(Press-News.org) Mental fatigue may make rewards more desirable, according to a study in rats and humans. Exerting cognitive effort has been linked with making unhealthy choices. In the past, the link has been explained via a weaking of inhibitory control or will power. Marcello Solinas and colleagues explore the possibility that cognitive effort may also make unhealthy choices more tempting by increasing the perceived reward. Rats who completed a cognitively demanding task self-administered more cocaine than rats who did not complete a cognitive demanding task—or rats who were allowed to rest to 2–4 hours after completing the complex task. Humans who were given a task that requires significant cognitive effort—suppressing the thought of a white bear while listing other thoughts—ate more potato chips and rated the chips as better-tasting than controls who had not completed an effortful task, suggesting that cognitive effort intensified participants’ hedonic experience of snacking on the salty and fatty snack. To rule out the possibility that cognitive effort increases the likelihood that humans make extreme judgments in general, a follow-up study using difficult and easy writing tasks found that ratings of chocolate increased after cognitive effort but ratings of the length of a pen or the brightness of a yellow post-it note did not. The authors suggest that this sequence is not a mere byproduct of evolution but could be adaptive in some contexts. According to the authors, the results have implication for the management of addiction and other unhealthy behaviors.
END
Cognitive effort whets the appetite for reward
2024-10-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
European funders and organizations partner to promote sustainable research
2024-10-22
A significant step forwards in changing research practices towards sustainability has been taken with the publication of the Heidelberg Agreement on Environmental Sustainability in Research Funding. The agreement provides a framework for research funders to play an active role and incentivize sustainable practices in research. It outlines principles for transitioning to a more sustainable research system and practical recommendations on how to implement sustainability in funding schemes.
A key focus of the Heidelberg Agreement is to ensure that research funders take a proactive approach to promoting sustainability in scientific ...
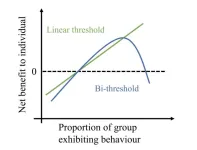
A model for the decline of trends, fads, and information sharing
2024-10-22
A model of human behavior finds that people will share information if enough—but not too many—of their contacts do so. Humans are social creatures, and many behaviors and beliefs can spread from person to person. Understanding the dynamics of behavioral diffusion can help encourage healthy or sustainable behaviors or stop the spread of misinformation. Linear threshold models assume that people will adopt a behavior when the number of their social contacts that have done so passes a threshold. Pouria Ramazi and colleagues propose an addition to the model, ...
Plastic mulch is contaminating agricultural fields
2024-10-22
Using plastic sheets for weed control, even under current best management practices, pollutes soil with macro- and micro-plastics and negatively affect critical soil functions, according to a study. The United Nations considers soil plastic contamination an environmental health and food security threat. Around the world, over 25 million acres of farmland is seasonally covered with opaque plastic films used as “mulch” to prevent weeds, retain moisture, and warm soil—a practice known ...
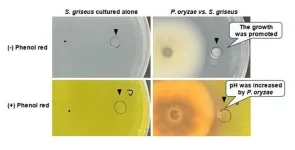
Scientists discover how fungi interact with soil actinomycetes
2024-10-22
In the world of agriculture, rice is a staple food for more than half of the global population, making its cultivation crucial for food security. However, the rice blast fungus Pyricularia oryzae (syn. Magnaporthe oryzae) poses a significant threat to rice crops, causing extensive damage and leading to substantial yield losses. Traditional methods of controlling this pathogen often rely on chemical fungicides, which can have detrimental environmental impacts and contribute to the development of resistant strains. Therefore, researchers are increasingly exploring alternative strategies that leverage natural ...
Beyond longevity: The critical role of mental health in Japan’s well-being
2024-10-22
The Japanese population is known for its longest life expectancy (LE) at birth. Extensive studies have been conducted on the physical health of the Japanese population, mainly on mortality outcomes. However, research on mental health is limited due to the social stigma against mental illnesses. This is alarming since mental health problems such as anxiety, substance use disorders, and suicide rates have largely increased over the years.
Additionally, previous studies have examined the physical and mental health of the Japanese population separately, which makes it harder to understand the relationship between them.
Against this backdrop, Associate Professor Yuka Minagawa ...
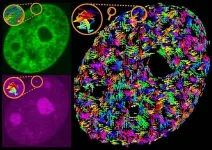
Stirred, not shaken — Scientists uncover how transcription drives motion within the genome
2024-10-22
A team of scientists has discovered surprising connections among gene activity, genome packing, and genome-wide motions, revealing aspects of the genome’s organization that directly affect gene regulation and expression.
The findings, reported in the journal Nature Communications, bolster our understanding of the mechanics behind transcription-dependent motions of single genes—the dysfunction of which may lead to neurological and cardiovascular disorders as well as to cancer.
“The genome is ‘stirred’ by transcription-driven ...
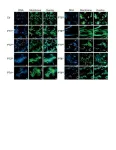
Engineering creates molecules that target cancer-causing proteins
2024-10-22
For some proteins, a single mutation, or change in its DNA instructions, is all it takes to tip the balance between functioning normally and causing cancer. But despite causing major disease, these slightly mutated proteins can resemble their normal versions so closely that treatments designed to target mutants could also harm healthy cells.
Led by researchers at NYU Langone Health and its Perlmutter Cancer Center, a new study describes the development of a biologic, a drug derived from natural biological systems, that targets a mutant cancer protein called HER2 (human epidermal growth factor receptor 2) without attacking ...
Wearable cameras allow AI to detect medication errors
2024-10-22
A team of researchers says it has developed the first wearable camera system that, with the help of artificial intelligence, detects potential errors in medication delivery.
In a test whose results were published today, the video system recognized and identified, with high proficiency, which medications were being drawn in busy clinical settings. The AI achieved 99.6% sensitivity and 98.8% specificity at detecting vial-swap errors.
The findings are reported Oct. 22 in npj Digital Medicine.
The system could ...
New bacterial toxins discovered: A key to fighting infections
2024-10-22
Researchers have discovered a new group of bacterial toxins that can kill harmful bacteria and fungi, opening the door to potential new treatments for infections. These toxins, found in over 100,000 microbial genomes, can destroy the cells of bacteria and fungi without harming other organisms. The study revealed how some bacteria use these toxins to compete with other microbes, and the findings could lead to new ways to fight infections, especially as antibiotic resistance becomes a growing concern.
A new ...
AI eye to eye with ophthalmologists in diagnosing corneal infections, study finds
2024-10-22
Eye care specialists could see artificial intelligence help in diagnosing infectious keratitis (IK), a leading cause of corneal blindness worldwide, as a new study finds that deep learning models showed similar levels of accuracy in identifying infection.
In a meta-analysis study published in eClinicalMedicine, Dr Darren Ting from the University of Birmingham conducted a review with a global team of researchers analysing 35 studies that utilised Deep Learning (DL) models to diagnose infectious keratitis.
AI models ...