Some wildfire suppressants contain heavy metals and could contaminate the environment
2024-10-30
(Press-News.org) In fire-prone areas, water isn’t the only thing used to quell blazes. Wildland firefighters also apply chemical or synthetic suppressants. Researchers reporting in ACS’ Environmental Science & Technology Letters explored whether these suppressants could be a source of elevated metal levels sometimes found in waterways after wildfires are extinguished. Several products they investigated contained high levels of at least one metal, including chromium and cadmium, and could contribute to post-fire increases in the environment.
“Wildfires are associated with the release of toxic heavy metals to the environment, but until now, it was assumed that these metals came from natural sources like soil,” says Daniel McCurry, principal investigator of the study. “We now know that fire retardants may contribute to these metal releases.”
Wildfire suppressant products, which are intended to inhibit fire activity before and after water evaporates, include fire retardants, water enhancers and foams. As wildfires have become more frequent and severe, larger volumes of water along with chemical and synthetic suppressants — sprayed from the ground and dropped from planes — have been required to extinguish them. Although manufacturers identify most of the active ingredients in suppressants, some components are proprietary. In addition, previous researchers have observed increased concentrations of potentially toxic metals in soil and streams after wildfires. So, McCurry and colleagues at the University of Southern California wondered if the suppressants contain metals and could contaminate the environment.
The researchers tested samples from 14 fire suppression products sold by commercial retailers. They analyzed samples for 10 metals that have known toxicity or are regulated by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Every product contained at least one metal with a concentration that exceeded the EPA’s Maximum Contaminant Level regulations for drinking water. In particular, the two suppression products classified as fire retardants contained eight metals (chromium, cadmium, arsenic, lead, vanadium, manganese, antimony and thallium) that greatly exceeded the EPA’s drinking water regulations. And one of the retardants exceeded California’s hazardous waste regulations for three of those metals. The researchers say these results indicate the potential for fire retardants to contaminate the aquatic environment and potentially drinking water, if these products enter bodies of waters.
From the volume of fire retardants dropped on wildfires in the U.S. between 2009 and 2021, the researchers determined that the total amount of metals applied was variable year to year but generally increased over time. And for one Southern California wildfire, they estimate that the increased concentration of cadmium in a nearby stream could be explained by 31% of the reported fire retardant used to contain the fire. They say these results show that fire suppression activities could contribute to elevated metal levels in the environment but that more work is needed to determine potential risks to human and environmental health.
The authors acknowledge funding from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF), an NSF Graduate Research Fellowship, and a University of Southern California Graduate School and Women in Science and Engineering Fellowship.
The paper’s abstract will be available on Oct. 30 at 8 a.m. Eastern time here: http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.estlett.4c00727
###
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, e-books and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world’s scientific knowledge. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
Registered journalists can subscribe to the ACS journalist news portal on EurekAlert! to access embargoed and public science press releases. For media inquiries, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Note: ACS does not conduct research but publishes and publicizes peer-reviewed scientific studies.
Follow us: X, formerly Twitter | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-10-30
As a leader in academic health and biomedical research training, the Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center (TTUHSC) covers the West Texas region that comprises half of the state’s land mass and is home to 10% of its population. Research at TTUHSC drives innovation and discovery, changing the lives of those it serves and attracting talented faculty, staff and students.
During the latest reporting period (2020-2022), TTUHSC received an average of $12,539,679 annually in National Institutes ...
2024-10-30
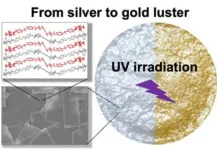
Societies of the past and present have given high regard to precious metals like gold and silver. Both metals remind us of nobility and luxury. However, they are quite expensive, which restricts their applications. Therefore, materials with attractive but artificial gold- and silver-like metallic lusters are popular, finding use in jewelry, reflective materials, inks, and cosmetics.
Unfortunately, typical metallic luster materials cause environmental harm, rendering them unsustainable. Thus, scientists are actively searching for metal-free alternatives. In this direction, the research fraternity ...
