(Press-News.org) New Haven, Conn. — Expanding access to new, highly effective weight-loss medications could prevent more than 40,000 deaths a year in the United States, according to a new study led by researchers at Yale School of Public Health and the University of Florida.
The findings highlight the critical need to remove existing barriers that are hindering people’s access to effective weight loss treatments and impeding public health efforts to address the national obesity crisis, the researchers said. According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, about 74% of Americans are considered overweight, with about 43% of those individuals considered obese.
Obesity's widespread impact on health is well-documented. It exacerbates conditions such as type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and certain cancers. Yet, despite its severe consequences, the development and deployment of highly effective treatments for obesity have been lacking. Recent advancements in pharmaceutical interventions however, particularly the introduction of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, such as Ozempic and Wegovy, and dual gastric inhibitory polypeptide and GLP-1 (GIP/GLP-1) receptor agonists, such as tirzepatide, have demonstrated substantial efficacy in weight loss. These medications have shown promise in clinical trials and are increasingly being used for weight management.
In conducting their study, the researchers aimed to quantify the potential mortality impact of increased access to these weight-loss drugs. They integrated data on mortality risk associated with different body mass index (BMI) categories, obesity prevalence, and the current limitations on drug access due to high costs and insurance restrictions.
According to the findings, if access to these new medications were expanded to include all eligible individuals, the U.S. could see up to 42,027 fewer deaths annually. This estimate includes approximately 11,769 deaths among individuals with type 2 diabetes — a group particularly vulnerable to the complications of obesity. Even under current conditions of limited access, the researchers project that around 8,592 lives are saved each year, primarily among those with private insurance.
The study highlights a critical disparity in drug access. Currently, the high cost of these medications, which can exceed $1,000 per month without insurance, limits their availability. For example, Medicare — one of the largest insurance programs for older adults — does not cover these drugs for weight loss, impacting many who could benefit from them. Medicaid coverage varies widely by state, and private insurance often imposes high deductibles and copays, further restricting access, the researchers said.
"Expanding access to these medications is not just a matter of improving treatment options but also a crucial public health intervention," said Alison P. Galvani, one of the study's corresponding authors and the Burnett and Stender Families Professor of Epidemiology (Microbial Diseases) at the Yale School of Public Health. "Our findings underscore the potential to reduce mortality significantly by addressing financial and coverage barriers."
The study also explored how expanded access could affect different regions and socioeconomic groups. States with high obesity and diabetes rates, such as West Virginia, Mississippi, and Oklahoma, stand to benefit the most from increased medication availability. In these areas, expanding access could lead to the largest per capita reductions in mortality.
However, the study's authors caution that while the potential benefits are substantial, several challenges remain. The high price of these medications is a significant barrier, and there are concerns about the pharmaceutical industry's profit margins. Furthermore, supply constraints and production limitations continue to hamper widespread availability.
"Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach," said Dr. Burton H. Singer, PhD, another corresponding author of the study and adjunct professor of mathematics at the Emerging Pathogens Institute at the University of Florida. "We need to ensure that drug prices are more aligned with manufacturing costs and increase production capacity to meet demand. At the same time, we must tackle the insurance and accessibility issues that prevent many people from getting the treatment they need."
The researchers also considered the impact of socioeconomic factors on the effectiveness of expanded drug access. They adjusted their estimates to account for income disparities, finding that even with these adjustments, the potential for lives saved remains significant. The results suggest that improving access to these medications could reduce health care costs associated with obesity-related conditions and improve overall quality of life for many Americans.
The study appears in the peer-reviewed journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Science.
Abhishek Pandey, a research scientist at the Yale School of Public Health, is lead author of the study. Yale postdoctoral research associates Yang Ye and Chad R. Wells are coauthors.
###
END
In a paper published in PLOS Sustainability and Transformation, an international team of researchers looked at how science could play a more active role in managing crises. The paper builds on the outcomes of the international conference “What Role for Science in Crisis Times? Outlook in the Health, Environment, and Agriculture Interconnected Areas”, held in Montpellier in 2022.
To enhance science’s contribution to crisis management, the paper emphasises the need for interdisciplinarity, where science is integrated across disciplines, and transdisciplinarity, which incorporates various societal actors and stakeholders. By co-designing and co-producing ...
