(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, Oct. 15, 2024 – The U.S. is ramping up plans for a major increase in offshore wind production, with 30 gigawatts of new installations expected by 2030 and a total of 110 gigawatts by 2050. But to be successful, the country needs to design turbines that can withstand the challenges of tropical storms.
“Extreme weather impacts on offshore wind turbines are not fully understood by the industry,” author Jiali Wang said. “Manufacturers design wind turbines based on international design standards, but better models and data are needed to study the impacts of extreme weather to inform and revise design standards.”
In a comprehensive review published this week in the Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy, by AIP Publishing, Wang and colleagues at Argonne National Laboratory, the National Science Foundation National Center of Atmospheric Research, the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Michigan Technological University, and Pacific Northwest National Laboratory critically examined the landscape of tropical storm observation technology. They also reviewed advanced physics-based modeling and data-driven models that use AI and machine learning.
“The intensity of extreme weather events is not well predicted by traditional methods,” Wang said. “After reviewing the state-of-the-science technologies and methods, we need to do the work to bridge between the scales of weather data, whole wind farms, and individual wind turbines.”
For example, offshore wind turbine standards created by the International Electrotechnical Commission do not account for the complexity of extreme weather impacts on turbines, and they could benefit from robust data from a variety of new technologies and data-sharing collaborations.
The authors note advanced modeling techniques are rapidly developing, such as deep neural networks that downscale existing regional data to point-scale data using super-resolution techniques. Another key advancement is using machine learning methods for dynamic warm potential predictions, which can better predict the intensity of a storm.
“We need models that address problems at very small scales, such as understanding what happens from one turbine to another,” Wang said. “Satellites and other remote sensing technologies that can scan a region autonomously are helpful during extreme weather conditions, but their accuracy may be affected by heavy rain, and they cannot provide wind information at multiple altitudes like rotor heights.”
Implementing data that reflect complex interactions of multiple storm effects at different scales is important for updating models and turbine design standards, the authors note, along with understanding the impacts climate change will have on storm predictions.
“Both high winds and waves are damaging, because waves can create energy that can drive ocean currents,” Wang said. “These three components of wind, waves, and ocean currents can come from and go in different directions. This is known as misalignment and makes the turbine more vulnerable.”
###
The article “Modeling and observations of North Atlantic cyclones: Implications for U.S. offshore wind energy” is authored by Jiali Wang, Eric Hendricks, Christopher M. Rozoff, Matt Churchfield, Longhuan Zhu, Sha Feng, William J. Pringle, Mrinal Biswas, Sue Ellen Haupt, Georgios Deskos, Chunyong Jung, Pengfei Xue, Larry K. Berg, George Bryan, Branko Kosovic, and Rao Kotamarthi. It will appear in Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy on Oct. 15, 2024 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0214806). After that date, it can be accessed at https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0214806.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy is an interdisciplinary journal that publishes across all areas of renewable and sustainable energy relevant to the physical science and engineering communities. Topics covered include solar, wind, biofuels and more, as well as renewable energy integration, energy meteorology and climatology, and renewable resourcing and forecasting. See https://pubs.aip.org/aip/jrse.
###
END
Updating offshore turbine designs to reflect storms’ complexity is key
New designs for wind turbines require addressing problems at smaller scales
2024-10-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Hospital strain during the COVID-19 pandemic and outcomes in older racial and ethnic minority adults
2024-10-15
About The Study: In this cross-sectional study, older adults hospitalized with sepsis were more likely to die or experience major morbidity as the hospital COVID-19 burden increased. These increases in adverse outcomes were greater in magnitude among members of minority populations than for white individuals.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Laurent G. Glance, MD, email laurent_glance@urmc.rochester.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.38563)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, ...
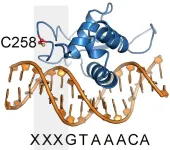
Scientists unveils key role of “selfish DNA” in early human development
2024-10-15
A critical transition in early human development is regulated not by our own genes, but by DNA elements called transposons that can move around the genome, Sinai Health researchers have found.
This remarkable discovery challenges our previous understanding of these elusive DNA segments, shedding new light on the roles they play in human development and disease.
“People tend to think of transposons as akin to viruses where they hijack our cells for the sole purpose of propagating themselves,” says study’s senior co-author Dr. Miguel Ramalho-Santos, Senior Investigator at the Lunenfeld-Tanenbaum Research Institute (LTRI), part of Sinai Health, and Professor ...
Bonobos may be more vulnerable than previously thought, suggests genetics study
2024-10-15
Bonobos, endangered great apes that are among our closest relatives, might be more vulnerable than previously understood, finds a genetics study led by a UCL researcher that reveals three distinct populations.
The three groups of bonobos have been living separately in different regions in Central Africa for tens of thousands of years, according to the study published in Current Biology by an international research team co-led by UCL, University of Vienna, and Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology ...
Scripps Research scientists discover chemical probes for previously “undruggable” cancer target
2024-10-15
LA JOLLA, CA—Hormone-driven cancers, like those of the breast and prostate, often rely on a tricky-to-target protein called Forkhead box protein 1 (FOXA1). FOXA1 mutations can enable these types of cancers to grow and proliferate. Today, FOXA1 is notoriously difficult to block with drugs—but that may soon change.
Scripps Research scientists have identified a crucial binding site on FOXA1 that could pave the way for future cancer treatments. The team’s findings, which were published in Molecular Cell on October 15, 2024, also mapped out how tiny drug-like chemical compounds—called small molecules—interact with the protein.
While ...
