(Press-News.org)
University of Oxford researchers have made a significant step towards realising miniature, soft batteries for use in a variety of biomedical applications, including the defibrillation and pacing of heart tissues. The work has been published today in the journal Nature Chemical Engineering.
The development of tiny smart devices, smaller than a few cubic millimeters, demands equally small power sources. For minimally invasive biomedical devices that interact with biological tissues, these power sources must be fabricated from soft materials. Ideally, these should also have features such as high capacity, biocompatibility and biodegradability, triggerable activation, and the ability to be controlled remotely. To date, there has been no battery that can fulfil these requirements all at once.
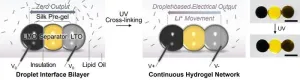
To address these requirements, researchers from the University of Oxford’s Department of Chemistry and Department of Pharmacology have developed a miniature, soft lithium-ion battery constructed from biocompatible hydrogel droplets. Surfactant-supported assembly (assembly aided by soap-like molecules), a technique reported by the same group last year in the journal Nature (DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06295-y), is used to connect three microscale droplets of 10 nanolitres volume. Different lithium-ion particles contained in each of the two ends then generate the output energy.
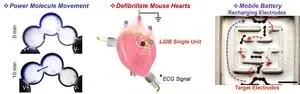
‘Our droplet battery is light-activated, rechargeable, and biodegradable after use. To date, it is the smallest hydrogel lithium-ion battery and has a superior energy density’ said Dr Yujia Zhang (Department of Chemistry, University of Oxford), the lead researcher for the study and a starting Assistant Professor at the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne. ‘We used the droplet battery to power the movement of charged molecules between synthetic cells and to control the beating and defibrillation of mouse hearts. By including magnetic particles to control movement, the battery can also function as a mobile energy carrier.’
Proof-of-concept heart treatments were carried out in the laboratory of Professor Ming Lei (Department of Pharmacology), a senior electrophysiologist in cardiac arrhythmias. He said: ‘Cardiac arrhythmia is a leading cause of death worldwide. Our proof-of-concept application in animal models demonstrates an exciting new avenue of wireless and biodegradable devices for the management of arrhythmias.’
Professor Hagan Bayley (Department of Chemistry), the research group leader for the study, said: ‘The tiny soft lithium-ion battery is the most sophisticated in a series of microscale power packs developed by Dr Zhang and points to a fantastic future for biocompatible electronic devices that can operate under physiological conditions.’
The researchers have filed a patent application through Oxford University Innovation. They envisage that the tiny versatile battery, particularly relevant to small-scale robots for bioapplications, will open up new possibilities in various areas including clinical medicine.
Notes for editors:
Images of this work can be downloaded here: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1kAom8uTc0Dcchi_RUA0z3_M1yC3c3FH3?usp=drive_link
These images are for editorial purposes only and MUST be credited. They MUST NOT be sold on to third parties.
For media enquiries, including interview requests, contact:
Professor Yujia Zhang, University of Oxford / École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne: yujia.zhang@epfl.ch
Professor Ming Lei, University of Oxford: ming.lei@pharm.ox.ac.uk
Professor Hagan Bayley, University of Oxford: hagan.bayley@chem.ox.ac.uk
The study ‘A microscale soft lithium-ion battery for tissue stimulation’ will be published in Nature Chemical Engineering on 25 October 2024 at 10:00 (London time), 25 October 2024 at 05:00 (US Eastern Time), and will be available at DOI: 10.1038/s44286-024-00136-z. Once published online, it will be available at the following URL: https://www.nature.com/articles/s44286-024-00136-z
About the University of Oxford
Oxford University has been placed number 1 in the Times Higher Education World University Rankings for the ninth year running, and number 3 in the QS World Rankings 2025. At the heart of this success are the twin-pillars of our ground-breaking research and innovation and our distinctive educational offer.
Oxford is world-famous for research and teaching excellence and home to some of the most talented people from across the globe. Our work helps the lives of millions, solving real-world problems through a huge network of partnerships and collaborations. The breadth and interdisciplinary nature of our research alongside our personalised approach to teaching sparks imaginative and inventive insights and solutions.
Through its research commercialisation arm, Oxford University Innovation, Oxford is the highest university patent filer in the UK and is ranked first in the UK for university spinouts, having created more than 200 new companies since 1988. Over a third of these companies have been created in the past three years. The university is a catalyst for prosperity in Oxfordshire and the United Kingdom, contributing £15.7 billion to the UK economy in 2018/19, and supports more than 28,000 full time jobs.
END
FINDINGS
UCLA scientists have identified the protein GPNMB as a critical regulator in the heart’s healing process after a heart attack.
