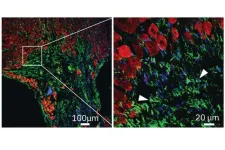
Experts call for clear and concise regulation of exosome-based treatments
2024-10-24
(Press-News.org) Clinics that offer exosome therapies claim they have the ability to repair and regenerate tissues and treat inflammatory and other immune-related conditions in a noninvasive way. Now, a team of bioethicists and legal scholars from Japan is sounding the alarm on the urgent need for stronger regulations surrounding these unproven interventions. Their letter appears October 24 in the journal Stem Cell Reports.
“Administering these treatments to patients without scientific evidence or a clear regulatory framework involves significant risks,” says first author Misao Fujita, a professor at Kyoto University. “Our paper highlights how the lack of regulation has led to unsafe medical practices and stresses the importance of clarifying regulations both to protect patients and foster the development of research on these products.”
Exosomes are a type of extracellular vesicle responsible for intercellular communication. Similar to unproven stem cell-based interventions, exosome therapies are promoted as treatments for a range of conditions, from hair loss to degenerative diseases to inflammation related to cardiovascular disease and other serious conditions. Some clinics offer both stem cell- and exosome-based interventions, often at a significant financial cost to patients. In the United States and the European Union, exosome treatments are regulated as biological products and require safety review before being administered to patients. To date, however, there are no therapies using exosomes that have been approved based on clinical efficacy, and these interventions can cause serious harm to the human body.
In Japan, where there is no clear regulation of these products, it is difficult to even track and report adverse events, further increasing the risk to patients, Fujita says. “There have been media reports covering patient deaths and severe complications, but there is no national system in place to accurate track or assess these incidents,” she adds. “We believe that sharing this problem and collaborating globally is the way to find solutions that are essential for ensuring patient safety.”
The authors hope their paper will reach scientists interested in the medical applications of stem cells and exosomes, as well as researchers and policymakers focused on bioethics and building regulatory frameworks. They also want to raise these issues among the healthcare professionals and industry stakeholders who are involved in offering these interventions to patients.
Moving forward, the team plans to deepen their research in this area and continue to raise public awareness among both professionals and members of the public.
###
This study was funded by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science and the Uehiro Foundation on Ethics and Education. Declarations of interest are provided in the manuscript.
Stem Cell Reports, Fujita et al. “The urgent need for clear and concise regulations on exosome-based interventions” https://www.cell.com/stem-cell-reports/fulltext/S2213-6711(24)00270-4
Stem Cell Reports (@stemcellreports), published by Cell Press for the International Society for Stem Cell Research (@ISSCR), is a monthly open-access peer-reviewed publication communicating basic discoveries across the spectrum of stem cell research and translational and clinical studies. The journal focuses on shorter, single-point manuscripts that report original research with conceptual or practical advances that are of broad interest to scientists and clinicians across the continuum of stem cell science and application. Visit http://www.cell.com/stem-cell-reports. To receive Cell Press media alerts, please contact press@cell.com.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-10-24
When early cartographers undertook perilous expeditions to map unknown corners of the world with sextants, compasses, and hand-drawn diagrams, it’s unlikely they imagined that someday anyone with an internet connection would have access to a seamless view of the entire planet from the comfort of their own home. Today, pioneering scientists are working to create a similar experience for a much tinier, but no less important domain: developing embryos. The goal is to track and map the behavior of each and every cell working together to create an adult lifeform, and present that map in a clickable, ...
2024-10-24
Using a few zaps of electricity to the skin, researchers can stop bacterial infections without using any drugs. For the first time, researchers designed a skin patch that uses imperceptible electric currents to control microbes. The results appear October 24 in the Cell Press journal Device.
“This opens up exciting possibilities for drug-free treatments, especially for skin infections and wound healing, where antibiotic-resistant bacteria pose a serious challenge,” says University of Chicago’s Bozhi Tian, one of the paper’s ...
2024-10-24
About The Study: These interim findings demonstrate the feasibility of targeted interpretation of a predefined set of genes from genome sequencing in a population of different racial and ethnic groups. DNA sequencing offers an additional method to improve screening for conditions already included in newborn screening and to add those that cannot be readily screened because there is no biomarker currently detectable in dried blood spots. Additional studies are required to understand if these findings are generalizable to populations of different racial and ethnic groups and ...
2024-10-24
Early results from a study of newborn screening methods show that DNA analysis picks up many more preventable or treatable serious health conditions than standard newborn screening and is favored by most parents who are offered the option.
The study—called GUARDIAN—is one of the first large-scale studies in the world to use genome sequencing as a method for newborn screening and is the first to publish preliminary results.
“The results show us that genome sequencing can radically improve children’s medical care,” says Joshua Milner, professor of Pediatrics, director of Allergy/Immunology and Rheumatology ...
2024-10-24
About The Study: In this cohort study, non-Hispanic Black race was associated with increased odds of not receiving guideline-concordant care (GCC) and less timely treatment initiation. Non-Hispanic Black race was associated with increased all-cause mortality, which was reduced after adjusting for GCC and clinical and sociodemographic factors. These findings suggest that optimizing timely receipt of GCC may represent a modifiable pathway to improving inferior survival outcomes among older non-Hispanic Black ...
2024-10-24
About The Study: This cross-sectional study found that absolute concentrations of fentanyl, methamphetamine, and cocaine in urine specimens increased from 2013 to 2023, with a decrease in heroin concentration during that period. The findings suggest that exposure to these substances, as well as the illicit drug supply, has fundamentally changed in many parts of the U.S., highlighting the need to reinforce surveillance initiatives and accelerate efforts to treat individuals with illicitly manufactured fentanyl and/or stimulant exposure.
Corresponding Author: To ...
2024-10-24
Scientists at the Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Research at UCLA have developed a first-of-its-kind experimental therapy that has the potential to enhance heart repair following a heart attack, preventing the onset of heart failure.
Cardiovascular disease continues to be the world’s leading cause of death, contributing to one-third of deaths annually. After a heart attack, the heart’s innate ability to regenerate is limited, causing the muscle to develop scars to maintain its structural integrity. ...
2024-10-24
HOUSTON ― Researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center demonstrated that anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy in combination with mutation-directed targeted therapy extended overall survival (OS) in patients with anaplastic thyroid carcinoma (ATC). Findings from the Phase II single center study published today in JAMA Oncology.
The trial enrolled 42 patients across three cohorts to evaluate mutation-matched targeted therapy and the immune checkpoint inhibitor atezolizumab. The median OS across all cohorts was 19 months, which compares favorably to historical OS of five months for patients with ATC. ...
2024-10-24
Producing materials such as steel, plastics and cement in the United States alone inflicts $79 billion a year in climate-related damage around the world, according to a new study by engineers and economists at the University of California, Davis. Accounting for these costs in market prices could encourage progress toward climate-friendly alternatives.
“We wanted to look at the cost to society to produce these materials,” said Elisabeth Van Roijen, a recent Ph.D. graduate from the UC Davis Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering ...
2024-10-24
On-demand ride services or ride-sourcing services have been experiencing fast development and steadily reshaping the way people travel in the past decade. Various optimization algorithms, including reinforcement learning approaches, have been developed to help ride-sourcing platforms design better operational strategies to achieve higher efficiency. However, due to cost and reliability issues, it is commonly infeasible to validate these models and train/test these optimization algorithms within real-world ride-sourcing platforms. Acting as a proper test bed, a simulation platform for ride-sourcing systems will thus be essential for both ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Experts call for clear and concise regulation of exosome-based treatments