(Press-News.org) A single treatment with, a CRISPR-Cas9 based gene editing therapy, is enough to replace the daily medication of patients with hereditary angioedema (HAE), a condition characterized by severe, painful and sudden onset of swelling, sometimes resulting in death. Confirming the findings published earlier this year from researchers from Amsterdam UMC, the University of Auckland and Cambridge University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust. This phase two study is published today in the New England Journal of Medicine and presented at American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology's annual congress on the 26th of October.
"The results of this double-blind, placebo-controlled portion of the study confirm our promising findings from the phase 1 study, showing dramatic reductions of angioedema swellings following a single-dose treatment with this gene editing based therapy,” says Danny Cohn, internist at Amsterdam UMC and first author of the study.
Expanding on the phase one study, which included ten patients, researchers from across the world led by Amsterdam UMC, tested the CRISPR-based therapy on 27 patients with two different dosages compared to placebo. They found that both dosages led to a reduction in angioedema attacks as well as a sustained and meaningful reduction in kallikrein levels in HAE patients.
"This reduction is perhaps the most crucial as it shows us that the therapy is working. Kallikrein acts as messenger that triggers swelling and in patients with HAE, this protein is basically let loose. The fact that we can reduce its presence tells us that we're on the right track,” says Dr Hilary Longhurst, an honorary senior lecturer at the University of Auckland.
HAE affects an estimated 50,000 patients worldwide and this rarity often results in misdiagnosis. It's also part of the reason why this trial included national excellence centers from a wide range of nations including, as well as the aforementioned partners from the United Kingdom and New Zealand as well as Australia, Germany and France and an industry sponsor, Intellia, from the United States.
"For many decades, patients with HAE were faced with a very limited number of treatment options to control angioedema attacks. The prospect of a potential, functional cure following a single-time treatment is overwhelming both for patients and physicians,” says Cohn.
Cambridge University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust consultant in clinical immunology and allergy, Dr Padmalal Gurugama described phase two of the trail as another “fantastic team effort” by clinicians around the world, and their patients.
“The results from phase two convincingly build on those from phase one, and offer real hope to patients suffering from a condition that until now had very few treatment options. It is absolutely vital for patients, and those clinicians who care for them, that this game-changing work continues,” he adds.
This expert work will continue as the CRISPR-Cas9 therapy NTLA-2002 moves into the third phase of the clinical development program. This trial will include more patients and once again be executed by the same international group of researchers. on the first phase of this research here: Gene-editing offers hope for people with hereditary disorder (amsterdamumc.org)
END
Phase Two results with CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing support further development as treatment for hereditary angioedema (HAE)
Amsterdam UMC led study reinforces phase one findings from earlier this year
2024-10-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Take aim at the pause!
2024-10-24
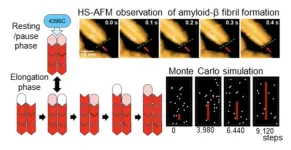
A collaborative research group, including researchers from Exploratory Research Center on Life and Living Systems and Institute for Molecular Science of National Institutes of Natural Sciences, as well as Nagoya City University, Nagoya University, and University of Tsukuba, has uncovered a new mechanism in the growth of amyloid β (Aβ) fibrils, which are closely associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Using advanced high-speed atomic force microscopy (HS-AFM), the team was able to observe Aβ fibril growth at the molecular ...
Pistachios may help improve eye health, new study finds
2024-10-24
A new study1 from researchers at the Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy at Tufts University has found that consuming pistachios daily may significantly improve eye health by increasing macular pigment optical density (MPOD), due to the plant pigment lutein, a key factor in protecting the eyes from blue (visible) light and age-related damage.
The randomized controlled trial showed that compared to eating a usual diet alone, eating 2 ounces (57 grams) of pistachios per day for 12 weeks as part of a usual diet resulted in a significant increase in MPOD in otherwise healthy middle-aged to older adults. MPOD is an important indicator of eye health, ...
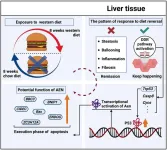
Transcriptomic landscape analysis reveals a persistent DNA damage response in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis post-dietary intervention
2024-10-24
Background and Aims
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and its more advanced form, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis, have emerged as the most prevalent liver diseases worldwide. Currently, lifestyle modification is the foremost guideline-recommended management strategy for MASLD. However, it remains unclear which detrimental signals persist in MASLD even after disease remission. Thus, we aimed to examine the persistent changes in liver transcriptomic profiles following ...