Using animal models, they demonstrate that bone marrow-derived immune cells called macrophages secrete GPNMB, which binds to the receptor GPR39, promoting heart repair. These findings offer a new understanding of how the heart heals itself and could lead to new treatments aimed at improving heart function and preventing the progression to heart failure.
BACKGROUND
Every 40 seconds, ...
News coverage of the 2024 election season has often centered on how partisan division has affected our politics. But a new analysis shows that political polarization also poses significant health risks—by obstructing the implementation of legislation and policies aimed at keeping Americans healthy, by discouraging individual action to address health needs, such as getting a flu shot, and by boosting the spread of misinformation that can reduce trust in health professionals.
“Compared to other high-income countries, the United States has a disadvantage when it comes to the health of its citizens,” ...
**EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL OCT. 25 AT 5 A.M. ET**
A newly described stage of a lymph node-like structure seen in liver tumors after presurgical immunotherapy may be vital to successfully treating patients with hepatocellular carcinoma, according to a study by researchers from the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center.
The study, published Oct. 25 in Nature Immunology, provides new information about lymph node-like structures called tertiary lymphoid structures. These structures, which are highly organized ...
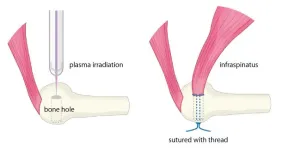
The human body, filled with muscles and moving parts, is far from indestructible. Injuries are common, especially where tendons and bones connect. In Japan, rotator cuff tears affect approximately 1 in 4 people over age 50, and reports state that even after surgery, about 20% of cases result in re-tears. To combat this, new healing methods to bolster current clinical practices are needed.
Graduate student Katsumasa Nakazawa, Associate Professor Hiromitsu Toyoda, and then Professor Hiroaki Nakamura at Osaka Metropolitan University’s ...
San Diego, CA (October 24, 2024) — Investigators recently uncovered key insights into newly defined rejection entities in kidney transplantation that may offer improved patient risk categorization post-transplant. The research will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2024 October 23– 27.
Kidney transplant rejection continues to threaten the long-term success of kidney transplants, with microvascular inflammation (inflammation within capillaries) playing a pivotal role in graft failure. Due to its complex nature, this inflammation poses a major challenge in clinical practice. In response, the international Banff classification—the ...
**Embargo: 23.30 [UK time] / 06.30pm [US ET] Thursday 24th October 2024**
Peer reviewed / Literature review, systematic review and meta-analysis, opinion / People
Embargoed access to the Commission report and contact details for authors are available in Notes to Editors at the end of the release.
The Lancet Public Health: New Commission calls for regulatory reform to tackle the health impacts of the rapid global expansion of commercial gambling
Gambling harms are far more substantial than previously understood, exacerbated by rapid global expansion ...
Barcelona, Spain: Researchers have shown that they can accurately re-create clinical trials of new treatments using ‘digital twins’ of real cancer patients. The technology, called FarrSight®-Twin, which is based on algorithms used by astrophysicists to discover black holes, will be presented today (Friday) at the 36th EORTC-NCI-AACR [1] Symposium on Molecular Targets and Cancer Therapeutics in Barcelona, Spain.
The researchers say that this approach could be used by cancer ...
Barcelona, Spain: Researchers have shown for the first time that it is possible for a specially-designed ‘mini-protein’ to deliver a radiation dose directly to tumour cells expressing a protein on their cell surfaces called Nectin-4, which is often found in a number of different cancers.
In a study presented on Friday at the 36th EORTC-NCI-AACR [1] Symposium on Molecular Targets and Cancer Therapeutics in Barcelona, Spain, Mike Sathekge, Professor and Head of the Nuclear Medicine Department at the University of Pretoria ...
Barcelona, Spain: Patients with advanced bladder cancer that had spread to other parts of the body (metastasised) have responded well in a phase I clinical trial of an investigational drug, TYRA-300. The drug targets changes in the FGFR3 gene that drive tumour growth in about 10%-20% of these patients.
Associate Professor, Ben Tran, a medical oncologist at Peter McCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne, Australia, presented the first results as of 15 August 2024 from 41 patients enrolled in the SURF301 study in a late-breaking oral presentation at the 36th EORTC-NCI-AACR [1] Symposium on Molecular Targets and Cancer Therapeutics ...
Barcelona, Spain: Researchers have discovered key mutations in certain cancer cells that make them resistant to WRN inhibitors, a new class of anti-cancer drugs. The yet-to-be-published findings are presented on Friday at the 36th EORTC-NCI-AACR [1] Symposium on Molecular Targets and Cancer Therapeutics in Barcelona, Spain.
Werner helicase (WRN) inhibitors are already being evaluated in phase I clinical trials in patients with tumours that have microsatellite instability (MSI) – a condition in which the genes responsible for monitoring and repairing mistakes in DNA replication stop functioning, and errors are introduced. This is also ...