A paper-aluminum combo for strong, sustainable packaging
2024-10-31
(Press-News.org) Takeout containers get your favorite noodles from the restaurant to your dining table (or couch) without incident, but they are nearly impossible to recycle if they are made from foil-lined plastics. Research published in ACS Omega suggests that replacing the plastic layer with paper could create a more sustainable packaging material. The researchers used mechanical demonstrations and computer simulations to identify paper-aluminum laminate designs that won’t compromise on performance.
Protective packaging, like containers made from polyethylene and aluminum laminates, combines the strength and durability of plastic with the moisture- and light-blocking properties of aluminum foil. While these materials are effective, there’s been a shift toward consumers desiring less plastic and more environmentally friendly materials in the packaging that comes into their homes. To create such an option for protective packaging without sacrificing functionality, Hamed Zarei and colleagues designed a variety of paper-aluminum laminates and compared their strength and durability to common polyethylene-aluminum packaging.
First, Zarei’s team manufactured two paper-aluminum laminates:
A machine-direction (MD) laminate made from aluminum and paper with fibers that run parallel to the direction of machine loading (with the grain).
A cross-direction (CD) laminate made from aluminum and paper with fibers that run perpendicular to the direction of machine loading (against the grain).
The researchers then compared the tensile strength of MD and CD paper-aluminum laminates to polyethylene-aluminum laminate by stretching samples of each material with gradually increasing force on laboratory machines. They also created a digital model, verified with their tensile strength data, that could replicate these laminate stretching tests and reliably predict the material’s response under different scenarios.
In tensile strength tests, the polyethylene-aluminum laminate could be stretched further without breaking than both paper-aluminum laminates. And of the two paper-containing materials, the one made from MD paper could be stretched further but formed cracks along the paper’s grain faster than the CD paper. By running simulations of the MD, CD and a mixed MD/CD paper on their digital model, the researchers predicted that an aluminum film paired with a paper layer made from both MD and CD fibers would result in mechanical properties nearly identical to conventional polyethylene-aluminum laminate.
While they haven’t yet created the MD/CD paper-aluminum laminate in the lab, the researchers say this study provides packaging engineers with information to create sustainable materials that could perform like conventional options.
The authors acknowledge funding from the Tuscany Region Development and Cohesion Fund.
###
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, e-books and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world’s scientific knowledge. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
Registered journalists can subscribe to the ACS journalist news portal on EurekAlert! to access embargoed and public science press releases. For media inquiries, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Note: ACS does not conduct research but publishes and publicizes peer-reviewed scientific studies.
Follow us: X, formerly Twitter | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-10-31
Relief carvings or relief sculptures are cultural heritage objects with figures that protrude from a background such as a wall or slab, creating a sense of depth. Commonly found at historical sites worldwide, these artworks are considered to be of immense historical and cultural value. Unfortunately, many such relief carvings at heritage sites across the world suffer from varying degrees of damage and deterioration over time. While modern 3D scanning and photogrammetry techniques can digitally preserve their current form, they cannot restore the original appearance of these carvings before damage. Additionally, traditional methods for restoring ...
2024-10-31
A common yet underdiagnosed sleep disorder contributes to the development of dementia among adults — particularly women, a Michigan Medicine study suggests.
Investigators uncovered this by examining survey and cognitive screening data from more than 18,500 adults to determine the potential effect of known or suspected obstructive sleep apnea on the risk for dementia.
Obstructive sleep apnea is a chronic sleep disorder characterized by episodes disrupted or restricted breathing during sleep.
For all adults age 50 and older, having known obstructive sleep apnea or its symptoms — as people often do not know they have the problem ...
2024-10-31
Imagine a sweater that powers electronics to monitor your health or charge your mobile phone while running. This development faces challenges because of the lack of materials that both conduct electricity stably and are well suited for textiles. Now a research group, led by Chalmers University of Technology in Sweden, presents an ordinary silk thread, coated with a conductive plastic material, that shows promising properties for turning textiles into electricity generators.
Thermoelectric textiles convert temperature differences, for example between our bodies and the surrounding ...
