(Press-News.org) PHILADELPHIA — Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, may help reduce patients’ risk of postoperative delirium, according to a study presented at the ANESTHESIOLOGY® 2024 annual meeting.
“Postoperative delirium is a serious complication associated with a risk for health problems and even death after surgery,” said Steven M. Frank, M.D., co-author of the study and a professor in the Department of Anesthesiology and Critical Care Medicine at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. “Anesthesiologists use several methods to try to prevent this complication, and our research shows that a simple intervention such as giving patients an NSAID could be another very effective option.”
Postoperative delirium is a change in mental function that can cause confusion and occurs in up to 15% of surgical patients. In certain high-risk patients, such as those with hip fractures, the incidence can be even higher. It is a significant complication in older adults. Pain, age, stress, anxiety and insomnia are known to contribute to the risk for postoperative delirium.
In the study, researchers analyzed a large medical records database to identify patients who had surgery with anesthesia between 2014 and 2023. The researchers grouped patients by age (18-64 and 65 or older) and the medications they received — acetaminophen only, salicylate NSAIDs (e.g., aspirin) only, and non-salicylate NSAIDs (e.g., ibuprofen, ketorolac or celecoxib) only — and compared their rates of delirium over a seven-day period after surgery. Patients received the medications either orally or intravenously on the day of surgery, before or during the procedure. For both age groups, non-salicylate NSAIDs lowered the risk of delirium when compared to acetaminophen and salicylate NSAIDs.
For patients aged 18 to 64:
The non-salicylate NSAIDs vs. acetaminophen comparison included a total of 210,678 patients, with 105,339 patients in each group. Overall, patients in this age group who were given non-salicylate NSAIDs had a 22% lower risk for postoperative delirium than those given acetaminophen.
The non-salicylate NSAIDs vs. salicylate NSAIDs comparison included a total of 32,538 patients, with 16,269 patients in each group. Overall, patients in this age group who were given non-salicylate NSAIDs had a 70% lower risk for postoperative delirium than those given salicylate NSAIDs.
For patients aged 65 or older:
The non-salicylate NSAIDs vs. acetaminophen comparison included a total of 72,130 patients, with 36,065 patients in each group. Overall, patients in this age group who were given non-salicylate NSAIDs had a 33% lower risk for postoperative delirium than those given acetaminophen.
The non-salicylate NSAIDs vs. salicylate NSAIDs comparison included a total of 24,960 patients, with 12,480 patients in each group. Overall, patients in this age group who were given non-salicylate NSAIDs had a 45% lower risk for postoperative delirium than those given salicylate NSAIDs.
“Recent studies show acetaminophen helps reduce the risk of postoperative delirium, but our study is the largest to show non-salicylate NSAIDs like ibuprofen could be even better at reducing this risk,” said Dr. Frank. “Our findings suggest that using a non-salicylate NSAID may make surgical procedures safer by reducing postoperative delirium, possibly by using fewer opioids. Although additional research should be done on this topic, our findings are promising.”
Dr. Frank added that all NSAIDs can have side effects, including nausea and vomiting, impaired kidney function, and an increased risk of bleeding or excessive clotting during surgery, which may outweigh the benefit for those at the lowest risk for postoperative delirium, such as younger patients. It’s important to assess a patient’s overall health and risk factors before using NSAIDs to reduce postoperative delirium, he said.
Postoperative delirium can significantly impact recovery by increasing the cost of care, length of hospital stay and risk of more serious outcomes, such as cognitive decline, dementia, decline in physical function, placement in a long-term care facility and death. To reduce these risks, anesthesiologists use various methods, including performing an assessment before surgery to identify those at risk and adjusting their anesthesia plan as needed. During surgery, anesthesiologists monitor anesthesia levels to ensure appropriate sedation and use non-opioid pain medication when possible. After surgery, they monitor patients closely and ensure they are up and walking as soon as possible. Additionally, they talk with the family about how to help prevent their loved one from becoming disoriented by being present by their bedside and ensuring they have any needed hearing aids or eyeglasses.
*** ANESTHESIOLOGY 2024 news releases may contain updated data that was not originally available at the time abstracts were submitted.
THE AMERICAN SOCIETY OF ANESTHESIOLOGISTS
Founded in 1905, the American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) is an educational, research and scientific society with more than 58,000 members organized to advance the medical practice of anesthesiology and secure its future. ASA is committed to ensuring anesthesiologists evaluate and supervise the medical care of all patients before, during and after surgery. ASA members also lead the care of critically ill patients in intensive care units, as well as treat pain in both acute and chronic settings.
