(Press-News.org) In a new, large comprehensive analysis led by the American Cancer Society (ACS), researchers, using a form of Artificial Intelligence (AI), found that more than one-third of fundraising stories on the GoFundMe crowdfunding platform in the United States explicitly shared experiences of medical financial hardships and health-related social needs (HRSNs). The fundraising stories included hardships such as housing and food insecurities, transportation barriers, income loss, lack of sick leave, and disruptions to both work and school. The findings are published today in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) Oncology.
“Sadly, financial hardship is common among cancer survivors across the country, forcing a growing number of patients and their families to use personal crowdfunding as an alternative source to raise money,” said Dr. Zhiyuan “Jason” Zheng, senior principal scientist, health services research at the American Cancer Society and lead author of the study. “These findings show the intense difficulties in meeting basic medical and social needs, underscoring the fragility of safety nets in the U.S.”
For the study, researchers analyzed data from all cancer-related fundraising stories from January 1, 2021, to May 31, 2023, retrieved from the publicly available crowdfunding website GoFundMe. Scientists utilized extensive natural language processing (NLP) modeling (Open AI’s ChatGPT 3.5) to examine cancer-related crowdfunding campaigns, specifically their fundraising stories about reasons for financial assistance, including medical financial hardship and HRSNs. The advances in NLP enabled researchers to transform qualitative data to quantitative data and to help perform statistical analyses.
Study results showed a total of 91,113 cancer-related crowdfunding campaigns were identified and more than 24 million words were analyzed. The proportions with NLP outputs for individual campaign characteristics were age (19.6%), sex (61.1%), marital status (5.1%), family size (12.8%), health insurance coverage (18.3%), employment status (20.6%), living with dependent children (16.4%), and school attendance (9.2%). 79% had NLP interpretations (outputs) for cancer type. 33.9% for stage at diagnosis, 43.3% for new versus recurrent cancer status, 52.6% for cancer-related treatments, and 31% for time from diagnosis to campaign initiation. Among all fundraising stories, 25.5% had NLP outputs for any medical financial hardship, and 24.1% had mentioned HRSNs. Overall, 35.9% of fundraiser stories had NLP outputs with any medical financial hardship or HRSNs.
Dr. Robin Yabroff is senior author of the study. Other ACS researchers contributing to the report include Dr. Shaojun Yu, Dr. Farhad Islami and Dr. Jingxuan Zhao.
# # #
About the American Cancer Society
The American Cancer Society is a leading cancer-fighting organization with a vision to end cancer as we know it, for everyone. For more than 110 years, we have been improving the lives of people with cancer and their families as the only organization combating cancer through advocacy, research, and patient support. We are committed to ensuring everyone has an opportunity to prevent, detect, treat, and survive cancer. To learn more, visit cancer.org or call our 24/7 helpline at 1-800-227-2345. Connect with us on Facebook, X, and Instagram.
END
The portion of our nervous systems responsible for the “fight or flight” response can shape the severity of potentially deadly C. difficile infections, new research from the University of Virginia School of Medicine reveals.
The findings suggest that doctors may be able to save patients from the infections – a plague for hospitals and nursing homes – by using drugs to quiet the hyperactive nervous system response, the researchers say.
“Compared to how much we know about immune system influences in C. difficile infections, the field is just scratching ...
Results of the first phase of a Ceramide Ring Trial have just been published in the renowned journal Nature Communications, representing a significant landmark in the field of lipidomics. This achievement, involving researchers at the University of Vienna and scientific teams in Singapore, Julich and Espoo, represents a groundbreaking advance in the establishment of ceramide reference values, plasma lipids involved in such as cardiovascular diseases. The ring trial was performed under the umbrella of the International Lipidomics Society ...
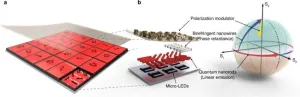
Seoul National University(SNU) College of Engineering announced that a joint research team led by Professor Ki Tae Nam from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at SNU and Professor Junil Choi from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) has developed a novel visible light communication encryption technology with high security using chiral nanoparticles.
Just as a lighthouse provides a guiding beam in the vast darkness of the sea, light-based information transmission has been a crucial means of communication throughout human history. ...
DURHAM, N.C. – Researchers from the HIV Prevention Trials Network (HPTN) presented results from HPTN 091 (“I Am Study”) at the HIVR4P 2024 conference in Lima, Peru. The study examined the acceptability and feasibility of an integrated multicomponent strategy to enhance daily oral HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) uptake and adherence among transgender women in a randomized immediate versus deferred design. The integrated care strategy included the provision of gender-affirming hormone ...
INDIANAPOLIS --More than 8 million people, ages 40 and older, living in the U.S. are affected by peripheral arterial disease, a lifelong medical condition and the most common cause of limb amputation in the country. A data scientist, health services researcher and vascular surgeon who studies health equity, Andrew A. Gonzalez, M.D., J.D., MPH, of the Regenstrief Institute and the Indiana University School of Medicine, has received a 2024 Ralph W. and Grace M. Showalter Research Trust award to conduct a new study, Exploring Causes of Racial Disparities in Amputation Rates in Indiana.
Dr. ...
Mount Sinai’s Department of Rehabilitation and Human Performance has announced the grand opening of the Cohen Center for Recovery From Complex Chronic Illnesses (CoRE), providing clinical care for patients with conditions such as long Lyme disease/Lyme+, long COVID, and other infection-associated complex chronic illnesses such as myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS).
Supported by philanthropy from various donors, including an inaugural gift from Beth and ...
PHILADELPHIA— A $14M grant will fund research on gene-editing therapies for rare metabolic diseases at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania (Penn) and Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP). The research will focus specifically on developing therapies for urea cycle disorders, which impact roughly 1 in every 35,000 children. Using a form of CRISPR technology, the ultimate vision of the four-year grant is to create a platform for rapid development of personalized gene-editing therapies for ...
Imagine yourself sometime in the far future aboard a routine rocket to Mars. Someone just spilled their drink. Without gravity, it collects in floating blobs that ripple right before your eyes. Now freeze.
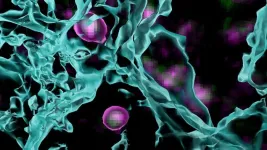
What you see might look something like the above image from Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory’s (CSHL’s) Cheadle lab. But those purple and green blobs aren’t the floating remains of somebody’s drink. They’re mysterious cells in the brain’s visual cortex called OPCs.
The visual cortex processes everything we see. Incoming visual information is ...
In many countries in Africa, up to nine out of ten children suffer from a skin problem, and there are far too few local dermatologists. Artificial intelligence could help with diagnosis, but needs to be trained with the relevant images, so researchers have created a new data set for dark skin tones.
Demand is high, the lack of dermatologists acute: in many countries in Africa, there is less than one dermatology specialist per one million people – compared to the World Health Organization (WHO) recommendation of ...
Smiling during conversations creates warmth, making people feel more comfortable and connected. For example, a friendly smile when meeting someone new can ease nervousness. A smile can soften tension in a debate, showing respect among the participants despite disagreement. In fact, extensive studies have been conducted in the past in an attempt to understand smiling interactions in a natural conversation. Despite these studies, however, little is known about the extent to which one’s smile influences or gets affected by the other person’s smile during a conversation.
A new study sought to investigate this by quantifying ...