Traces of ancient immigration patterns to Japan found in 2000-year-old genome
Genetic analysis of an individual from the Yayoi period reveals immigration patterns from the Korean Peninsula
2024-10-15
(Press-News.org)
A joint research group led by Jonghyun Kim and Jun Ohashi of the University of Tokyo has demonstrated that the majority of immigration to the Japanese Archipelago in the Yayoi and Kofun periods (between 3000 BCE and 538 CE) came from the Korean Peninsula. The researchers analyzed the complete genome of a “Yayoi” individual and found that, among the non-Japanese populations, the results bore the most similarity to Korean populations. Although it is widely accepted that modern Japanese populations have a dual ancestry, the discovery provides insight into the details of immigration patterns to the archipelago that have eluded scientists thus far. The findings were published in the Journal of Human Genetics.
Today, Japan is an international hub for both business and pleasure. However, this was not always the case. The Japanese Archipelago was relatively isolated during the Jomon period until around 3000 BCE. Then, during the Yayoi and Kofun periods, immigration to the islands from continental Asia began.
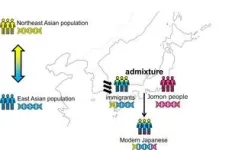
“East Asian-related and Northeast Asian-related ancestries account for over 80% of nuclear genomes of the modern Japanese population,” explains Ohashi, the principal investigator of the study. “However, how the Japanese population acquired these genetic ancestries—that is, the origins of the immigration—is not fully understood.”
Various theories have been proposed to explain the genetic variety in the modern population. Currently, the two contenders are the two-way and three-way admixture models. According to the two-way model, the main source of immigration was the same during the Yayoi and Kofun periods, while the three-way model assumes two different sources. To investigate which model was the better fit, the researchers analyzed the complete nuclear genome of an individual from the Doigahama Site, the archeological site of a Yayoi period cemetery in Yamaguchi prefecture, Japan.
The researchers compared the genome of this Yayoi-period individual with the genome of ancient and modern populations in East Asia and Northeast Asia. The comparison showed close similarity to Kofun period individuals with distinct Jomon-related, East Asian-related, and Northeast Asian-related ancestries. However, a comparison with modern genomes also revealed that the Yayoi individual, except for modern Japanese populations, was the closest to modern Korean populations, which also have both East Asian-related and Northeast Asian-related ancestries.
“Our results suggest that between the Yayoi and Kofun periods, the majority of immigrants to the Japanese Archipelago originated primarily from the Korean Peninsula,” says Ohashi. “The results also mean the three-way admixture model, which posits that a Northeast Asian group migrated to the Japanese Archipelago during the Yayoi period and an East Asian group during the Kofun period, is incorrect.”
Despite the significance of these findings, Ohashi is already looking ahead.
“Since our study has identified the primary origins of the immigrants, our next goal is to examine the genomes of more Yayoi individuals to clarify why more than 80% of the genomic components of the modern Japanese population are derived from immigration and how the admixture between continental Asian and indigenous Jomon people progressed within the Japanese Archipelago.”
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-10-14
DURHAM, N.C. -- Since 1970, 37 countries have cut the probability of their citizens dying before they reach age 70 in half, a milestone that signals the remarkable progress many countries have made in preventing and treating disease. But a new report argues that this goal isn’t out of reach for any country that chooses to cut its premature mortality, even those afflicted by war or poverty.
The report, published Oct. 14 by The Lancet Commission on Investing in Health, lays out a roadmap for every nation that chooses to do so to cut ...
2024-10-14
A team of 50 leading international experts, the Lancet Commission on Investing in Health (CIH), explored this question, resulting in clear, actionable, and achievable measures for achieving this ambitious goal worldwide. Six of the 50 commission members are affiliated with the Bergen Centre for Ethics and Priority Setting in Health (BCEPS), a Norwegian Centre of Excellence based at the University of Bergen, Norway, including BCEPS Director and Professor Ole Frithjof Norheim, BCEPS PhD Research Fellow Sarah Bolongaita, and BCEPS-affiliated researchers Angela Chang (University ...
