(Press-News.org)
A low-sugar diet in utero and in the first two years of life can meaningfully reduce the risk of chronic diseases in adulthood, a new study has found, providing compelling new evidence of the lifelong health effects of early-life sugar consumption.
Published in Science, the study finds that children who experienced sugar restrictions during their first 1,000 days after conception had up to 35% lower risk of developing Type 2 diabetes and as much as 20% less risk of hypertension as adults. Low sugar intake by the mother prior to birth was enough to lower risks, but continued sugar restriction after birth increased the benefits.
Taking advantage of an unintended “natural experiment” from World War II, researchers at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences, McGill University in Montreal, and the University of California, Berkeley, examined how sugar rationing during the war influenced long-term health outcomes.
The United Kingdom introduced limits on sugar distribution in 1942 as part of its wartime food rationing program. Rationing ended in September 1953.
The researchers used contemporary data from the U.K. Biobank, a database of medical histories and genetic, lifestyle and other disease risk factors, to study the effect of those early-life sugar restrictions on health outcomes of adults conceived in the U.K. just before and after the end of wartime sugar rationing.
“Studying the long-term effects of added sugar on health is challenging,” says study corresponding author Tadeja Gracner, senior economist at the USC Dornsife Center for Economic and Social Research. “It is hard to find situations where people are randomly exposed to different nutritional environments early in life and follow them for 50 to 60 years. The end of rationing provided us with a novel natural experiment to overcome these problems.”
Sugar intake during rationing was about 8 teaspoons (40 grams) per day on average. When rationing ended, sugar and sweets consumption skyrocketed to about 16 teaspoons (80 grams) per day.
Notably, rationing did not involve extreme food deprivation overall. Diets generally appeared to have been, in fact, within today’s guidelines set by the U.S. Department of Agriculture and the World Health Organization, which recommend no added sugars for children under two and not more than 12 teaspoons (50g) of added sugar daily for adults.
The immediate and large increase in sugar consumption but no other foods after rationing ended created an interesting natural experiment: Individuals were exposed to varying levels of sugar intake early in life, depending on whether they were conceived or born before or after September 1953. Those conceived or born just before the end of rationing experienced sugar-scarce conditions compared to those born just after who were born into a more sugar-rich environment.
The researchers then identified those born around this time in the U.K. Biobank data collected over 50 years later. Using a very tight birth window around the end of sugar rationing allowed the authors to compare midlife health outcomes of otherwise similar birth cohorts.
While living through the period of sugar restriction during the first 1,000 days of life substantially lowered the risk of developing diabetes and hypertension, for those who were later diagnosed with either of those conditions, onset of disease was delayed by four years and two years, respectively.
Notably, exposure to sugar restrictions in utero alone was enough to lower risks, but disease protection increased postnatally once solids were likely introduced.
The magnitude of this effect is meaningful as it can save costs, extend life expectancy and, perhaps more importantly, quality of life, say the researchers.
In the United States, people with diabetes incur annual medical expenditures of about $12,000 on average. Further, earlier diagnosis of diabetes means significantly shorter life expectancy, with every decade earlier that a diagnosis of diabetes is made cutting three to four years off of life expectancy.
These numbers underscore the value of early interventions that could delay or prevent this disease, the researchers note.
Experts’ concerns about children’s long-term health as they consume excessive amounts of added sugars during their early life, a critical period of development, continue to mount. Adjusting child sugar consumption, however, is not easy — added sugar is everywhere, even in baby and toddler foods, and children are bombarded with TV ads for sugary snacks, say the researchers.
“Parents need information about what works, and this study provides some of the first causal evidence that reducing added sugar early in life is a powerful step towards improving children’s health over their lifetimes,” says study co-author Claire Boone of McGill University and the University of Chicago.
Co-author Paul Gertler of UC Berkeley and the National Bureau of Economics Research adds: “Sugar early in life is the new tobacco, and we should treat it as such by holding food companies accountable to reformulate baby foods with healthier options and regulate the marketing and tax sugary foods targeted at kids.”
This study is the first of a larger research effort exploring how early-life sugar restrictions affected a broader set of economic and health outcomes in later adulthood, including education, wealth, and chronic inflammation, cognitive function and dementia.
END
New Orleans - Ochsner Health physicians Dr. Richard Zweifler and Dr. Joseph Tarsia are co-authors on a post hoc analysis carried out in the ARCADIA randomized clinical trial, comparing the effectiveness of apixaban versus aspirin in preventing adverse clinical outcomes in patients with a history of cancer and cryptogenic stroke. The research found no significant difference in the risk of major ischemic and hemorrhagic events between those taking apixaban and aspirin. The ...
