Transcriptomics-based study on the mechanism of heart failure amelioration by water decoction and water-soluble alkaloids of Fuzi
2024-10-29
(Press-News.org) Background and objectives
Fuzi, the processed product of daughter roots of Aconitum carmichaelii Debx., is a well-known Chinese medicine for the treatment of heart failure (HF) and related cardiac diseases. This study aimed to investigate the molecular mechanism of the cardioprotective effects of Fuzi water decoction (FWD) and Fuzi water-soluble alkaloids (FWA) on the model of HF.
Methods
The HF model of rats was prepared through intravenous injection of propafenone hydrochloride. The normal group, model group, FWD-treated groups (1.25 g/kg, 2.5 g/kg, 5 g/kg) and positive group (Shenfu Injection, 3.3 mL/kg) were set up. Heart rate, LV+dp/dtmax, and LV-dp/dtmax were recorded at 5 m, 10 m, 20 m, 30 m, and 60 m after drug administration, respectively. The contents of atrial natriuretic peptide, brain natriuretic peptide (BNP), angiotensin II, and aldosterone in serum were determined 20 m post-administration. An in vitro cardiomyocyte hypertrophy model with HDAC2 overexpression was constructed and verified by lentivirus transfection. The experiment included a blank group, FWD-treated groups (3 mg/mL, 1.5 mg/mL), and FWA-treated groups (4 mg/mL, 2 mg/mL). For transcriptome analysis, the model group, blank group, and FWD-treated group (2.5 g/kg) at 20 m and 60 m in vivo, and different dose groups in vitro, were selected to analyze the therapeutic mechanisms of FWD and FWA.
Results
All FWD treatment groups showed an increased heart rate, among which the groups with 2.5 g/kg and 5 g/kg FWD showed better effects, significantly increasing LV+dp/dtmax and LV-dp/dtmax after 20 m of administration and significantly reducing BNP and aldosterone serum levels. In the constructed cardiomyocyte hypertrophy model, HDAC2 expression, atrial natriuretic peptide and BNP protein levels, and cell surface area increased. Transcriptome data from both in vivo and in vitro showed that FWD and FWA could exert cardioprotective effects through pathways such as the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, NF-κB signaling pathway, and ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters, involving key genes such as ITGB1, TLR2, and CDKN1A. Fuzi inhibited the hypertrophic gene HDAC2. Additionally, based on weighted gene co-expression network analysis, ABC transporters may be an important molecular pathway for FWA in treating HF.
Conclusions
Both FWD and FWA can ameliorate HF by regulating apoptosis, proliferation, and anti-fibrosis, with ABC transporters potentially being the main pathway for the action of FWA.
Full text:
https://www.xiahepublishing.com/2835-6357/FIM-2024-00005
The study was recently published in the Future Integrative Medicine.
Future Integrative Medicine (FIM) publishes both basic and clinical research, including but not limited to randomized controlled trials, intervention studies, cohort studies, observational studies, qualitative and mixed method studies, animal studies, and systematic reviews.
Follow us on X: @xiahepublishing
Follow us on LinkedIn: Xia & He Publishing Inc.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-10-29
Background and objectives
Albumin is a major prognostic factor for patients with advanced liver disease, dependent on its concentration and biological activity. This study aimed to improve the method of active albumin detection and elucidate its predictive validity of albumin activity across hepatic disease progression and etiology.
Methods
This study synthesized a novel ratiometric fluorescent probe with an improved structure of 2′-FBPBN. The technique was used to detect native human albumin (HA) activity in 244 patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis (LC) and 66 patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Clinical and laboratory data were also collected.
Results
Patients ...
2024-10-29
A groundbreaking study led by Prof. Dr. Hitoshi Yamamoto (Rissho University) and his collaborators from, Soka University, Koriyama Women’s College, and the RINRI Institute has made significant strides in the field of indirect reciprocity: a key mechanism for sustaining cooperation in human societies. Their research unveils new insights into the social norms that protect cooperative behaviour from defector invasion and reputation costs, thereby deepening our understanding of how large-scale societies maintain stability. The results of the study were published in Scientific Reports.
Indirect reciprocity is characterised by cooperative ...
2024-10-29
An international coalition of researchers from the United States and Italy has discovered a novel strain of cyanobacteria, or algae, isolated from volcanic ocean vents that is especially adept at growing rapidly in the presence of CO2 and readily sinks in water, making it a prime candidate for biologically-based carbon sequestration projects and bioproduction of valuable commodities. This strain, nicknamed “Chonkus,” was found off the coast of the island of Vulcano in Sicily, Italy — an environment in which marine CO2 is abundant due to shallow volcanic vents. The discovery is described in a paper published ...
