(Press-News.org) FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Thursday, October 10, 2024
Contact:
Jillian McKoy, jpmckoy@bu.edu
Michael Saunders, msaunder@bu.edu
##
By nature of their living situation, people experiencing homelessness (PEH) are considered one of the most vulnerable populations to the health impacts of extreme weather.
PEH are particularly vulnerable to heat, and the impact of heat on mortality in this group is substantially greater than for the general population, according to a new study by Boston University School of Public Health (BUSPH).
Published in the American Journal of Epidemiology, the study examined mortality rates in two hot-climate US counties—Clark County in Nevada, which includes Las Vegas, and Los Angeles County in California—and found that daily heat played a significant role in mortality among PEH.
This association was especially notable in Clark County, where nearly 50 percent of deaths during the study period were attributable to higher daily temperatures. Although LA County observed a smaller percentage of heat-attributable deaths, at 5.2 percent, daily heat appeared to contribute to many more deaths than daily cold in both counties.
The study is the first to examine heat-attributable mortality among PEH, providing valuable public health insight as the West Coast reels from an unprecedented October heatwave that has prompted numerous heat alerts in parts of LA and Las Vegas, where temperatures soared to 111 degrees and 104 degrees, respectively, in recent days. Both cities also continue to grapple with persistently high homelessness rates that far exceed the national average. Quantifying the impacts of extreme heat on PEH can inform new interventions and policies that reduce illness and mortality rates among this largely unsheltered population.
“It wasn’t a surprise that our team found an association between heat and mortality for unhoused people, but the magnitude was staggering,” says study senior and corresponding author Dr. Jonathan Jay, assistant professor of community health sciences at BUSPH. “Our estimates are 10 to 100 times greater than the known associations between daily heat and mortality for the general population in LA and Las Vegas, and this finding highlights the moral imperative for our systems to do more.”
He says the new findings also show that heat exposure is an important factor amplifying the vast health inequities for PEH, and highlight the need to center the most marginalized populations in research on climate and health.
For the study, Dr. Jay and colleagues from BUSPH and the David Geffen School of Medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles utilized mortality and daily temperature data for Clark and Los Angeles counties from January 2015 to August 2022 (for Clark County) and November 2022 (for LA County). The team analyzed deaths from all causes, rather than just deaths that were acutely heat- or cold-related (such as fatal heat stroke or hyperthermia), to ensure that the analysis captured all external causes of death as a result of high temperatures. Hot weather was defined as daily temperatures above the minimum mortality temperature (MMT)—the temperature at which mortality risk is lowest in each area—which was 11.6 Celsius (52.8 degrees Fahrenheit) for Clark County and 19.3 Celsius for LA County (66.7 degrees Fahrenheit).
After accounting for long-term and seasonal trends, days of the week, and cumulative effects of consecutive days’ temperatures, the researchers found that mortality risk among PEH increased in both hotter and colder temperatures. The heat was especially harmful in Clark County, where 15 percent of deaths were due to acutely heat-related causes, compared to 0.2 percent in LA County. Extremely hot days accounted for nearly 25 percent of all deaths in Clark County and 2.2 percent of all deaths in LA County.
“It was important to see that deaths increased as daily temperatures increased, from cool days to warmer days, and they spiked on hotter days, starting around 90 degrees Fahrenheit and higher,” Dr. Jay says. “That’s hot, but it’s not even close to the hottest temperatures these cities experience,” he adds, which suggests that public health advocates should be extra vigilant in providing heat-related support beyond the summer season, as climate change continues to extend the number and length of heat waves each year.
Public health strategies that can mitigate heat impacts among PEH in communities include cooling centers, water stations, greening, and reflective painting, the researchers say. But, ultimately, these strategies should embrace a “Housing First” approach, as the primary cause of homelessness is a lack of affordable housing. California, in particular, is consistently ranked as one of the most expensive states to live in the US. Policies that promote stable housing and other financial support for PEH are even more critical following the Supreme Court’s ruling in June that permits cities to ban people from sleeping and camping in public places.
“Too much of our policy is driven by the impulse to hide homelessness from view, rather than to recognize people’s dignity, protect their health, and improve our systems,” says Dr. Jay. “The idea that policing is key to solving this problem is false, and it’s a miscalculation we make over and over again as a society.”
The lead author of the study is Dr. Zihan Lin, a BUSPH postdoctoral fellow at the time of the study and a current assistant professor of biological, geographical and environmental sciences at Cleveland State University.
**
About Boston University School of Public Health
Founded in 1976, Boston University School of Public Health is one of the top ten ranked schools of public health in the world. It offers master's- and doctoral-level education in public health. The faculty in six departments conduct policy-changing public health research around the world, with the mission of improving the health of populations—especially the disadvantaged, underserved, and vulnerable—locally and globally.
END
Extreme heat may substantially raise mortality risk for people experiencing homelessness
A new study found that deaths among unhoused people in two major West Coast cities were 10 to 100 times greater than heat-attributable deaths among the general population
2024-10-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UTA professor earns NSF grants to study human-computer interaction
2024-10-10
Fillia Makedon, a Distinguished Professor in the Computer Science and Engineering Department at The University of Texas at Arlington, has been awarded two new National Science Foundation (NSF) grants involving human-computer interaction. In one, she will study extended reality to assess attention levels in people with attention deficit hyperactivity disorders (ADHD); in the other, she will look at how human-robot interaction could help visually impaired persons perform job duties remotely from home using telerobotic technologies.