2024-10-31
A drug commonly used to treat glaucoma has been shown in zebrafish and mice to protect against the build-up in the brain of the protein tau, which causes various forms of dementia and is implicated in Alzheimer’s disease.
Researchers in the UK Dementia Research Institute at the University of Cambridge screened more than 1,400 clinically-approved drug compounds using zebrafish genetically engineered to make them mimic so-called tauopathies. They discovered that drugs known as carbonic anhydrase inhibitors – of which the glaucoma drug methazolamide is one – clear tau build-up and reduce signs of the disease in zebrafish and mice carrying the mutant forms of tau ...
2024-10-31
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – A long-standing goal of neuroscience is to understand how molecules and cellular structures on a microscale give rise to communication between brain regions at the macroscale. A study published in Nature Neuroscience now identifies, for the first time, hundreds of brain proteins that explain inter-individual differences in functional connectivity and structural covariation in the human brain.
“A central goal of neuroscience is to develop an understanding of the brain that ultimately describes the mechanistic basis of human cognition and behavior,” said Jeremy Herskowitz, Ph.D., associate professor in the University of Alabama at Birmingham ...
2024-10-31
They say a picture is worth a thousand words.
A new method, developed by University of Michigan researchers, creates images that are worth many gigabytes of data, which could revolutionize the way biologists study gene expression. Seq-Scope, developed by Jun Hee Lee, Ph.D., Hyun Min Kang, Ph.D., and their colleagues, was first described in Cell in 2021 as the first method to analyze gene expression at sub micrometer-scale spatial resolution.
To compare, a single human hair ranges from 20 to 200 micrometers in width.
The team has since improved Seq-Scope, making it more versatile, ...
2024-10-31
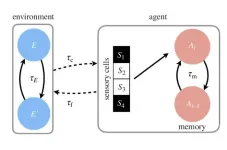
Researchers at the Complexity Science Hub and Santa Fe Institute have developed a model to calculate how quickly or slowly an organism should ideally learn in its surroundings. An organism’s ideal learning rate depends on the pace of environmental change and its life cycle, they say.
Every day, we wake to a world that is different, and we adjust to it. Businesses face new challenges and competitors and adapt or go bust. In biology, this is a question of survival: every organism, from bacteria to blue whales, faces the challenge of adapting to environments that ...
2024-10-31
Toronto, ON, – New research from the University of Toronto found that childhood neglect, even in the absence of childhood sexual abuse and physical abuse, is linked with a wide range of mental and physical health problems in adulthood.
“While a large body of research has established the detrimental impact of childhood physical and sexual abuse on adult health outcomes, much less is known about whether neglect, in the absence of abuse, has similar negative outcomes,” said first author, Linxiao Zhang, a PhD student at the Factor-Inwentash Faculty of Social Work (FIFSW) at the University of Toronto. “Our research underlines the importance of health professionals ...
2024-10-31
In perhaps the first long-term study of CO2 fluxes in northern forests growing on permafrost, an Osaka Metropolitan University-led research team has found that climate change increased not only the sources of carbon, but also the CO2 sinks.
The 20-year observation from 2003-2022 in the interior of Alaska showed that while CO2 sinks turned into sources during the first decade, the second decade showed a nearly 20% increase in CO2 sinks.
Graduate School of Agriculture Associate Professor Masahito Ueyama and colleagues found that warming led to wetness, which in turn aided the growth of black spruce trees. During photosynthesis, the growing trees were using the increasing ...
2024-10-31
WASHINGTON — Researchers have developed a new ultrafast laser platform that generates ultra-broadband ultraviolet (UV) frequency combs with an unprecedented one million comb lines, providing exceptional spectral resolution. The new approach, which also produces extremely accurate and stable frequencies, could enhance high-resolution atomic and molecular spectroscopy.
Optical frequency combs — which emit thousands of regularly spaced spectral lines — have transformed fields like metrology, spectroscopy and precision timekeeping via optical atomic clocks, earning the 2005 Nobel Prize in Physics.
The ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A paper-aluminum combo for strong, sustainable packaging