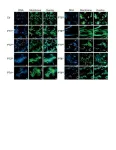
(Press-News.org) A team of researchers says it has developed the first wearable camera system that, with the help of artificial intelligence, detects potential errors in medication delivery.
In a test whose results were published today, the video system recognized and identified, with high proficiency, which medications were being drawn in busy clinical settings. The AI achieved 99.6% sensitivity and 98.8% specificity at detecting vial-swap errors.
The findings are reported Oct. 22 in npj Digital Medicine.
The system could become a critical safeguard, especially in operating rooms, intensive-care units and emergency-medicine settings, said co-lead author Dr. Kelly Michaelsen, an assistant professor of anesthesiology and pain medicine at the University of Washington School of Medicine.
“The thought of being able to help patients in real time or to prevent a medication error before it happens is very powerful,” she said. “One can hope for a 100% performance but even humans cannot achieve that. In a survey of more than 100 anesthesia providers, the majority desired the system to be more than 95% accurate, which is a goal we achieved.”
Drug administration errors are the most frequently reported critical incidents in anesthesia, and the most common cause of serious medical errors in intensive care. In the bigger picture, an estimated 5% to 10% of all drugs given are associated with errors. Adverse events associated with injectable medications are estimated to affect 1.2 million patients annually at a cost of $5.1 billion.
Syringe and vial-swap errors most often occur during intravenous injections in which a clinician must transfer the medication from vial to syringe to the patient. About 20% of mistakes are substitution errors in which the wrong vial is selected or a syringe is mislabeled. Another 20% of errors occur when the drug is labeled correctly but administered in error.
Safety measures, such as a barcode system that quickly reads and confirms a vial’s contents, are in place to guard against such accidents. But practitioners might sometimes forget this check during high-stress situations because it is an extra step in their workflow.
The researchers’ aim was to build a deep-learning model that, paired with a GoPro camera, is sophisticated enough to recognize the contents of cylindrical vials and syringes, and to appropriately render a warning before the medication enters the patient.
Training the model took months. The investigators collected 4K video of 418 drug draws by 13 anesthesiology providers in operating rooms where setups and lighting varied. The video captured clinicians managing vials and syringes of select medications. These video snippets were later logged and the contents of the syringes and vials denoted to train the model to recognize the contents and containers.
The video system does not directly read the wording on each vial, but scans for other visual cues: vial and syringe size and shape, vial cap color, label print size.
“It was particularly challenging, because the person in the OR is holding a syringe and a vial, and you don’t see either of those objects completely. Some letters (on the syringe and vial) are covered by the hands. And the hands are moving fast. They are doing the job. They aren’t posing for the camera,” said Shyam Gollakota, a coauthor of the paper and professor at the UW's Paul G. Allen School of Computer Science & Engineering.
Further, the computational model had to be trained to focus on medications in the foreground of the frame and to ignore vials and syringes in the background.
“AI is doing all that: detecting the specific syringe that the healthcare provider is picking up, and not detecting a syringe that is lying on the table,” Gollakota said.
This work shows that AI and deep learning have potential to improve safety and efficiency across a number of healthcare practices. Researchers are just beginning to probe the potential, Michaelsen said.
The study also included researchers from Carnegie Mellon University and Makerere University in Uganda. The Toyota Research Institute built and tested the system.
The Washington Research Foundation, Foundation for Anesthesia Education and Research, and a National Institutes of Health grant (K08GM153069) funded the work.
The authors’ declared their potential conflicts of interest in their paper, which will be made available on request.
Access downloadable video files showing how AI recognizes vial-swap errors and appropriate medication transfers in real time.
END
Wearable cameras allow AI to detect medication errors
With high proficiency, a deep-learning model identified contents of vials and syringes, confirming whether medication transfers were correct.
2024-10-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New bacterial toxins discovered: A key to fighting infections
2024-10-22
Researchers have discovered a new group of bacterial toxins that can kill harmful bacteria and fungi, opening the door to potential new treatments for infections. These toxins, found in over 100,000 microbial genomes, can destroy the cells of bacteria and fungi without harming other organisms. The study revealed how some bacteria use these toxins to compete with other microbes, and the findings could lead to new ways to fight infections, especially as antibiotic resistance becomes a growing concern.
A new ...
AI eye to eye with ophthalmologists in diagnosing corneal infections, study finds
2024-10-22
Eye care specialists could see artificial intelligence help in diagnosing infectious keratitis (IK), a leading cause of corneal blindness worldwide, as a new study finds that deep learning models showed similar levels of accuracy in identifying infection.
In a meta-analysis study published in eClinicalMedicine, Dr Darren Ting from the University of Birmingham conducted a review with a global team of researchers analysing 35 studies that utilised Deep Learning (DL) models to diagnose infectious keratitis.