ECOG-ACRIN and Caris Life Sciences partner to interrogate landmark TAILORx breast cancer trial
2024-10-24
ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group (ECOG-ACRIN) and Caris Life Sciences®(Caris) announced today a multi-year research collaboration wherein Caris is pairing its highly sophisticated and comprehensive genomic, transcriptomic and proteomic profiling, advanced artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms with ECOG-ACRIN’s immense research capabilities. The first project is underway and leverages the tumor tissue samples from the Trial Assigning Individualized Options for Treatment (Rx) or TAILORx, breast cancer clinical trial. TAILORx is one of the world's largest breast cancer research resources. The TAILORx trial and its associated biospecimen ...
Ion-pairing: A new approach to lyotropic chromonic liquid crystal assembly
2024-10-24
Self-assembling molecules into organized structures is highly valuable for developing new materials. One notable class of these materials is lyotropic chromonic liquid crystals (LCLCs), which are molecular assemblies of amphiphilic π-electronic molecules, with water-absorbing and water-repelling parts. The term “lyotropic” refers to liquid crystal phases that depend on the concentration of the molecules in a solvent, while “chromonic” indicates that these molecules are stacked into columnar assemblies. In a solvent, these structures are stabilized by π–π interactions and hydrophobic effects. Examples of ...
Popular diabetes and weight-loss drug may reduce risk of Alzheimer’s disease
2024-10-24
CLEVELAND—Researchers at the Case Western Reserve School of Medicine have found that, when compared to seven other anti-diabetic drugs, semaglutide, a popular diabetes and weight-loss drug, may lower the risk of Alzheimer’s disease in people with type 2 diabetes (T2D).
Alzheimer’s disease is a brain disorder that slowly destroys memory and thinking skills. According to the Alzheimer’s Association, nearly 7 million Americans 65 and older are living with the disease, and there are more deaths from Alzheimer’s than breast and prostate cancer combined.
The study, published ...
Feeding practices play a central role in infants’ rapid weight gain, UNC Greensboro researchers find
2024-10-24
A UNC Greensboro (UNCG) study following 299 women and their infants from pregnancy to toddlerhood examined mul ple psychological, biological, and social factors in the context of infants’ rapid weight gain. They found infant feeding practices associated with obesity, known as obesogenic practices, are strongly correlated with rapid infant weight gain.
Examples of obesogenic practices described in their recent Pediatric Obesity paper include watching television while feeding a baby, formula feeding, and supplementing a bottle with additional foods.
“The key take ...
New AI tool predicts protein-protein interaction mutations in hundreds of diseases
2024-10-24
Scientists from Cleveland Clinic and Cornell University have designed a publicly-available software and web database to break down barriers to identifying key protein-protein interactions to treat with medication.
The computational tool is called PIONEER (Protein-protein InteractiOn iNtErfacE pRediction). Researchers demonstrated PIONEER’s utility by identifying potential drug targets for dozens of cancers and other complex diseases in a recently published Nature Biotechnology article.
Genomic research is key in drug discovery, but it is not always enough on its own, says Feixiong Cheng, PhD, study co-lead author and director of Cleveland Clinic’s Genome Center. When ...
Gene named for mythical Irish land could aid muscle function after traumatic nerve injuries
2024-10-24
BUFFALO, N.Y. — The key to recovering from traumatic nerve injuries, like those sustained in motor vehicle accidents or gunshot wounds, may be a gene named for the land of everlasting youth in Irish folklore.
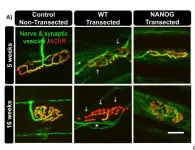
In a study published today (Oct. 24) in Nature Communications, a University at Buffalo-led research team describes how the gene, called NANOG, can improve the regrowth of damaged nerves and re-establish innervation (the process of nerves growing and connecting with organs or tissues) after traumatic severing of peripheral nerves.
The gene’s name is derived from Tír na nÓg, which is a mythical ...
Virginia Tech team creates new method of flexing on electronics
2024-10-24
If a phone or other electronic device was made of soft materials, how would that change its use? Would it be more durable? If hospital health monitoring equipment was made of less rigid components, would it make it easier for patients to wear?
While electronics of that type may still be far in the future, Virginia Tech researchers have developed an innovative method for constructing the soft electronic components that make them up. The focus of a project from the team of Michael Bartlett, principal investigator and associate professor in the Department of Mechanical Engineering, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
Researchers develop a biomimetic platform to enhance CAR T cell therapy against leukemia
[Press-News.org] Phase Two results with CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing support further development as treatment for hereditary angioedema (HAE)Amsterdam UMC led study reinforces phase one findings from earlier this year