(Press-News.org) DURHAM, N.H.—(October 22, 2024)—Political affiliation may not make a difference on everyday purchases for individuals, but it can play a role when buying for friends, family and co-workers, new research from the University of New Hampshire has found. This may have implications for gift buying this holiday season and beyond.
“We performed five different studies, each looking at buying different products, and asked people to make a choice for themselves and then a gift for someone they knew really well and found that politics played a bigger role when people were purchasing gifts, because that's a case where people are making a decision based on how they think others feel,” said Justin Pomerance, assistant professor of marketing at UNH’s Peter T. Paul College of Business and Economics and lead author.
In their paper, recently published in the International Journal of Research in Marketing, Pomerance and his co-author, Leaf Van Boven, professor of psychology at the University of Colorado, showed how political party played a bigger role than type of product. In a series of five studies, online participants and college students were asked a series of purchasing questions. In their first study, participants were asked to create music playlists for themselves and another person. When choosing for themselves, only 58% of the songs they chose for themselves came from artists who aligned with their political ideology. However, when making a playlist for someone else, that number increased to 64% of the songs matching their target’s political leanings. A similar pattern emerged when participants chose paintings for others, favoring politically aligned art for others more than for themselves.
In the series of studies, choices ranged from selecting songs and paintings, to predicting how much others would enjoy experiences versus material goods. All focused on how political cues—like product labeling or the political views of a specific artist—impacted consumer preferences when buying for others. Each study revealed a similar pattern, with participants consistently putting more weight on how much others cared about politics even in one of the studies where the product information was ambiguous. Even though images of paintings were blurred, 61% of participants chose politically aligned items for others compared to only 54% for themselves.
To take it a step further, researchers also compared political cues to other identity markers like gender and race, telling participants that the major donor of a museum was either conservative, liberal or identified by gender or minority status. The results revealed that political cues had a stronger effect on participants’ perceptions than either gender or race.
"There are a few reasons for this," said Pomerance. "For one, it seems more socially acceptable to like or dislike people based on politics than on race or gender. Political identity feels more like a choice and more reflective of personal preferences.”
The researchers say these findings lend further evidence to earlier research and have important implications for businesses because while companies may believe that taking a political stand or sending political signals will significantly influence their customers' purchasing decisions, the research suggests otherwise. However, understanding judgements by consumers is important because people frequently make purchases for others, such as co-workers, friends, family and others in their community.
They believe this research could offer a silver lining—while polarization may dominate political discussions, it shows that most people are not constantly thinking about it when making consumer decisions.
###
About UNH
The University of New Hampshire inspires innovation and transforms lives in our state, nation and world. More than 16,000 students from 50 states and 87 countries engage with an award-winning faculty in top-ranked programs in business, engineering, law, health and human services, liberal arts and the sciences across more than 200 programs of study. A Carnegie Classification R1 institution, UNH partners with NASA, NOAA, NSF, and NIH, and received over $252 million in competitive external funding in FY24 to further explore and define the frontiers of land, sea and space.
END
Note to Editors: Video clips available at: https://duke.box.com/s/wtq3ofu3kf84ayw3qr6jajxdizt0rwxc
DURHAM, N.C. – Imagine sitting in a dark movie theater wondering just how much soda is left in your oversized cup. Rather than prying off the cap and looking, you pick up and shake the cup a bit to hear how much ice is inside rattling around, giving you a decent indication of if you’ll need to get a free refill.
Setting the drink back down, you wonder absent-mindedly if the armrest is made of real wood. After ...
A world-renowned West Virginia University physician and researcher has received one of the highest honors in the fields of health and medicine.
Dr. Sally Hodder, director of the West Virginia Clinical and Translational Science Institute, associate vice president for clinical and translational science at WVU and Chancellor’s Preeminent Scholar Chair, was elected to the National Academy of Medicine for her accomplishments as an infectious diseases physician and researcher.
Hodder, the first person from WVU to be chosen for the National Academy of Medicine, is one of only 100 new members from around the world announced at the Oct. 21 NAM ...
New study reveals that in arid ecosystems, larger arthropods such as termites and beetles play a crucial role in decomposition, challenging the traditional view that microbial activity dominates this process in dry environments. By demonstrating that macro-decomposition can peak during the summer in arid sites and that overall decomposition rates in these regions can be similar to or even exceed those in wetter climates, the research provides new insights into how decomposition functions in drylands and its implications for global carbon ...
NASA has revealed the first look at a full-scale prototype for six telescopes that will enable, in the next decade, the space-based detection of gravitational waves — ripples in space-time caused by merging black holes and other cosmic sources.
The LISA (Laser Interferometer Space Antenna) mission is led by ESA (European Space Agency) in partnership with NASA to detect gravitational waves by using lasers to measure precise distances — down to picometers, or trillionths of a meter — between a trio of spacecraft distributed in a vast configuration larger than the Sun. Each side of the triangular array ...
A majority of Americans worry this year’s general election will be tainted by fraud, according to a recent NPR/PBS News/Marist poll released earlier this month—an ominous indication of the state of democracy in the U.S.
“When citizens lose trust in the electoral process, they may question the legitimacy of elected officials and the institutions they represent, which undermines the foundational principle that government authority is derived from the will of the people,” ...
A study of patients with metastatic lung cancer by researchers based in Brazil and the United States has found that their performance in simple physical tests such as sitting down, standing and walking can help physicians arrive at a prognosis and approach to treatment.
An article on the study is published in the European Journal of Clinical Investigation.
The findings also included identification in the volunteers’ blood plasma of two substances – serine and M22G – with the potential to become biomarkers capable of indicating which patients are most likely to respond to chemotherapy.
The study was supported by FAPESP (projects 16/20187-6 and 19/17009-7), ...
New Haven, Conn. — Expanding access to new, highly effective weight-loss medications could prevent more than 40,000 deaths a year in the United States, according to a new study led by researchers at Yale School of Public Health and the University of Florida.
The findings highlight the critical need to remove existing barriers that are hindering people’s access to effective weight loss treatments and impeding public health efforts to address the national obesity crisis, the researchers said. According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, about 74% of Americans are considered overweight, with about 43% of those individuals ...
In a paper published in PLOS Sustainability and Transformation, an international team of researchers looked at how science could play a more active role in managing crises. The paper builds on the outcomes of the international conference “What Role for Science in Crisis Times? Outlook in the Health, Environment, and Agriculture Interconnected Areas”, held in Montpellier in 2022.
To enhance science’s contribution to crisis management, the paper emphasises the need for interdisciplinarity, where science is integrated across disciplines, and transdisciplinarity, which incorporates various societal actors and stakeholders. By co-designing and co-producing ...
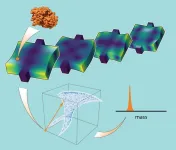
Caltech scientists have developed a method driven by machine learning that allows them to accurately measure the mass of individual particles and molecules using complex nanoscale devices. The new technique opens the possibility of using a variety of devices for the measurement of mass and, therefore, the identification of proteins, and could pave the way to determining the sequence of the complete proteome, the collection of all the proteins in an organism.
Proteins are the engines of living systems. Which proteins are made, ...
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Flathead catfish — native to the Mississippi River basin — were first detected in the Susquehanna River in Pennsylvania in 2002, according to the U.S. Geological Survey. In the two decades since then, the invasive species has spread throughout the river basin. The impact of the large predator on the waterway’s food webs and ecology was unknown, but now a research team is beginning to understand what Susquehanna flatheads are eating and how their presence is affecting native aquatic species in the river.
The findings, which the team said state ...