2024-10-14
Copenhagen, Denmark: Wearing a helmet can prevent brain injury and deaths in cyclists, yet many do not wear a helmet. New research presented at the European Emergency Medicine Congress today (Tuesday) suggests that this is largely due to issues of convenience and comfort. [1]
The study also suggests that more adult cyclists would wear helmets if they were encouraged and incentivised to do so, for example if they were provided with a free helmet, education, and periodic reminders.
The research was presented by Dr Steven Friedman, an emergency doctor at Toronto General Hospital and associate professor at the University ...
2024-10-14
Copenhagen, Denmark: Half of all patients with sepsis admitted to an emergency medical department died within two years, according to Danish researchers investigating factors that could predict outcomes for these patients.
Dr Finn E. Nielsen, a senior scientist in the Department of Clinical Epidemiology at Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark, told the European Emergency Medicine Congress today (Tuesday) [1] that he and his colleagues examined deaths over a long follow-up period in a prospective study of 714 adult patients admitted to the emergency department with sepsis. Their findings ...
2024-10-14
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 14 October 2024
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent. ...
2024-10-14
St. Louis, MO (October 14, 2024) According to the Centers for Disease Control, nearly 20% of children and teens are considered obese. Research shows it can have a dramatic impact on a variety of health conditions, including arthritis, heart conditions and other metabolic problems, and the American Academy of Pediatrics now recommends early and intensive treatment to combat obesity. Over the last four years, Shriners Children’s St. Louis researchers have been working to develop a new way to prevent the effects of childhood obesity.
Using gene therapy, Shriners Children’s St. Louis Director of Research Dr. Farshid Guilak and Senior Scientist Dr. Ruhang Tang ...
2024-10-14
About The Study: Mpox is a viral infection transmitted primarily through close skin to skin contact that typically causes a self-resolving illness but can result in severe illness and death in immunocompromised individuals. First-line therapy is supportive care, although patients with severe mpox infection may be treated with advanced therapeutics. Mpox vaccination is effective and, if available, should be offered to individuals at risk of exposure to mpox.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Jason Zucker, MD, MS, email Jz2700@cumc.columbia.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media ...
2024-10-14
About The Study: Preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) use increased between 2013 and 2023, with generic tenofovir disoproxil fumarate/emtricitabine (TDF/FTC) being the most frequently prescribed medication since 2021. Injectable PrEP use was low likely because of barriers such as the high cost of stocking this expensive medication in clinics.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Laura M. Mann, PhD, MPH, email lmann@cdc.gov.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.21493)
Editor’s ...
2024-10-14
About The Study: Most U.S. hospital websites explicitly included sexual and gender minority (SGM) populations in their nondiscrimination policies, but only a quarter of adult hospitals had an SGM-friendly clinician directory and provided information about SGM-related resources or hospital-based services. Pediatric hospitals more frequently posted SGM-related information than adult hospitals. Hospitals in states with more discriminatory policies were less likely to provide SGM-related information online.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Alex S. Keuroghlian, MD, MPH, email akeuroghlian@mgb.org.
To ...
2024-10-14
Study finds use of naloxone by Good Samaritans is up, but not nearly enough
Ohio State and National Registry of EMTs research highlights importance of public’s help in opioid overdose response
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Use of a lifesaving drug to reverse opioid drug overdoses is growing, but not fast enough. That’s according to new research in JAMA Network Open from The Ohio State University College of Medicine, College of Public Health and the National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians.
In the first study of its kind, the research team looked at national use of naloxone by people without medical training to treat an opioid drug overdose.
“Naloxone ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Traces of ancient immigration patterns to Japan found in 2000-year-old genome
Genetic analysis of an individual from the Yayoi period reveals immigration patterns from the Korean Peninsula



