(Press-News.org) Europe is facing a seed dispersal “crisis,” due to extinction threats and population changes among the animals that do the seed dispersing, according to a new synthesis by Sara Beatriz Mendes and colleagues. Their literature review of animal and plant dispersal pairs helped them reconstruct the first European-wide seed dispersal network. Seed dispersal by animals is a critical part of maintaining healthy ecosystems, especially in fragmented environments like those found throughout Europe. Lack of seed dispersal to connect populations could prevent declining plant populations from recovering. Researchers have thought that the loss of animal species in the region might impact this important process, but little is known about how these disperser-plant pairs are disrupted by species loss. Beatriz Mendes et al. found that one-third of these crucial interactions are of high concern, meaning that the species participating in them are listed as near threatened, threatened, or with declining populations by the IUCN Red List. They further note that 30% of plant species have most of their dispersers in the high concern category. Each animal species dispersed on average 13 plant species, while each plant species had on average nine dispersers. While the researchers acknowledge that there are significant gaps in disperser relationship data, they suggest their findings could be used to target conservation efforts to preserve high-concern disperser relationships.
END
Seed dispersal “crisis” may impact plant species’ future in Europe
Summary author: Becky Ham
2024-10-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Nitrogen deposition has shifted European forest plant ranges westward over decades
2024-10-10
Researchers have documented a shift in plant species ranges toward the poles or higher latitudes in the face of climate warming, but Pieter Sanczuk and colleagues now reveal another unexpected pattern of range shift. For decades, understory plants in European temperate forests have been on the move westward, spurred by differences in nitrogen deposition rates. Westward species distribution shifts were 2.6 times more likely than northward ones, according to the researchers, who also noted that forest canopy changes played a role in this shift as well. The findings suggest that factors beyond climate change, such as atmospheric pollution, are also an important part of redistributing biodiversity. ...
Loss of lake ice has wide-ranging environmental and societal consequences
2024-10-10
Pasadena, CA—The world’s freshwater lakes are freezing over for shorter periods of time due to climate change. This shift has major implications for human safety, as well as water quality, biodiversity, and global nutrient cycles, according to a new review from an international team of researchers led by Carnegie Science’s Stephanie Hampton.
Undertaken by scientists based in the United States, Canada, and Sweden, this analysis represents a major call-to-action for wintertime freshwater ecology research. It is published in Science.
The world has millions of freshwater lakes, most of which freeze during the winter. The team’s rigorous review indicates ...
From chaos to structure
2024-10-10
Pipetting liquids into tiny test tubes, analyzing huge datasets, poring over research publications—all these tasks are part of being a scientist. But breaking this routine is essential. Time away from the usual work environment can spark creative ideas. Lab retreats, for instance, offer a great setting where researchers can engage with other peers, often leading to new collaborations.
The latter was true for Bernat Corominas-Murtra and Edouard Hannezo from the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA). Fascinated by a dataset showcased during a poster session at a collaborative ...
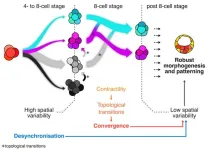
Variability in when and how cells divide promotes healthy development in embryos
2024-10-10
There is variability in when and how cells divide during the development of embryos. While researchers traditionally believed this variability was an obstacle that needed to be regulated, the Hiiragi group now found that it actually promotes healthy development. The results, published in Science on 11 October 2024, encourage other scientists to see the potential of variability and could have significant impact on assisted reproductive technology.
An embryo consists of cells. These cells divide to make new cells, allowing the embryo to grow. The cells experience variability in how and when they divide and in how they interact with each other. Scientists ...
Hidden biological processes can affect how the ocean stores carbon
2024-10-10
New Stanford-led research unveils a hidden factor that could change our understanding of how oceans mitigate climate change. The study, published Oct. 11 in Science, reveals never-before seen mucus “parachutes” produced by microscopic marine organisms that significantly slow their sinking, putting the brakes on a process crucial for removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. The surprising discovery implies that previous estimates of the ocean’s carbon sequestration potential may have been overestimated, but also paves the way toward improving climate models and informing ...
European forest plants are migrating westwards, nitrogen main cause
2024-10-10
New research reveals nitrogen pollution, and to a lesser extent climate change, unexpectedly as the key driver behind surprising westward shifts in the distribution of plants.
A recent study has uncovered that many European forest plant species are moving towards the west due to high nitrogen deposition levels, defying the common belief that climate change is the primary cause of species moving northward. This finding reshapes our understanding of how environmental factors, and in particular nitrogen pollution, influence biodiversity.
While it is widely assumed that rising temperatures are pushing many species toward cooler, northern areas, this research shows that westward ...
Macronutrient and micronutrient intake among US women ages 20 to 44
2024-10-10
About The Study: This cross-sectional study of pregnant and nonpregnant women of reproductive age found that vitamin A, vitamin C, and iron intake decreased over the past 2 decades, which may have substantial maternal and fetal health implications. By identifying these nutrient gaps and trends in inadequate intake in this at-risk population, scientific, health care, and regulatory communities may be better poised to adopt recommendations to improve nutrient intake.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Derek Miketinas, PhD, RD, email dmiketinas@twu.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website ...
Payments by drug and medical device manufacturers to us peer reviewers of major medical journals
2024-10-10
About The Study: More than half of the 1,962 U.S. physicians included in this study who peer reviewed for the most influential medical journals received industry payments in 2020-2022, with most payments for research. Research payments, especially those provided to an institution, may have different implications than general payments for conflicts of interest.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Christopher J. D. Wallis, MD, PhD, email wallis.cjd@gmail.com.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.17681)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article ...
One-third of cancer-related crowdfunding campaigns share medical financial hardship and health-related social needs, new research shows
2024-10-10
In a new, large comprehensive analysis led by the American Cancer Society (ACS), researchers, using a form of Artificial Intelligence (AI), found that more than one-third of fundraising stories on the GoFundMe crowdfunding platform in the United States explicitly shared experiences of medical financial hardships and health-related social needs (HRSNs). The fundraising stories included hardships such as housing and food insecurities, transportation barriers, income loss, lack of sick leave, and disruptions to both work and school. The findings are published today ...
Faulty 'fight or flight' response drives deadly C. difficile infections, research reveals
2024-10-10
The portion of our nervous systems responsible for the “fight or flight” response can shape the severity of potentially deadly C. difficile infections, new research from the University of Virginia School of Medicine reveals.
The findings suggest that doctors may be able to save patients from the infections – a plague for hospitals and nursing homes – by using drugs to quiet the hyperactive nervous system response, the researchers say.
“Compared to how much we know about immune system influences in C. difficile infections, the field is just scratching ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
Modernization can increase differences between cultures
Cannabis intoxication disrupts many types of memory
Heat does not reduce prosociality
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
New molecular switch that boosts tooth regeneration discovered
Jeonbuk National University researchers track mineral growth on bioorganic coatings in real time at nanoscale
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
How AI is integrated into clinical workflow lowers medical liability perception
New biotech company to accelerate treatments for heart disease
One gene makes the difference: research team achieves breakthrough in breeding winter-hardy faba beans
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
[Press-News.org] Seed dispersal “crisis” may impact plant species’ future in EuropeSummary author: Becky Ham