AI models ...
Virginia Tech researcher works to preserve the white shark in the Mediterranean Sea
2024-10-22
The Mediterranean Sea is a paradise.
Pristine waters and an incredible coastline spanning multiple continents that are renowned the world over.
Below those picturesque, and sometimes crowded, waters swim a legendary creature facing a treacherous and uncertain future: the white shark.
Francesco Ferretti, an assistant professor in the College of Natural Resources and Environment, is working to save one of the most endangered white shark populations on the planet. The research team located signs of the remaining white sharks ...
How the coronavirus defeats the innate immune response
2024-10-22
The novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 has an enzyme that can counteract a cell’s innate defense mechanism against viruses, explaining why it is more infectious than the previous SARS and MERS-causing viruses. The Kobe University discovery may point the way to the development of more effective drugs against this and possibly similar, future diseases.
When a virus attacks, the body’s immune response has two basic layers of defense: the innate and the adaptive immune systems. While the adaptive immune system grows stronger against a specific pathogen as the body ...
APA Poll: Future of nation, economy and presidential election top U.S. stressors
2024-10-22
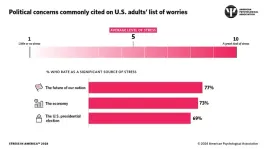
WASHINGTON — More than 7 in 10 adults said the future of the nation (77%) is a significant source of stress in their lives, with the economy (73%) and the 2024 U.S. presidential election (69%) following closely behind, according to the latest Stress in America™ survey released today by the American Psychological Association.
At the same time, the poll found many common stressors among people with different political party affiliations. The survey was conducted by The Harris Poll on behalf of APA among more ...
Towards better solar cells: Exploring an anomalous phenomenon of electricity generation
2024-10-22
The bulk photovoltaic (BPV) effect is an uncommon phenomenon that may enable certain materials to outperform the conventional p–n junctions used in solar cells. In a recent study, researchers from Japan have experimentally demonstrated the BPV effect in alpha-phase indium selenide (α-In2Se3) for the first time along the out-of-plane direction, validating previous theoretical predictions. The remarkable conversion efficiency recorded in their α-In2Se3 device signals a promising advancement for future solar cell technologies and photosensors.
A firm understanding ...
KERI’s innovation in anode materials for solid-state batteries selected as a cover article
2024-10-22
The KERI's research on anode materials for solid-state batteries (SSBs), conducted in collaboration with Kumoh National Institute of Technology and Inha University, has been selected as the cover article of a world-leading journal in the energy field.
The SSBs have replaced the combustible liquid electrolyte that transfers ions between the anode and cathode with a solid electrolyte, significantly reducing the risk of fire or explosion. However, SSBs, due to their 'solid' nature, require much advanced technology, such as ensuring electro-chemo-mechanical stability during the charging and discharging processes. In particular, since the anode has a ...
A visit from the stork brings genomic hope for this endangered species
2024-10-22
A Visit from the Stork Brings Genomic Hope for this Endangered Species
A new genomic study of the endangered Oriental Stork reveals that the population's genetic health is still surprisingly strong, with high genetic diversity and low levels of inbreeding. This is an uncommon finding in most endangered species populations, which makes it more difficult to rescue those species from extinction. Thus, despite the human-caused decline in the Oriental stork numbers, the findings in this study provide hope for the species' long-term ...
Study uncovers the true burden of asthma in African pupils, highlighting need for better access to asthma diagnosis and care
2024-10-21
Peer reviewed | Observational study | People
Rapid urbanisation and population growth in sub-Saharan Africa has increased the incidence of asthma in young people, but the lack of diagnosis and care means that many young people are suffering from untreated symptoms of asthma, according to research from Queen Mary University of London.
The team who led the study, whose pioneering research on the impact of pollution on lung health was instrumental in introducing the Ultra Low-Emission Zone (ULEZ) in London, are calling for better access to asthma diagnosis and care in areas of ...
A remote-controlled car for cancer immunotherapy
2024-10-21
OCTOBER 21, 2024, NEW YORK – Ludwig Cancer Research scientists have devised new types of chimeric antigen-receptor (CAR) T cells—a type of cancer immunotherapy—that can be switched on to varying degrees of intensity and then switched off on demand with existing drugs. The design and preclinical evaluation of the CAR-T cells, led by Melita Irving and Greta Maria Paola Giordano Attianese of the Lausanne Branch of the Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research, is detailed in this week’s issue of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“CAR-T cells are already used today to treat a number of blood cancers, but ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
[Press-News.org] Wearable cameras allow AI to detect medication errorsWith high proficiency, a deep-learning model identified contents of vials and syringes, confirming whether medication transfers were correct.