doctor.
“This ...
Speakers to tackle global health challenges at WISH 2024
2024-10-08
7 October 2024. Doha, Qatar – The World Innovation Summit for Health (WISH) has today released the first details of speakers confirmed for its upcoming global conference, to be held on 13 and 14 November 2024.
Among those featured at the summit will be WISH executive chair Lord Ara Darzi of Denham and Médecins Sans Frontières’ international president Christos Christou.
Lord Darzi, who recently led an independent investigation on the state of the National Health Service in England, will ...
Mental health app could help prevent depression in young people at high risk
2024-10-08
A cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) app has been found to significantly prevent increases in depression in young people who are at high risk - and could be implemented as a cost effective public mental health measure.
Globally, concern is growing about the high and steadily increasing rates of anxiety and depression in young people. Effective and scalable ways of preventing poor mental health in this group are needed, and digital tools such as mobile apps have been proposed as part of the solution.
Whilst there is emerging evidence ...
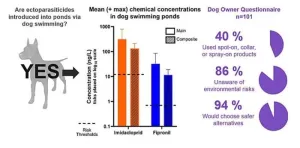
Dogs contaminate London ponds with parasite medications
2024-10-08
Most dog owners didn’t know that flea and tick treatments are dangerous to aquatic life, suggesting more awareness could ease the problem.
A study on Hampstead Heath shows that ponds where dogs are allowed to swim contain levels of two pesticides harmful to invertebrate life.
These pesticides, imidacloprid and fipronil, are used as parasite treatments for flea and tick infestations in cats and dogs, using ‘spot-on’ formulas and flea collars. This is despite these chemicals being banned for agricultural use in 2018 due to their toxicity to bees and other ...
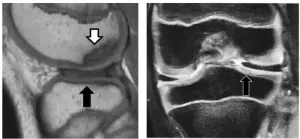
Oh my meniscus: age poses risk of further knee injury in children
2024-10-08
Growing pains are common in maturing children, but sometimes this growth can be irregular and cause injury. Discoid lateral meniscus (DLM), a misshapen knee cartilage, is one such occurrence that can degenerate into osteochondritis dissecans, a joint disorder where the bone and joint begin to separate from the rest of the bones. It has been reported that osteochondritis dissecans of the femoral condyle occurs in approximately 14.5% of cases of DLM, but there has been little analysis of its treatment to date.
Dr. Ken Iida and Specially ...
Increase access to nature in all daily environments and in education
2024-10-08
Although access to nature is a basic human right, people’s actual use of green spaces is subject to inequalities. A Kobe University-led research team analyzed what conditions make it more likely that people are exposed to nature across generations: the availability of green spaces around where they live, work and shop, as well as nature relatedness and past natural experiences. Their findings may inform policies for urban planning and education for the improvement of human health.
Visiting green spaces is good for people’s health, both psychologically and physiologically. ...