(Press-News.org) Promising findings by researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and collaborating institutions could lead to the development of a non-invasive stool test and a new therapy for endometriosis, a painful condition that affects nearly 200 million women worldwide. The study appeared in the journal Med.
“Endometriosis develops when lining inside the womb grows outside its normal location, for instance attached to surrounding intestine or the membrane lining the abdominal cavity. This typically causes bleeding, pain, inflammation and infertility,” said corresponding author Dr. Rama Kommagani, associate professor in the Department of Pathology and Immunology at Baylor. “Generally, it takes approximately seven years to detect endometriosis and is often diagnosed incorrectly as a bowel condition. Thus, delayed diagnosis, together with the current use of invasive diagnostic procedures and ineffective treatments underscore the need for improvements in the management of endometriosis.”
“Our previous studies in mice have shown that the microbiome, the communities of bacteria living in the body, or their metabolites, the products they produce, can contribute to endometriosis progression,” Kommagani said. “In the current study, we took a closer look at the role of the microbiome in endometriosis by comparing the bacteria and metabolites present in stools of women with the condition with those of healthy women. We discovered significant differences between them.”
The findings suggested that stool metabolites found in women with endometriosis could be the basis for a non-invasive diagnostic test as well as a potential strategy to reduce disease progression.
The researchers discovered a combination of bacterial metabolites that is unique to endometriosis. Among them is the metabolite called 4-hydroxyindole. “This compound is produced by ‘good bacteria,’ but there is less of it in women with endometriosis than in women without the condition,” said first author Dr. Chandni Talwar, postdoctoral associate in Kommagani’s lab.
“These findings are very exciting,” Talwar said. “There are studies in animal models of the disease that have shown specific bacterial metabolite signatures associated with endometriosis. Our study is the first to discover a unique metabolite profile linked to human endometriosis, which brings us closer to better understanding the human condition and potentially identifying better ways to manage it.”
Furthermore, extensive studies also showed that administering 4-hydroxyindole to animal models of the disease prevented the initiation and progression of endometriosis-associated inflammation and pain.
“Interestingly, our findings also may have implications for another condition. The metabolite profile we identified in endometriosis is similar to that observed in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), revealing intriguing connections between these two conditions,” Kommagani said. “Our findings support a role for the microbiome in endometriosis and IBD.”
The researchers are continuing their work toward the development of a non-invasive stool test for endometriosis. They are also conducting the necessary studies to evaluate the safety and efficacy of 4-hydroxyindole as a potential treatment for this condition.
Other contributors to this work include Goutham Venkata Naga Davuluri, Abu Hena Mostafa Kamal, Cristian Coarfa, Sang Jun Han, Surabi Veeraragavan, Krishna Parsawar, Nagireddy Putluri, Kristi Hoffman, Patricia Jimenez and Scott Biest. The authors are affiliated with one or more of the following institutions: Baylor College of Medicine, University of Arizona –Tucson and Washington University School of Medicine – St. Louis.
This work was funded by NIH/NICHD grants (R01HD102680, R01HD104813) and a Research Scholar Grant from the American Cancer Society.
###
END
A potential non-invasive stool test and novel therapy for endometriosis
2024-10-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Racial and ethnic disparities in age-specific all-cause mortality during the COVID-19 pandemic
2024-10-11
About The Study: In this cross-sectional study of the U.S. population during the COVID-19 public health emergency, excess mortality occurred in all racial and ethnic groups, with disparities affecting several minoritized populations. The greatest relative increases occurred in populations ages 25 to 64. Documented differences deviated from pre-pandemic disparities.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Jeremy Samuel Faust, MD, MS, email jsfaust@bwh.harvard.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.38918)
Editor’s ...
Delft scientists discover how innate immunity envelops bacteria
2024-10-11
Delft scientists discover how innate immunity envelops bacteria
The protein GBP1 is a vital component of our body’s natural defence against pathogens. This substance fights against bacteria and parasites by enveloping them in a protein coat, but how the substance manages to do this has remained unknown until now. Researchers from Delft University of Technology have now unravelled how this protein operates. This new knowledge, published in Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, could aid in the development of medications ...
Workforce diversity is key to advancing One Health
2024-10-11
[Vienna, October 11, 2024] – A new article highlights a critical issue in the One Health approach—an emerging global framework for tackling complex health challenges at the intersection of human, animal, and environmental health. In the article in The Lancet Planetary Health, scientists Amélie Desvars-Larrive and Fariba Karimi from the Complexity Science Hub (CSH) point out that One Health's current framework fails to explicitly address workforce diversity.