2024-10-30
In space exploration, long-distance optical links can now be used to transmit images, films and data from space probes to Earth using light. But in order for the signals to reach all the way and not be disturbed along the way, hypersensitive receivers and noise-free amplifiers are required. Now, researchers at Chalmers University of Technology, in Sweden, have created a system that, with a silent amplifier and record-sensitive receiver, paves the way for faster and improved space communication.
Space communication systems are increasingly based on optical laser beams rather than radio waves, as the signal loss has been shown to be less when light is used ...
2024-10-30
Embargoed Until 10/30/24 at 7 am
PhD in Public Health candidate Elaine Russell and her mentor Kenneth Griffin, professor in the department of Global and Community Health, in George Mason University’s College of Public Health, worked with Tolulope Abidogun, also a PhD in Public Health student, and former Global and Community Health professor Lisa Lindley, now of Lehigh University, to analyze data from the American College Health Association National College Health Assessment (ACHA-NCHA III) in an effort to understand how university ...
2024-10-30
PHNOM PENH, Cambodia (October 30, 2024) – The first-ever camera trap study of the Central Cardamom Mountains Landscape has recorded 108 species, 23 of which are listed at risk (Vulnerable or above) on the IUCN Red List, underscoring the significance of the region as a global stronghold for biodiversity and rare and threatened species.
Editors please note: Use these links to access camera trap footage and the full report.
The report, released today by the Cambodian Ministry of Environment (MoE), the United States Agency ...
2024-10-30
An international team of geoscientists led by a volcanologist at Rutgers University-New Brunswick has discovered that, contrary to present scientific understanding, ancient volcanoes continued to spew carbon dioxide into the atmosphere from deep within the Earth long past their period of eruptions.
In doing so, the research team has solved a long-standing mystery over what caused prolonged episodes of warming during turning points in Earth’s climate history. The work is detailed in today’s issue of the journal Nature Geoscience.
“Our ...
2024-10-30
In the face of increased human pressures and climate change, a team of Australian scientists led by Dr Georgina Wood at Flinders University have launched a new online tool to assist marine managers and restoration experts to bolster the resilience of marine habitat-forming species.
The ‘Reef Adapt’ initiative, developed by experts from the NSW Department of Primary Industries and Regional Development (NSW DPIRD), Flinders University and The University of Western Australia (UWA), aims to expand the tools available to promote diverse, adaptable and resilient ecosystems.
Described in a new article in Communications Biology, Reef Adapt harnesses genetic data ...
2024-10-30
"Sustainable development pathways are strategies that prevent dangerous climate change while at the same time moving towards a world that allows people to prosper on a healthy planet,” explains Bjoern Soergel, scientist at the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research PIK and lead author of the study published in Environmental Research Letters. This is the essence of the 17 SDGs agreed by the United Nations in 2015. “Our analysis shows that all three sustainable development pathways are far more effective than our current ‘business as usual’. They drive substantial progress towards the SDGs, for example reducing the number of people in extreme poverty ...
2024-10-30
In the past, African giant pouched rats have learned to detect explosives and the tuberculosis-causing pathogen. Now, a team of researchers have trained these rats to pick up the scent of pangolin scales, elephant ivory, rhino horn, and African blackwood. These animals and plants are listed as threatened and at high danger of extinction.
“Our study shows that we can train African giant pouched rats to detect illegally trafficked wildlife, even when it has been concealed among other substances,” ...
2024-10-30
Electrons spin even without an electric charge and this motion in condensed matter constitutes spin current, which is attracting a great deal of attention for next-generation technology such as memory devices. An Osaka Metropolitan University-led research group has been able to gain further insight into this important topic in the field of spintronics.
To investigate the characteristics of spin currents, OMU Graduate School of Science Professor Katsuichi Kanemoto’s group designed a multilayer device consisting of a ferromagnetic layer and an organic semiconductor ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Some wildfire suppressants contain heavy metals and could contaminate the environment