2024-10-29
Today, people increasingly seek non-alcoholic versions of beer or wine. Despite boasting different flavors, these two drinks share many aromas, which makes it difficult to produce alcohol-free versions that mimic the real thing. Researchers in ACS’ Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry report on a literature analysis and experiment to characterize the chemical compounds that give beer and wine their unique fragrances. They say their findings could aid the development of flavorful, non-alcoholic substitutes.
Food and beverage researchers are working to recreate the enjoyable aromas and flavors of beer and wine in alcohol-free substitutes. However, because both beer and ...
2024-10-29
Imagine harnessing the power of ocean currents to generate clean, renewable energy right off the coast of Southeast Florida. Florida Atlantic University’s Southeast National Marine Renewable Energy Center (SNMREC) has been awarded an $800,000 grant from the United States Department of Energy’s Water Power Technologies Office to enable the commercial readiness of ocean energy technologies.
SNMREC, in collaboration with a team of experts including The City of Lake Worth Beach Electric Utility, 3U Technologies, 48 North Solutions, IDOM Incorporated, Braid Theory, and the European Marine Energy Centre (EMEC), ...
2024-10-29
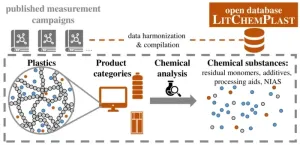
About this study: Plastics contain a vast number of chemicals, some of which greatly impact the environment and human health. However, information on the presence of individual substances in plastic products is oftentimes not publicly available. In a peer-reviewed study, set to be published on 29 October 2024, in Environmental Science and Technology Letters, a new publicly accessible database on chemicals measured in plastics is presented - LitChemPlast. The database contains over 3’500 substances measured in over 47'000 samples of plastic products across 372 studies.
Key findings:
• Contamination of recycled plastics:
The database shows that, due to ...
2024-10-29
Complaining about your allergies online might provide valuable data to researchers. Over 25% of Americans experience seasonal allergies, but how the prevalence of seasonal allergies varies across space and time remains obscure, in part because allergies seldom warrant visits to healthcare providers. Elias Stallard-Olivera and Noah Fierer mined Twitter (now X) posts and Google searches from 2016–2020 to extrapolate spatial and temporal allergy patterns. A natural language processing model sorted posts that indicated symptoms (e.g., “My allergies are really bad today!!”) from posts that include key words but did not indicate the presence of symptoms (e.g., “Gluten ...
2024-10-29
[11:00 GMT - 29 Oct 2024] A groundbreaking, nine-year study has revealed that elephants approaching small-scale farms in Kenya avoid beehive fences housing live honey bees up to 86% of the time during peak crop seasons, helping to reduce human-elephant conflict for local farmers and boost income. Link to images and video of the project available
Key findings include:
Beehive fences are a proven success in reducing human-elephant conflict in Africa.
Savannah elephants avoid beehive fences housing live honey bees up to 86% of the time during peak crop seasons.
Across all seasons and the entire study period, the fences deterred an annual average of 76% of 3,999 ...
2024-10-29
In the fight against antibiotic resistance, a new technology developed at Chalmers University of Technology, in Sweden, can be of great importance when, for example, hip and knee implants are surgically inserted. By heating up small nanorods of gold with near-infrared light (NIR), the bacteria are killed, and the surface of the implant becomes sterile. The researchers are now presenting a new study that increases the understanding of how the gold rods are affected by light and how the temperature in them can be measured.
Infections can occur during surgical procedures, with the risk increasing significantly when foreign materials, ...
2024-10-29
29 October 2024. Doha, Qatar – The World Innovation Summit for Health (WISH), an initiative of Qatar Foundation, has shortlisted 12 innovators for two awards within the 2024 WISH Global Healthcare Innovation Competition. Selected from more than 150 applications, the 12 will showcase their groundbreaking innovations to global policymakers and healthcare leaders at this year’s summit in Doha, 13-14 November.
In addition to the chance to receive one of two investment awards of US$10,000, shortlisted innovators will have access to mentoring sessions with industry experts to learn ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Transcriptomics-based study on the mechanism of heart failure amelioration by water decoction and water-soluble alkaloids of Fuzi