(Press-News.org) Artificial Intelligence has learned to master language, generate art, and even beat grandmasters at chess. But can it crack the code of abstract reasoning—those tricky visual puzzles that leave humans scratching their heads? Researchers at USC Viterbi School of Engineering Information Sciences Institute (ISI) are putting AI’s cognitive abilities to the test, pushing the multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) to solve visual problems once reserved for human IQ tests. The result? A glimpse into how far AI has come—and where it still stumbles.
USC Viterbi ISI Research Assistants Kian Ahrabian and Zhivar Sourati recently investigated whether MLLMs can perform nonverbal abstract reasoning, tasks that require both visual perception and logical reasoning, and presented their findings at the Conference on Language Modeling (COLM 2024) in Philadelphia, PA October 7-9, 2024.
Jay Pujara, research associate professor of computer science at the USC Viterbi School of Engineering and an author on the paper said, “Every day we’re bombarded with new headlines about what AI can (and can’t) do, which are often very surprising. We still have such a limited understanding of what new AI models can do, and until we understand these limitations we can’t make AI better, safer, and more useful. This paper helps fill in a missing piece of the story of where AI struggles.”
The Challenge: Can AI See and Think?
“We wanted to see if this new generation of large models, which are able to process images, can reason on their own,” Ahrabian explained. “For example, if you see a yellow circle turning into a blue triangle, can the model apply the same pattern in a different scenario?”
To answer this question, the team tested 24 different MLLMs on puzzles based on Raven’s Progressive Matrices, a well-known test of abstract reasoning. They found that open-source models struggled significantly. “They were really bad. They couldn’t get anything out of it,” Ahrabian said plainly.
In contrast, closed-source models, such as GPT-4V—models developed by private companies and not publicly available for modification—performed better. These models are typically trained with more advanced resources, including larger datasets and more powerful computing systems, giving them a noticeable edge. “We saw some nontrivial results with closed-source models,” Ahrabian added, “Specifically, GPT-4V was relatively good at reasoning, but it’s far from perfect.”
Where the AI Stumbles
A critical part of the study involved dissecting where these models were failing. One key issue was the AI’s ability to accurately process visual information. “We wanted to know if the models could see the details—like colors or lines colliding—and whether that was where they were going wrong,” Ahrabian said.
To isolate the problem, the researchers provided detailed textual descriptions of the images, ensuring the models had all the necessary information in a different format “Even when we removed the visual element and just gave them text, many models still couldn’t reason effectively,” Sourati explained. This revealed a crucial insight: the issue wasn’t just with visual processing—it was with the reasoning itself. Now, the team had a clearer picture of what wasn’t working, which allowed them to refine their focus and guide future improvements.
The Path Forward: Improving AI’s Reasoning
One promising method the researchers explored was “Chain of Thought prompting,” where the AI is prompted to think step by step through reasoning tasks. This approach led to significant improvements in some cases. “By guiding the models with hints, we were able to see up to 100% improvement in performance,” Ahrabian noted.
Despite the remaining challenges, the researchers are optimistic. The study’s findings highlight both the current limitations of AI and the exciting possibilities for future advancements. As these models continue to develop, USC’s research could pave the way for AI that not only understands but reasons—blurring the line between machine intelligence and human cognition.
New Research at a New Conference
Ahrabian and Sourati, Ph.D students at the Thomas Lord Department of Computer Science, presented the paper, The Curious Case of Nonverbal Abstract Reasoning with Multi-Modal Large Language Models, at COLM this week, marking the conference’s inaugural year.
Pujara, who is also the director of the Center on Knowledge Graphs at ISI, commented, “AI is undergoing a major shift with the advent of language models. The emergence of new conferences like COLM to support this evolution is a great way to foster collaboration and inspire students eager to contribute to this rapidly advancing field.”
END
Can advanced AI can solve visual puzzles and perform abstract reasoning?
2024-10-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
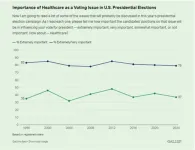
West Health-Gallup poll: Healthcare may be sleeper issue in U.S. presidential campaign
2024-10-09
WASHINGTON, D.C. – Oct. 9, 2024 – Though in this year’s presidential election healthcare has seemingly taken a back to other issues including the economy and democracy, nearly eight in 10 registered voters still say the issue that has been critical in nearly every presidential campaign in modern history, remains extremely (37%) or very important (42%) to whom they cast their vote, according to a new a West Health-Gallup poll of voters. This sentiment is consistent with what’s been expressed in most previous elections, although slightly more ...
UC Irvine scientists track and analyze lofted embers that cause spot fires
2024-10-09
Irvine, Calif., Oct. 9, 2024 — In the chaos of a wildfire, heat, wind, flames and fuel interact to produce embers that are lofted into surrounding areas, starting new spot fires and spreading destruction and property loss in California’s wildland-urban interface. Researchers at the University of California, Irvine have conducted first-of-their-kind field experiments to better understand the physics of these firebrands, and their results can help authorities better model the outcomes of disasters that are happening with greater frequency in a warming climate.
