Complete response to encorafenib + binimetinib in BRAF V600E-mutant tumor
“This case report highlights the importance of full tumor genotyping to identify potentially actionable targets in rare tumors such as malignant glomus tumors”
2024-10-29
(Press-News.org)
“This case report highlights the importance of full tumor genotyping to identify potentially actionable targets in rare tumors such as malignant glomus tumors.”
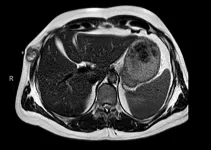
BUFFALO, NY- October 29, 2024 – A new case report was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on October 11, 2024, entitled “Complete response to encorafenib plus binimetinib in a BRAF V600E-mutant metastasic malignant glomus tumor.”
As highlighted in the abstract, glomus tumors (GT) are rare mesenchymal neoplasms originating in dermal arteriovenous structures involved in thermoregulation. While generally benign, some can exhibit malignant features, leading to aggressive behavior, metastasis, and limited response to standard chemotherapy. The identification of the BRAF V600E mutation in certain malignant GT cases offers a promising therapeutic target.
In their paper, researchers Marta Arregui, Antonio Calles, María del Mar Galera, Ana Gutiérrez, Carlos López-Jiménez, Carolina Agra, Adriana Fernández, Natalia Gutiérrez, María de Toro and Rosa Álvarez from Gregorio Marañón University Hospital and Fundación Jiménez Díaz University Hospital in Madrid, Spain, document a remarkable clinical and metabolic response in a case of metastatic BRAF V600E-mutated glomangiosarcoma treated with the combination of encorafenib and binimetinib.
They report on a 45-year-old male patient with stage IV malignant GT carrying a BRAF V600E mutation, who was treated systemically with encorafenib and binimetinib. This approach led to a swift clinical and radiological improvement.
“To our knowledge, our patient represents the first reported case of a metastatic malignant GT successfully treated with BRAF and MEK inhibitors, achieving a long-lasting complete morpho-metabolic response.”
Continue reading: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.28654
Correspondence to: Carlos López-Jiménez - clopezjimenez@atbsarc.org
Video short: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xjbj3Iu16P4
Keywords: cancer, malignant glomus tumor, glomangiosarcoma, BRAF V600E, agnostic treatment, targeted therapy
Click here to sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article.
About Oncotarget:
Oncotarget (a primarily oncology-focused, peer-reviewed, open access journal) aims to maximize research impact through insightful peer-review; eliminate borders between specialties by linking different fields of oncology, cancer research and biomedical sciences; and foster application of basic and clinical science.
Oncotarget is indexed and archived by PubMed/Medline, PubMed Central, Scopus, EMBASE, META (Chan Zuckerberg Initiative) (2018-2022), and Dimensions (Digital Science).
To learn more about Oncotarget, visit Oncotarget.com and connect with us on social media:
X
Facebook
YouTube
Instagram
LinkedIn
Pinterest
Spotify, and available wherever you listen to podcasts
Click here to subscribe to Oncotarget publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Oncotarget Journal Office
6666 East Quaker St., Suite 1
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957 (option 2)
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-10-29
UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL 15:00 GMT / 11:00 ET TUESDAY 29 OCTOBER 2024
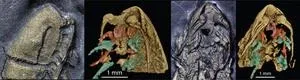
Gold bugs: spectacular new fossil arthropod preserved in fool’s gold
Images available via link in the notes section
A new 450-million-year-old fossil arthropod, preserved in 3D by iron pyrite (fool’s gold), has been unveiled by scientists.
The new species, Lomankus edgecombei, is distantly related to spiders, scorpions, and horseshoe crabs.
The findings have been published today (29 Oct) in the journal Current Biology.
A team of researchers led by Associate Professor Luke Parry, Department of Earth Sciences, University of Oxford, have unveiled a spectacular ...
2024-10-29
WASHINGTON, Oct. 29, 2024 – While many smoking rooms in U.S. airports have closed in recent years, they are still common in other airports around the world. These lounges can be ventilated, but how much does it actually help the dispersion of smoke?
Research published in Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, shows that not all standing positions in airport smoking lounges are created equal.
Researchers from the University of Hormozgan in Iran studied nicotine particles in a simulated airport smoking room and found that the thermal environment and positioning of smokers influenced how particles ...
