The molecular mechanism of Shufeng Jiedu capsules in the treatment of influenza: A comprehensive analysis based on network pharmacology, bioinformatics, and molecular docking
2024-10-29
(Press-News.org) Background and objectives
Shufeng Jiedu Capsules (SFJD), a traditional Chinese medicine preparation, are widely used in the clinical treatment of influenza, yet their mechanism of action remains unclear. This study aimed to systematically explore the molecular mechanism of SFJD in the treatment of influenza using network pharmacology and bioinformatics techniques.
Methods
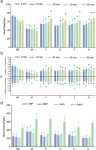
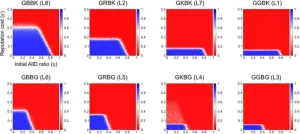
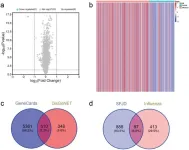
The active ingredients of SFJD were retrieved from traditional Chinese medicine databases, and their targets were identified using the Swiss Target Prediction and TCMSP databases. Influenza disease genes were obtained from the GEO, GeneCards, and DisGeNET databases, and a Venn diagram was used to identify potential targets by mapping SFJD targets to influenza disease genes. Network construction and analysis of potential therapeutic targets were performed using the STRING12.0 database and Cytoscape3.9.1 software, leading to the identification of key targets. The expression of potential therapeutic targets in tissues and cells was retrieved using the BioGPS database. Functional enrichment analysis of these targets was conducted using the DAVID database. Molecular docking was then used to assess the interactions between key targets and core active ingredients.
Results
SFJD contains 193 active ingredients and 985 targets. There are 510 influenza disease genes, 97 of which are potential therapeutic targets for SFJD in treating influenza, with 27 key targets identified through network construction and analysis. Tissue/cell-specific analysis revealed that 39 potential therapeutic targets are highly expressed in 37 specific tissues/cells. Functional enrichment analysis highlighted pathways such as the C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway, tumor necrosis factor signaling pathway, and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 signaling pathway. Molecular docking results indicated strong interactions between the core active ingredients and the key targets.
Conclusions
This study systematically reveals that the mechanism of action of SFJD in treating influenza is complex, involving multiple targets and pathways related to antiviral, anti-inflammatory, and immune regulation effects. The findings provide valuable reference information for future clinical treatment and basic research on influenza.
Full text:
https://www.xiahepublishing.com/2835-6357/FIM-2024-00030
The study was recently published in the Future Integrative Medicine.
Future Integrative Medicine (FIM) publishes both basic and clinical research, including but not limited to randomized controlled trials, intervention studies, cohort studies, observational studies, qualitative and mixed method studies, animal studies, and systematic reviews.
Follow us on X: @xiahepublishing
Follow us on LinkedIn: Xia & He Publishing Inc.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-10-29
Routine use of an orbital atherectomy device to remove calcium from severely blocked coronary arteries before patients undergo cardiac stenting procedures does not improve outcomes, a Mount Sinai-led study has found.
The results of the ECLIPSE study were announced during a late-breaking trial presentation at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics Annual Meeting on Tuesday, October 29. This is the first large-scale study to study this specific device in severely calcified lesions, and the results support reserving its use for extreme cases.
“Operators across the United States currently have different thresholds ...
2024-10-29
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Knowing a patient’s symptoms helps radiologists in lumbar spine MRI interpretation and diagnosis, according to a study published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
MRI is the most important imaging exam in patients with back pain or sciatica because it shows nearly all degenerative and structural abnormalities of the spine.
However, MRI often shows spinal abnormalities in individuals who do not have symptoms. Because the same abnormalities can ...
2024-10-29
Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men, and almost 300,000 individuals are diagnosed with it each year in the U.S. To develop a consistent method of estimating prostate cancer size, which can help clinicians more accurately make informed treatment decisions, Mass General Brigham researchers trained and validated an AI model based on MRI scans from more than 700 prostate cancer patients. The model was able to identify and demarcate the edges of 85% of the most radiologically aggressive prostate lesions. Tumors with a larger volume, as estimated by the AI model, ...