In a paper published recently in the journal Physics of Fluids, UC Irvine team members describe their ...
Uncovering pandemic inequities
2024-10-09
More than four years after the COVID-19 pandemic caused the world to come to a standstill, lessons in pandemic response are still being learned. What we know: the global pandemic disproportionately affected racial and ethnic minority groups across the U.S., with Black and Hispanic individuals being three to four times more likely to die from COVID compared to white individuals.
Daniel Harris, Assistant Professor of Epidemiology in the University of Delaware's College of Health Sciences (CHS), took a deep dive into rarely obtained COVID-19 ...
Microbiome researcher awarded NIH Transformative Research Award to pursue personalized treatment for gut diseases
2024-10-09
Baylor University researcher Aaron Wright, Ph.D., has earned a $5.6 million National Institutes of Health (NIH) Director’s Transformative Research Award for a project that he and collaborators hope could lead to personalized – and revolutionary – treatments for gut microbiome diseases like Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), Crohn’s, Ulcerative Colitis and more. Wright, a nationally recognized microbiome researcher and chemical biologist who serves as The Schofield Endowed Chair in Biomedical Science in Baylor’s Department of Biology, will partner on the project with colleagues from Weill ...
Teresa Bowman, Ph.D., named Chair of Developmental & Molecular Biology at Albert Einstein College of Medicine
2024-10-09
October 9, 2024—(BRONX, NY)—Stem cell researcher Teresa Bowman, Ph.D., has been appointed chair of the department of developmental & molecular biology (DMB) at Albert Einstein College of Medicine after a comprehensive national search. Dr. Bowman will begin her new role on December 1, following the longtime leadership of Richard Stanley, Ph.D.
“Dr. Bowman has demonstrated her leadership abilities, commitment to mentorship, and dedication to the College of Medicine since she ...
Legal system fails to protect people from malicious copyright cases at the cost of sexual privacy, study warns
2024-10-09
Changes need to be made to the UK legal system to protect people from exploitative litigation designed to prey on vulnerabilities, a new study warns.
Reforms need to be made to protect adults from unfairness during copyright enforcement legal proceedings. This would also help to prevent children being exposed to adult pornography online.
The malicious litigation typically involves copyright holders or their agents of online pornographic works obtaining contact details of internet users via a court order to ...
Ancient climate analysis reveals unknown global processes
2024-10-09
According to highly cited conventional models, cooling and a major drop in sea levels about 34 million years ago should have led to widespread continental erosion and deposited gargantuan amounts of sandy material onto the ocean floor. This was, after all, one of the most drastic climate transitions on Earth since the demise of the dinosaurs.
Yet a new Stanford review of hundreds of studies going back decades contrastingly reports that across the margins of all seven continents, little to no sediment has ever been found dating back to this transition. The discovery of this globally extensive gap in the geologic record was published this week in Earth-Science Reviews.
“The ...
Gene therapy shows long-term benefit for patients with a rare pediatric brain disease
2024-10-09
Cerebral adrenoleukodystrophy (CALD) is a rare progressive, genetic brain disease that primarily presents in young boys, causing loss of neurological function and ultimately leading to early death. Researchers from Massachusetts General Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, Boston Children’s Hospital, and collaborators have shown that six years after treatment with the first gene therapy approved for CALD, 94 percent of patients have had no decline in neurological functioning, with over 80 percent remaining free of major disability. Findings, published in two articles in the New England Journal of Medicine, describe long-term outcomes ...
Do people with MS have an increased risk of cancer?
2024-10-09
MINNEAPOLIS – A new study has found some cancers to be slightly more frequent in people with multiple sclerosis (MS) than in people without MS. The study is published in the October 9, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. Types of cancers found to have a small increased risk include bladder, brain and cervical cancers. The study does not prove that MS increases a person’s risk of cancer. It only shows an association.
With MS, the body’s immune system attacks myelin, the fatty, white substance that insulates and protects the nerves. MS is chronic and can be unpredictable and disabling.
“People ...
New research on octopus-inspired technology successfully maneuvers underwater objects
2024-10-09
Using mechanisms inspired by nature to create new technological innovations is a signature of one Virginia Tech research team. The group led by Associate Professor Michael Bartlett has created an octopus-inspired adhesive, inspired by the shape of octopus suckers, that can quickly grab and controllably release challenging underwater objects.
Having the ability to grab and release these underwater objects like heavy rocks, small shells, and soft beads, and other debris could be a powerful tool for underwater salvage and even rescue operations. Their findings have been published in Advanced Science.
This work was performed with undergraduate researchers Austin Via, Aldo Heredia, ...