2024-10-29
AURORA, Colo. (Oct. 29, 2024) – An ancient gene mutation among First Nations inhabitants of Oceania may make them more susceptible to infectious diseases like influenza, according to a new study by scientists at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus.
“We found quite a diverse set of genes in this population but there was one allele that really stood out in terms of genetic composition,” said the study’s lead author Paul Norman, PhD, professor of biomedical informatics at the University of Colorado School of Medicine. “We did some investigating, and we suspect this allele ...
2024-10-29
New Haven, Conn. — Paleontologists have identified fossils of an ancient species of bug that spent the past 450 million years covered in fool’s gold in central New York.
The new species, Lomankus edgecombei, is a distant relative of modern-day horseshoe crabs, scorpions, and spiders. It had no eyes, and its small front appendages were best suited for rooting around in dark ocean sediment, back when what is now New York state was covered by water.
Lomankus also happens to be bright gold — thanks to layers of pyrite ...
2024-10-29
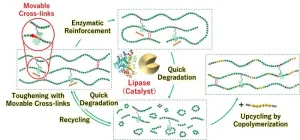
Osaka, Japan—Achieving a sustainable society requires the development of advanced degradable plastics, or polymers, which are molecules composed of long chains of repeating units. The goal of a resource-circulating society is now one step closer thanks to the efforts of a team from Osaka University that has developed tough biodegradable plastics by including movable crosslinking groups.
In a study published this month in Chem, the researchers have revealed that developing polymers with movable crosslinks not only increases their strength but also promotes degradation by enzymes under mild conditions.
Plastics and polymers need to achieve both desirable performance ...
2024-10-29
A new study by UCLA Health reveals that hospital emergency departments may be missing signs of suicidal thoughts and behaviors in children, boys and Black and Hispanic youth.
The research, published in the journal JAMA Open Network, analyzed electronic health records of nearly 3,000 children and teenagers presenting to two emergency departments in southern California for mental health reasons. Using machine learning algorithms, the researchers determined standard medical record surveillance methods miss youth with suicide-related emergencies. These methods disproportionately missed suicide-related visits among Black, Hispanic, male, and preteen youths, compared with ...
2024-10-29
Background and objectives
Shufeng Jiedu Capsules (SFJD), a traditional Chinese medicine preparation, are widely used in the clinical treatment of influenza, yet their mechanism of action remains unclear. This study aimed to systematically explore the molecular mechanism of SFJD in the treatment of influenza using network pharmacology and bioinformatics techniques.
Methods
The active ingredients of SFJD were retrieved from traditional Chinese medicine databases, and their targets were identified using the Swiss Target Prediction and TCMSP databases. Influenza disease genes were obtained from the GEO, GeneCards, and DisGeNET ...
2024-10-29
Routine use of an orbital atherectomy device to remove calcium from severely blocked coronary arteries before patients undergo cardiac stenting procedures does not improve outcomes, a Mount Sinai-led study has found.
The results of the ECLIPSE study were announced during a late-breaking trial presentation at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics Annual Meeting on Tuesday, October 29. This is the first large-scale study to study this specific device in severely calcified lesions, and the results support reserving its use for extreme cases.
“Operators across the United States currently have different thresholds ...
2024-10-29
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Knowing a patient’s symptoms helps radiologists in lumbar spine MRI interpretation and diagnosis, according to a study published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
MRI is the most important imaging exam in patients with back pain or sciatica because it shows nearly all degenerative and structural abnormalities of the spine.
However, MRI often shows spinal abnormalities in individuals who do not have symptoms. Because the same abnormalities can ...
2024-10-29
Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men, and almost 300,000 individuals are diagnosed with it each year in the U.S. To develop a consistent method of estimating prostate cancer size, which can help clinicians more accurately make informed treatment decisions, Mass General Brigham researchers trained and validated an AI model based on MRI scans from more than 700 prostate cancer patients. The model was able to identify and demarcate the edges of 85% of the most radiologically aggressive prostate lesions. Tumors with a larger volume, as estimated by the AI model, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Complete response to encorafenib + binimetinib in BRAF V600E-mutant tumor
“This case report highlights the importance of full tumor genotyping to identify potentially actionable targets in rare tumors such as malignant glomus tumors”