2024-10-29
A new synthesis of global evidence highlights a strong connection between family violence and long-term health consequences, significantly impacting the psychological and physical well-being of millions worldwide. This comprehensive review, the first of its kind, synthesises the findings from the most rigorous studies on child maltreatment and intimate partner violence, uncovering alarming patterns in the long-term effects of family violence.
According to the study, led by Matthias Burghart of the Max Planck Institute for the Study of Crime, Security, and Law, and Sophia ...
2024-10-29
Leading ethics experts and researchers have co-authored a breakthrough paper calling for new governance and legal rules to guide application of emerging technology to preserve organs for transplant.
Current law and guidance are inadequate for emerging biopreservation technologies that will allow long-term storage of human organs for transplantation. The technology is much needed to address the severe time constraints that currently limit the viability of donor organs. Those constraints have contributed to a severe organ shortage, which affects patients throughout ...
2024-10-29
Background and objectives
Fuzi, the processed product of daughter roots of Aconitum carmichaelii Debx., is a well-known Chinese medicine for the treatment of heart failure (HF) and related cardiac diseases. This study aimed to investigate the molecular mechanism of the cardioprotective effects of Fuzi water decoction (FWD) and Fuzi water-soluble alkaloids (FWA) on the model of HF.
Methods
The HF model of rats was prepared through intravenous injection of propafenone hydrochloride. The normal group, model group, FWD-treated groups (1.25 g/kg, 2.5 g/kg, 5 g/kg) and positive group (Shenfu Injection, 3.3 mL/kg) were set up. Heart rate, LV+dp/dtmax, and ...
2024-10-29
Background and objectives
Albumin is a major prognostic factor for patients with advanced liver disease, dependent on its concentration and biological activity. This study aimed to improve the method of active albumin detection and elucidate its predictive validity of albumin activity across hepatic disease progression and etiology.
Methods
This study synthesized a novel ratiometric fluorescent probe with an improved structure of 2′-FBPBN. The technique was used to detect native human albumin (HA) activity in 244 patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis (LC) and 66 patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Clinical and laboratory data were also collected.
Results
Patients ...
2024-10-29
A groundbreaking study led by Prof. Dr. Hitoshi Yamamoto (Rissho University) and his collaborators from, Soka University, Koriyama Women’s College, and the RINRI Institute has made significant strides in the field of indirect reciprocity: a key mechanism for sustaining cooperation in human societies. Their research unveils new insights into the social norms that protect cooperative behaviour from defector invasion and reputation costs, thereby deepening our understanding of how large-scale societies maintain stability. The results of the study were published in Scientific Reports.
Indirect reciprocity is characterised by cooperative ...
2024-10-29
An international coalition of researchers from the United States and Italy has discovered a novel strain of cyanobacteria, or algae, isolated from volcanic ocean vents that is especially adept at growing rapidly in the presence of CO2 and readily sinks in water, making it a prime candidate for biologically-based carbon sequestration projects and bioproduction of valuable commodities. This strain, nicknamed “Chonkus,” was found off the coast of the island of Vulcano in Sicily, Italy — an environment in which marine CO2 is abundant due to shallow volcanic vents. The discovery is described in a paper published ...
2024-10-29
Today, people increasingly seek non-alcoholic versions of beer or wine. Despite boasting different flavors, these two drinks share many aromas, which makes it difficult to produce alcohol-free versions that mimic the real thing. Researchers in ACS’ Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry report on a literature analysis and experiment to characterize the chemical compounds that give beer and wine their unique fragrances. They say their findings could aid the development of flavorful, non-alcoholic substitutes.
Food and beverage researchers are working to recreate the enjoyable aromas and flavors of beer and wine in alcohol-free substitutes. However, because both beer and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] The molecular mechanism of Shufeng Jiedu capsules in the treatment of influenza: A comprehensive analysis based on network pharmacology, bioinformatics, and molecular docking