For more information on the field of anesthesiology, visit the American Society of Anesthesiologists online at asahq.org. To learn more about how anesthesiologists help ensure patient safety, visit asahq.org/madeforthismoment. Join the ANESTHESIOLOGY® 2024 social conversation today. Like ASA on Facebook, follow ASALifeline on X and use the hashtag #ANES24.
# # #
END
PHILADELPHIA — A simple blood test could help doctors identify women in labor who are at risk for preeclampsia — a leading cause of maternal death — and take precautions to prevent it, according to research presented at the ANESTHESIOLOGY® 2024 annual meeting.
Between 5% and 10% of pregnant women develop preeclampsia (sudden high blood pressure and protein in the urine), according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Black women are 60% more likely to develop preeclampsia than white women, ...
PHILADELPHIA — People who have multiple orthopedic surgeries during the same hospital stay are more likely to suffer malnutrition due to repeated or prolonged fasting, which can slow recovery and increase the risk of death, according to a study of more than 28 million patients presented at the ANESTHESIOLOGY® 2024 annual meeting.
Because food or liquid retained in the stomach increases the risk of regurgitation and aspiration in the airway and lungs during general anesthesia and deep sedation, most patients are directed to fast for ...
About The Article: This article presents the 2024 revision of the World Medical Association’s Declaration of Helsinki, a set of principles to guide the ethical treatment of participants in medical research.
Corresponding Author: World Medical Association (wma@wma.net).
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.21972)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions ...
About The Study: This article examines ethical oversight of clinical research in the U.S. and offers practical recommendations that are consistent with current regulations and that could help to make research oversight better fit for purpose for different types of studies.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Nancy E. Kass, ScD, email nkass@jhu.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.0269)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, ...
Long-term, low-dose antiviral treatment reduces the risk for potentially vision-damaging bouts of inflammation and infection, as well as pain, which occur when shingles affects the eye, according to new research presented October 19 at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO) in Chicago.
Shingles occurs when the varicella-zoster virus, which causes chickenpox in children, lies dormant for decades in nerve cells and then starts multiplying again for reasons unknown. It commonly affects people 50 and older, and ...
Taking an antiviral medication for a year may prevent vision damage associated with shingles that affects the eye, according to new research led by faculty from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania and the NYU Grossman School of Medicine at NYU Langone Health.
“Up until now, there has been no proven long-term treatment for new, worsening, or repeated episodes of this disease, so the results of this study provide convincing evidence for using long-term, low-dose antiviral treatment,” said Bennie Jeng, MD, chair of Ophthalmology at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania ...
PHILADELPHIA — The American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) today presented Mary Dale Peterson, M.D., MSHCA, FACHE, FASA, with its 2023 Distinguished Service Award in recognition of her enduring contributions to advancing patient-centered, physician-led health care. Her dedicated service to the specialty and ASA includes her leadership as ASA president during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic. The award is the highest honor ASA bestows and is presented annually to a member who has transformed the specialty of anesthesiology.
Nationally recognized for her role in guiding health plans and hospitals, Dr. Peterson currently serves ...
The University of Tennessee, Knoxville’s Fibers and Composites Manufacturing Facility has a new home and IACMI – The Composites Institute has new headquarters with the dedication of Innovation South.
Innovation South is an 85,000-square-foot multiuse facility in UT’s Research Park at Cherokee Farm, located just off Alcoa Highway across the Tennessee River from the flagship university’s main campus. Developed and owned by Partners Development, the building includes a 40,000-square-foot ...
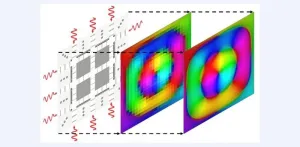
In the fields of physics, mathematics, and engineering, partial differential equations (PDEs) are essential for modeling various phenomena, from heat diffusion to particle motion and wave propagation. While some PDEs can be solved analytically, many require numerical methods, which can be time-consuming and computationally intensive. To address these challenges, scientists have been exploring alternative computing paradigms, including photonic computing.
Photonic computing leverages light–matter interactions to perform ...
STARKVILLE, Miss.—Mississippi State University is part of a European-American collaboration studying how human activities, like fertilizer use and polluting, are impacting nitrogen-fixing plants which are crucial for maintaining healthy ecosystems by adding nitrogen to the soil.
MSU Assistant Professor Ryan A. Folk of the Department of Biological Sciences co-authored a study published today [Oct. 18] in Science Advances, showing that increased nitrogen deposition from human activity is reducing the diversity and evolutionary distinctiveness of nitrogen-fixing plants. Lead author Pablo Moreno García, ...