Giant Magellan telescope begins primary mirror support system testing
2024-10-15
TUCSON, AZ — October 15, 2024 — The Giant Magellan Telescope today announced the successful installation of one of its completed 8.4-meter-diameter primary mirrors into a support system prototype at the University of Arizona’s Richard F. Caris Mirror Lab. This highly sophisticated system — comparable in size to half a basketball court and containing three times the number of parts of a typical car — is vital to the telescope’s optical performance and precision control. The milestone marks the start of a six-month optical testing phase to demonstrate that the support system can control the mirror as required, validating the revolutionary capabilities ...
Experimental cancer drug eliminates bone metastases caused by breast cancer in lab models
2024-10-15
In a new study led by Johns Hopkins Medicine, the drug RK-33 has demonstrated promise in treating breast cancer that has spread to the bone (breast cancer bone metastasis). RK-33 was previously shown to help treat other types of cancer and viral illnesses.
Patients with breast cancer and bone metastasis have limited treatment options and often rely on palliative care to ease difficult symptoms, including frailty and pain. In most cases, breast cancer with bone metastasis is incurable.
Now, corresponding author Venu Raman, Ph.D., ...
Political candidates who fight climate change stand to benefit in election
2024-10-15
A majority of Floridians expressed support for political candidates who fight climate change in a new Florida Atlantic University survey. The survey found that nearly 52% of respondents agreed that a candidate with a record of reducing climate impacts was more likely to get their vote.
The Invading Sea’s Florida Climate Survey also revealed strong support in the state for increasing renewable energy use and teaching climate science in K-12 classrooms. The survey is the 11th conducted by the FAU Center for Environmental Studies ...
Stand up to Cancer announces new grants supporting pioneering research in six cancer types
2024-10-15
LOS ANGELES – Oct. 15, 2024 – Stand Up To Cancer® (SU2C) today announced grants to several teams of leading cancer investigators in support of cutting-edge research in a variety of cancers including head and neck, pediatric, pancreatic, breast, rectal and gastro-esophageal cancers, as well as research focused on how the microbiome communicates with the immune system.
“These new grants emphasize SU2C’s support of collaborative, trailblazing research that pushes the field forward and helps people impacted by some of the most common or difficult-to-treat cancers,” said Julian Adams, Ph.D., president and CEO of SU2C. “With an emphasis on answering ...
Researchers awarded $1.3M to help military Veterans battling Acute Myeloid Leukemia
2024-10-15
CLEVELAND—With a new four-year, $1.3 million grant from the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, researchers at Case Western Reserve University are investigating a new approach to treat Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) in military Veterans.
AML is the most common form of blood cancer in adults, and many patients suffer relapses—especially Veterans, due to exposure to harmful chemicals and radiation during active duty, according to the National Center for Biotechnology Information.
There is no effective treatment for AML and, according to the National Institutes of Health, half of treated patients suffer a relapse after therapy—mainly ...
New hub for high-energy astrophysics — CTAO Science Data Management Centre opens at DESY in Zeuthen
2024-10-15
Zeuthen, Germany – On 14 October 2024, the Cherenkov Telescope Array Observatory (CTAO), along with hosting partners and shareholders Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron DESY, celebrated the official inauguration of the Science Data Management Centre (SDMC) on the DESY campus in Zeuthen, Germany.
The ceremony, chaired by Prof. Christian Stegmann, Head of DESY Zeuthen, was opened by Mario Brandenburg, Parliamentary State Secretary at the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF), and Tobias Dünow, State Secretary at ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Black soldier fly larvae show promise for safe organic waste removal
People with COPD commonly misuse medications
How periodontitis-linked bacteria accelerate osteoporosis-like bone loss through the gut
Understanding how cells take up and use isolated ‘powerhouses’ to restore energy function
Ten-point plan to deliver climate education unveiled by experts
Team led by UC San Diego researchers selected for prestigious global cancer prize
Study: Reported crop yield gains from breeding may be overstated
Stem cells from human baby teeth show promise for treating cerebral palsy
Chimps’ love for crystals could help us understand our own ancestors’ fascination with these stones
Vaginal estrogen therapy not linked to cancer recurrence in survivors of endometrial cancer
How estrogen helps protect women from high blood pressure
Breaking the efficiency barrier: Researchers propose multi-stage solar system to harness the full spectrum
A new name, a new beginning: Building a green energy future together
From algorithms to atoms: How artificial intelligence is accelerating the discovery of next-generation energy materials
Loneliness linked to fear of embarrassment: teen research
New MOH–NUS Fellowship launched to strengthen everyday ethics in Singapore’s healthcare sector
Sungkyunkwan University researchers develop next-generation transparent electrode without rare metal indium
What's going on inside quantum computers?: New method simplifies process tomography
This ancient plant-eater had a twisted jaw and sideways-facing teeth
Jackdaw chicks listen to adults to learn about predators
Toxic algal bloom has taken a heavy toll on mental health
Beyond silicon: SKKU team presents Indium Selenide roadmap for ultra-low-power AI and quantum computing
Sugar comforts newborn babies during painful procedures
Pollen exposure linked to poorer exam results taken at the end of secondary school
7 hours 18 mins may be optimal sleep length for avoiding type 2 diabetes precursor
Around 6 deaths a year linked to clubbing in the UK
Children’s development set back years by Covid lockdowns, study reveals
Four decades of data give unique insight into the Sun’s inner life
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
[Press-News.org] Updating offshore turbine designs to reflect storms’ complexity is keyNew designs for wind turbines require addressing problems at smaller scales