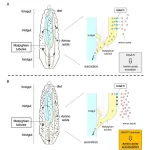
(Press-News.org) With the rapid increase in the global population, a "protein crisis" is expected in the near future, where the supply of protein will not be able to meet the rising demand. Fishmeal is the most common protein source that supports the production of livestock and aquaculture products, which are key protein sources for human consumption. However, global shortage of fishmeal and its rising prices have created an urgent need to find and secure an alternative protein source. Insects are gaining attention as novel protein sources due to their rich protein content and requires less water and space for their growth. The black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens, BSF) is one of the most promising insects for producing protein for animal feed, as its larvae can convert various organic wastes into high-quality protein. However, protein derived from BSF larvae has lower levels of some essential amino acids (AAs), such as histidine and methionine when compared to fishmeal, which can affect the growth performance of certain fish.
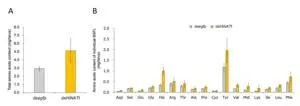
A research team from NARO and the University of Tokyo has successfully enhanced these essential AAs in BSF larvae through biotechnological approaches. In most insects, AAs are obtained from food, and any excess is excreted. By suppressing the expression of the HiNATt gene, which is responsible for AA excretion, the total amount of AAs retained in the BSF larvae increased by 1.8 times, with histidine and methionine levels boosted by over 2.5 times. This research was published in the Journal of Insects as Food and Feed on November 1st.
These findings demonstrate the possibility of manipulating AA levels in BSF larvae without changing their diet, significantly enhancing the nutritional and economic value of BSF larvae as an alternative protein source. This development is expected to contribute to a stable food supply and promote sustainable food production.
Dr. Chia-Ming Liu, the corresponding author of this article, remarked, “Research on the transport of nutritional AAs in the digestive and excretory systems has lagged behind, as it has garnered less attention compared to neurotransmitters. However, our findings suggest that more resources should be dedicated for the research of nutritional AA allocation. The findings will be applied to develop highly valuable BSF strains with tailored AA profiles for on-demand animal feed. Our research group is also working on breeding superior BSF strains and improving rearing techniques supported by the Cabinet Office, Government of Japan, Moonshot Research and Development Program for Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries (funding agency: Bio-oriented Technology Research Advancement Institution. Cabinet Office HP: https://www8.cao.go.jp/cstp/english/moonshot/top.html). By advancing research on the utilization of insects as feed, we aim to contribute to a stable food supply and sustainable food production with minimal environmental impact.
About National Agriculture and Food Research Organization (NARO)
NARO is the core institute in Japan for conducting research and development in a wide range of fields, from basic to applied, for the development of agriculture and food industries.
For more information, visit https://www.naro.go.jp/english/index.html .
END
Boosting the nutritional value of black soldier fly larvae with biotechnology
2024-11-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Medication decisions in pregnancy: A balancing act
2024-11-01
Most women use medication during pregnancy. Yet, selecting appropriate drugs and doses is challenging. In a new The Lancet article, physicians and researchers from the Radboud university medical center, Maastricht UMC+, Imperial College London, and the University of Liverpool introduce a shared decision-making approach combining ethical principles and a pregnant woman’s values with existing evidence. They use the example of sertraline, a commonly prescribed antidepressant in pregnancy, to illustrate the advocated decision-making process.
Although pregnant women often need medication, data on drug safety and efficacy in pregnancy remains limited. Historically seen as vulnerable research ...
Texas Tech researcher named Station Science Leader for Antarctica project
2024-10-31
Summary:
Texas Tech’s Natasja van Gestel has been named Station Science Leader by the National Science Foundation (NSF), enabling her to lead and coordinate research at Antarctica’s Palmer Station while advancing her work on climate change’s impact on glaciers. As a leader, she will oversee multiple scientific initiatives, manage resources and ensure compliance with the Antarctic Treaty’s regulations.
Why This Matters:
Climate Study: Her research contributes vital data on climate change effects in Antarctica, crucial for global climate assessments.
International Collaboration: ...
Restricting sugar consumption in utero and in early childhood significantly reduces risk of midlife chronic disease
2024-10-31
A low-sugar diet in utero and in the first two years of life can meaningfully reduce the risk of chronic diseases in adulthood, a new study has found, providing compelling new evidence of the lifelong health effects of early-life sugar consumption.