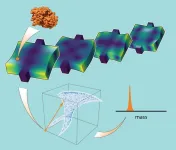
Caltech scientists have developed a method driven by machine learning that allows them to accurately measure the mass of individual particles and molecules using complex nanoscale devices. The new technique opens the possibility of using a variety of devices for the measurement of mass and, therefore, the identification of proteins, and could pave the way to determining the sequence of the complete proteome, the collection of all the proteins in an organism.
Proteins are the engines of living systems. Which proteins are made, ...
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Flathead catfish — native to the Mississippi River basin — were first detected in the Susquehanna River in Pennsylvania in 2002, according to the U.S. Geological Survey. In the two decades since then, the invasive species has spread throughout the river basin. The impact of the large predator on the waterway’s food webs and ecology was unknown, but now a research team is beginning to understand what Susquehanna flatheads are eating and how their presence is affecting native aquatic species in the river.
The findings, which the team said state ...
NORMAN, OKLA. – Alisa Javadi, Ph.D., professor at the University of Oklahoma School of Electrical and Computer Engineering and the Homer L. Dodge Department of Physics and Astronomy, has received funding from the U.S. Department of Energy Early Career Research Program for research that offers the potential for advancing quantum technology development.
Javadi’s research will test the use of cerium oxide as a host for quantum bits, or qubits. Qubits, the building blocks of quantum computing, need an environment free ...
Obesity Medicine Fellowship Created at Pennington Biomedical
Fellowship product of collaboration between Pennington Biomedical Research Center’s Metamor Clinic and Louisiana State University Health New Orleans School of Medicine
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Oct. 22, 2024
BATON ROUGE – A new Obesity Medicine Fellowship at Pennington Biomedical Research Center is now open for candidate applications. The one-year program is the result of a collaboration between Pennington Biomedical and Louisiana State University Health ...
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – The viruses that infect bacteria are the most abundant biological entities on the planet. For example, a recent simple study of 92 showerheads and 36 toothbrushes from American bathrooms found more than 600 types of bacterial viruses, commonly called bacteriophages or phages. A teaspoon of coastal seawater has about 50 million phages.
While largely unnoticed, phages do not harm humans. On the contrary, these viruses are gaining increasing popularity as biomedicines to eradicate pathogenic ...
A Ukrainian researcher has developed a new digital tool for detecting autism and developmental delay in children. Her research has been published in Cambridge University Press journal Cambridge Prisms: Global Mental Health.
The tool incorporates the basic principles of the Kids’ Development Diagnosis and Determining the Risk of Autism (KiDD) methodology, for children aged 1.5 to 6 years old, into mobile app form. It has the potential to help diagnose children more swiftly and efficiently, which could have major positive ...
Texas Accounting Chair Steven Kachelmeier Garners Coveted Award for Scholarship
AUSTIN, Texas — The American Accounting Association (AAA) presented its Lifetime Achievement Award for Behavioral Accounting Research to Steven Kachelmeier, a professor and chair of the Department of Accounting at The University of Texas McCombs School of Business. Kachelmeier, the Thomas O. Hicks Endowed Chair in Business, accepted this prestigious award during the weekend at the association’s 2024 Accounting ...
TORONTO, Oct. 22, 2024 – Today, the Centre for Aging + Brain Health Innovation (CABHI), powered by Baycrest launched Ignite, its new funding program to support Canadian innovators designing solutions for older persons. As Canada’s aging population rapidly grows – with nearly 20 per cent of people above the age of 65 – so too will the need for innovations that enhance the lives of older persons, including those impacted by dementia.
Canadian early-stage innovators – including researchers, point-of-care staff, and companies – are developing ...
A new artificial intelligence-based system can accurately assess the chromosomal status of in vitro-fertilized (IVF) embryos using only time-lapse video images of the embryos and maternal age, according to a study from investigators at Weill Cornell Medicine.
The new system, called "BELA,” and described in a paper published Sept. 5 in Nature Communications, is the team’s latest AI-based platform for assessing whether an embryo has a normal (euploid) or abnormal (aneuploid) number of chromosomes—a key determinant of IVF success. Unlike prior AI-based approaches, BELA does not need to consider embryologists' subjective assessments of embryos. ...