Traditional solutions for sleep disorders, including medications and cognitive behavioral therapies, often provide insufficient relief for military personnel, a problem researchers from the University of Arizona College of Medicine – Tucson will be hoping to solve with a $3 million grant from the Department of Defense Congressionally Directed Medical Research Program.
Sleep problems are among the top health concerns of military personnel, with an estimated 85% meeting criteria for a clinically relevant sleep ...
BALTIMORE, October 31, 2024— Kennedy Krieger Institute is proud to celebrate the 25th anniversary of the F.M. Kirby Research Center for Functional Brain Imaging at Kennedy Krieger Institute, a leader in advancements and research in understanding the human brain.
Established in 1999 in partnership with Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, the center has transformed neuroscience and medical imaging by developing cutting-edge magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques that allow researchers to examine and measure brain function and structure ...
Researchers at the University of Arizona’s Mel and Enid Zuckerman College of Public Health received a $1.75 million Centers for Disease Control and Prevention grant to conduct a community-based, participatory research study designed to improve vaccine uptake in Arizona’s rural and border communities.
Vaccination is a highly effective public health intervention that saves millions of lives per year, yet vaccination rates have declined in recent years for a variety of reasons, ranging from safety concerns to religious and philosophical objections.
“Vaccination is a cornerstone of public health,” said co-principal investigator Tomas ...
Macrophage cells are the immune system’s frontline soldiers, early on the scene to protect the body from foreign invaders. These cells answer the immune system's critical question for the rest of its troops: friend or foe?
As critical responders, macrophages can perceive helpful biotechnology as threats. If not created with the right materials or mechanical forces, these devices can trigger an immune response that can cause inflammation, scar tissue or device failure.
But what is the right material or the right mechanical force? In a meta-analysis co-led ...
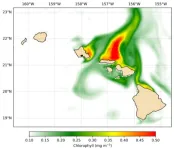
Beyond colorful coral reefs and diverse nearshore ecosystems, Pacific Ocean waters surrounding the Hawaiian Islands have comparatively little marine life and low biological productivity. New research published by University of Hawai‘i (UH) at Mānoa oceanographers showed that eddies on the leeward side of the Hawaiian Islands can supply nutrients, not only locally, but also to the opposite side of the island chain and stimulate blooms of phytoplankton, microscopic plant life that lives in the surface ocean.
The study, published in JGR Oceans, was selected by the American Geophysical Union’s editorial board as a featured article.
“While ...
Rice University together with Baylor College of Medicine and the Houston Methodist Academic Institute has awarded seed grants in support of research on health equity and digital health.
Spearheaded by Rice’s Educational and Research Initiatives for Collaborative Health (ENRICH) office in collaboration with the two partnering institutions in the Texas Medical Center (TMC), the seed grant opportunity followed the Health Equity Workshop hosted earlier this year by Rice’s Digital Health Initiative.
“To achieve equitable health outcomes, a comprehensive approach is essential — one ...
While many people believe that poor sleep during pregnancy is inevitable, new research has determined that cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBTi) while pregnant can not only improve sleep patterns but also address postpartum depression.
Researchers from UBC’s Okanagan and Vancouver campuses, as well as the University of Calgary, discovered that delivering CBTi during pregnancy significantly reduces postpartum depressive symptoms after a baby arrives.
“Early intervention is crucial for infant and parental mental health,” says Dr. Elizabeth Keys, an Assistant Professor in UBCO’s School of Nursing and a study co-author. “Our research explores how addressing ...
When light conditions rapidly change, our eyes have to respond to this change in fractions of a second to maintain stable visual processing. This is necessary when, for example, we drive through a forest and thus move through alternating stretches of shadows and clear sunlight. "In situations like these, it is not enough for the photoreceptors to adapt, but an additional corrective mechanism is required," said Professor Marion Silies of Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU). "Earlier work undertaken by her research group had already demonstrated that such a corrective 'gain control' mechanism exists ...
Researchers at the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG) in Barcelona have created the first blueprint of the human spliceosome, the most complex and intricate molecular machine inside every cell. The scientific feat, which took more than a decade to complete, is published today in the journal Science.
The spliceosome edits genetic messages transcribed from DNA, allowing cells to create different versions of a protein from a single gene. The vast majority of human genes – more than nine in ten – are edited by the spliceosome. Errors in the process are linked to a wide spectrum of diseases including most types of cancer, neurodegenerative conditions and genetic ...