According to Desvars-Larrive and Karimi, ...
Genome Research publishes a special issue on innovations in computational biology
2024-10-11
October 11, 2024 – Genome Research (https://genome.org) publishes a special issue highlighting novel advances in computational biology.
In collaboration with the International Conference on Research in Computational Molecular Biology (RECOMB), Genome Research publishes a collection of 20 computational methods and their applications in genomics including spatial, single-cell, and long-read sequencing. These include algorithmic innovations in genomic variation analysis, privacy-preserving algorithms, DNA structural properties, cancer genomics, ...
A quick and easy way to produce anode materials for sodium-ion batteries using microwaves
2024-10-11
The research team led by Dr. Daeho Kim and Dr. Jong Hwan Park at the Nano Hybrid Technology Research Center of the Korea Electrotechnology Research Institute (KERI) has developed a groundbreaking process technology that enables for ultrafast, 30-second preparation of hard carbon anodes for sodium-ion batteries using microwave induction heating.
One of the next-generation secondary batteries, the sodium-ion battery uses sodium (Na) in lieu of the current mainstay, lithium (Li). Sodium, the main component of salt, is more than a thousand times more abundant than lithium and is easier to extract and refine. Furthermore, its lower reactivity compared ...
‘Inside-out’ galaxy growth observed in the early universe
2024-10-11
Astronomers have used the NASA/ESA James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) to observe the ‘inside-out’ growth of a galaxy in the early universe, only 700 million years after the Big Bang.
This galaxy is one hundred times smaller than the Milky Way, but is surprisingly mature for so early in the universe. Like a large city, this galaxy has a dense collection of stars at its core but becomes less dense in the galactic ‘suburbs’. And like a large city, this galaxy is starting to sprawl, with star formation accelerating in the outskirts.
This is the earliest-ever detection of inside-out galactic growth. ...
Protein blocking bone development could hold clues for future osteoporosis treatment
2024-10-11
Scientists have identified a protein that blocks the activity of bone-forming cells (osteoblasts) by stopping them from maturing during the journey to sites of bone formation, a new study has found.
In a paper published in Communications Biology today (Friday 11 October 2024), a team of researchers led by Dr Amy Naylor and Professor Roy Bicknell along with their team including Dr Georgiana Neag from the University of Birmingham have found that protein CLEC14A, which is found on blood vessel cells called endothelial ...
A new method makes high-resolution imaging more accessible
2024-10-11
A classical way to image nanoscale structures in cells is with high-powered, expensive super-resolution microscopes. As an alternative, MIT researchers have developed a way to expand tissue before imaging it — a technique that allows them to achieve nanoscale resolution with a conventional light microscope.
In the newest version of this technique, the researchers have made it possible to expand tissue 20-fold in a single step. This simple, inexpensive method could pave the way for nearly any biology lab to perform nanoscale imaging.
“This democratizes imaging,” says Laura Kiessling, the Novartis Professor ...
Tiny magnetic discs offer remote brain stimulation without transgenes
2024-10-11
Novel magnetic nanodiscs could provide a much less invasive way of stimulating parts of the brain, paving the way for stimulation therapies without implants or genetic modification, MIT researchers report.
The scientists envision that the tiny discs, which are about 250 nanometers across (about 1/500 the width of a human hair), would be injected directly into the desired location in the brain. From there, they could be activated at any time simply by applying a magnetic field outside the body. The new particles could quickly find applications in biomedical research, and eventually, after sufficient testing, ...
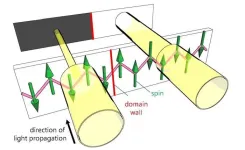
Illuminating quantum magnets: Light unveils magnetic domains
2024-10-11
When something draws us in like a magnet, we take a closer look. When magnets draw in physicists, they take a quantum look.
Scientists from Osaka Metropolitan University and the University of Tokyo have successfully used light to visualize tiny magnetic regions, known as magnetic domains, in a specialized quantum material. Moreover, they successfully manipulated these regions by the application of an electric field. Their findings offer new insights into the complex behavior of magnetic materials at the quantum level, paving the way for future technological advances.
Most of us are familiar with magnets that stick to metal surfaces. But what about those that do not? Among ...