Published in Science, the study finds that children who experienced sugar restrictions during their first 1,000 days after conception had up to 35% lower risk of developing Type 2 diabetes and as much as 20% less risk of hypertension as adults. Low sugar intake by the mother prior to birth was enough to lower risks, but ...
Apixaban vs aspirin in patients with cancer and cryptogenic stroke
2024-10-31
New Orleans - Ochsner Health physicians Dr. Richard Zweifler and Dr. Joseph Tarsia are co-authors on a post hoc analysis carried out in the ARCADIA randomized clinical trial, comparing the effectiveness of apixaban versus aspirin in preventing adverse clinical outcomes in patients with a history of cancer and cryptogenic stroke. The research found no significant difference in the risk of major ischemic and hemorrhagic events between those taking apixaban and aspirin. The ...
Can magnetic pulses aimed at the brain treat insomnia?
2024-10-31
Traditional solutions for sleep disorders, including medications and cognitive behavioral therapies, often provide insufficient relief for military personnel, a problem researchers from the University of Arizona College of Medicine – Tucson will be hoping to solve with a $3 million grant from the Department of Defense Congressionally Directed Medical Research Program.
Sleep problems are among the top health concerns of military personnel, with an estimated 85% meeting criteria for a clinically relevant sleep ...
F.M. Kirby Research Center honors 25 years of pioneering brain imaging research
2024-10-31
BALTIMORE, October 31, 2024— Kennedy Krieger Institute is proud to celebrate the 25th anniversary of the F.M. Kirby Research Center for Functional Brain Imaging at Kennedy Krieger Institute, a leader in advancements and research in understanding the human brain.
Established in 1999 in partnership with Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, the center has transformed neuroscience and medical imaging by developing cutting-edge magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques that allow researchers to examine and measure brain function and structure ...
$1.75M CDC grant funds study to boost vaccine acceptance in Arizona’s rural, border communities
2024-10-31
Researchers at the University of Arizona’s Mel and Enid Zuckerman College of Public Health received a $1.75 million Centers for Disease Control and Prevention grant to conduct a community-based, participatory research study designed to improve vaccine uptake in Arizona’s rural and border communities.
Vaccination is a highly effective public health intervention that saves millions of lives per year, yet vaccination rates have declined in recent years for a variety of reasons, ranging from safety concerns to religious and philosophical objections.
“Vaccination is a cornerstone of public health,” said co-principal investigator Tomas ...
Immune system review provides insight into more effective biotechnology
2024-10-31
Macrophage cells are the immune system’s frontline soldiers, early on the scene to protect the body from foreign invaders. These cells answer the immune system's critical question for the rest of its troops: friend or foe?
As critical responders, macrophages can perceive helpful biotechnology as threats. If not created with the right materials or mechanical forces, these devices can trigger an immune response that can cause inflammation, scar tissue or device failure.
But what is the right material or the right mechanical force? In a meta-analysis co-led ...
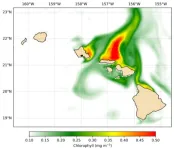
Remote control eddies: Upwelled nutrients boost productivity around Hawaiian Islands
2024-10-31
Beyond colorful coral reefs and diverse nearshore ecosystems, Pacific Ocean waters surrounding the Hawaiian Islands have comparatively little marine life and low biological productivity. New research published by University of Hawai‘i (UH) at Mānoa oceanographers showed that eddies on the leeward side of the Hawaiian Islands can supply nutrients, not only locally, but also to the opposite side of the island chain and stimulate blooms of phytoplankton, microscopic plant life that lives in the surface ocean.
The study, published in JGR Oceans, was selected by the American Geophysical Union’s editorial board as a featured article.
“While ...
Rice, Texas Medical Center institutions jointly award seed grants
2024-10-31
Rice University together with Baylor College of Medicine and the Houston Methodist Academic Institute has awarded seed grants in support of research on health equity and digital health.
Spearheaded by Rice’s Educational and Research Initiatives for Collaborative Health (ENRICH) office in collaboration with the two partnering institutions in the Texas Medical Center (TMC), the seed grant opportunity followed the Health Equity Workshop hosted earlier this year by Rice’s Digital Health Initiative.
“To achieve equitable health outcomes, a comprehensive approach is essential — one ...