The NSF awarded ...
How playing songs to Darwin’s finches helped UMass Amherst biologists confirm link between environment and the emergence of new species
2024-10-10
Embargoed: Not for Release Until 2:00 pm U.S. Eastern Time Thursday, 10 October 2024
October 10, 2024
AMHERST, Mass. – They say that hindsight is 20/20, and though the theory of ecological speciation — which holds that new species emerge in response to ecological changes — seems to hold in retrospect, it has been difficult to demonstrate experimentally, until now. In research recently published in Science, biologists from the University of Massachusetts Amherst have identified a key connection between ecology and speciation in Darwin’s finches, famous residents of the Galápagos Islands, Ecuador. Prior work on these birds ...
A holy grail found for catalytic alkane activation
2024-10-10
An organic catalyst offers chemists precise control over a vital step in activating hydrocarbons.
Researchers at Hokkaido University in Japan have made a significant breakthrough in organic chemistry by developing a novel method to activate alkanes, which are compounds that play a crucial role in the chemical industry. The new technique, published in Science, makes it easier to convert these building blocks into valuable compounds, offering advances in the production of medicines and cutting-edge materials.
Alkanes are a primary component of fossil fuels and are also vital building blocks in the production ...
Galápagos finches could be singing a different song after repeated drought—one that leads to speciation
2024-10-10
Galápagos finches use their beaks to crush seeds and sing songs, so what happens to their musical trills when their beaks change to respond to new menus available under drought? Jeffrey Podos and Katie Schroeder found that the song might not remain the same after six cumulative future drought events that would likely reshape the finch beak. The projected changes in male mating songs could be so significant that they provide a pathway for ecological speciation, the researchers suggest. The researchers tested this idea by digitally modifying ...
Hidden “tails” slow marine snow, impacting deep sea carbon transfer and storage
2024-10-10
Newly discovered microscopic mucus tails – trailing from particles of marine snow particles – slow these particles’ descent into the deep ocean, research finds. This doubles the particles’ residence time in the ocean's upper layers and significantly alters estimates of how much carbon is sequestered in the deep sea. The oceans serve as a vast reservoir and critical sink for atmospheric carbon dioxide. A key process driving carbon sequestration in the ocean is the biological pump, where photosynthetic activity ...
Seed dispersal “crisis” may impact plant species’ future in Europe
2024-10-10
Europe is facing a seed dispersal “crisis,” due to extinction threats and population changes among the animals that do the seed dispersing, according to a new synthesis by Sara Beatriz Mendes and colleagues. Their literature review of animal and plant dispersal pairs helped them reconstruct the first European-wide seed dispersal network. Seed dispersal by animals is a critical part of maintaining healthy ecosystems, especially in fragmented environments like those found throughout Europe. Lack of seed dispersal to connect populations could prevent declining plant populations from ...
Nitrogen deposition has shifted European forest plant ranges westward over decades
2024-10-10
Researchers have documented a shift in plant species ranges toward the poles or higher latitudes in the face of climate warming, but Pieter Sanczuk and colleagues now reveal another unexpected pattern of range shift. For decades, understory plants in European temperate forests have been on the move westward, spurred by differences in nitrogen deposition rates. Westward species distribution shifts were 2.6 times more likely than northward ones, according to the researchers, who also noted that forest canopy changes played a role in this shift as well. The findings suggest that factors beyond climate change, such as atmospheric pollution, are also an important part of redistributing biodiversity. ...
Loss of lake ice has wide-ranging environmental and societal consequences
2024-10-10
Pasadena, CA—The world’s freshwater lakes are freezing over for shorter periods of time due to climate change. This shift has major implications for human safety, as well as water quality, biodiversity, and global nutrient cycles, according to a new review from an international team of researchers led by Carnegie Science’s Stephanie Hampton.
Undertaken by scientists based in the United States, Canada, and Sweden, this analysis represents a major call-to-action for wintertime freshwater ecology research. It is published in Science.
The world has millions of freshwater lakes, most of which freeze during the winter. The team’s rigorous review indicates ...
From chaos to structure
2024-10-10
Pipetting liquids into tiny test tubes, analyzing huge datasets, poring over research publications—all these tasks are part of being a scientist. But breaking this routine is essential. Time away from the usual work environment can spark creative ideas. Lab retreats, for instance, offer a great setting where researchers can engage with other peers, often leading to new collaborations.
The latter was true for Bernat Corominas-Murtra and Edouard Hannezo from the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA). Fascinated by a dataset showcased during a poster session at a collaborative ...
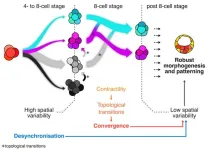
Variability in when and how cells divide promotes healthy development in embryos
2024-10-10
There is variability in when and how cells divide during the development of embryos. While researchers traditionally believed this variability was an obstacle that needed to be regulated, the Hiiragi group now found that it actually promotes healthy development. The results, published in Science on 11 October 2024, encourage other scientists to see the potential of variability and could have significant impact on assisted reproductive technology.
An embryo consists of cells. These cells divide to make new cells, allowing the embryo to grow. The cells experience variability in how and when they divide and in how they interact with each other. Scientists ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Extreme heat may substantially raise mortality risk for people experiencing homelessnessA new study found that deaths among unhoused people in two major West Coast cities were 10 to 100 times greater than heat-attributable deaths among the general population