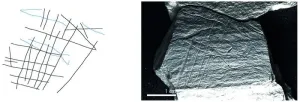
(Press-News.org) 15,800-year-old engraved plaquettes from modern-day Germany depict fishing techniques, including the use of nets, not previously known in the Upper Paleolithic
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0311302
Article Title: Upper Palaeolithic fishing techniques: Insights from the engraved plaquettes of the Magdalenian site of Gönnersdorf, Germany
Author Countries: Germany, U.K.
Funding: Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft DFG (Germany) - AHRC (UK) Memorandum of Understanding Grant DFG-Projekt GZ: GA 683/13-1 (AOBJ: 647648); AHRC (UK) AH/V002899/1) Kunst und Haushalt im Paläolithikum: Psychologie im häuslichen Alltag vor 16.000 Jahren in Gönnersdorf (Rheinland). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
15,800-year-old engraved plaquettes from modern-day Germany depict fishing techniques, including the use of nets, not previously known in the Upper Paleolithic
2024-11-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How plants evolved multiple ways to override genetic instructions
2024-11-06
Biologists at Washington University in St. Louis have discovered the origin of a curious duplication that gives plants multiple ways to override instructions that are coded into their DNA. This research could help scientists exploit a plant’s existing systems to favor traits that make it more resilient to environmental changes, like heat or drought stress.
The study led by Xuehua Zhong, a professor of biology in Arts & Sciences, was published Nov. 6 in Science Advances.
Zhong’s new research focuses on DNA methylation, a normal biological process in living cells wherein small chemical groups called methyl ...
Nasal swab tests predict COVID-19 disease severity, Emory study finds
2024-11-06
A wide variety of COVID-19 symptoms exist, ranging from mild to severe, and while current strains of the virus generally cause milder symptoms, those with co-morbidities are still at an exponentially greater risk of severe disease. Now, new research from Emory University is providing a more precise prediction of COVID-19 severity that can be found by looking at autoantibodies in the nasal cavity, leading to more personalized treatment plans. For high-risk individuals, this could provide critical information to inform immediate treatment options, including ...
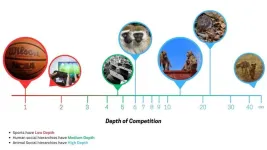
'Shallow' sports and 'deep' social hierarchies: Not all pecking orders are created equal
2024-11-06
University of Michigan researchers have added a new dimension to the mathematics used to predict the outcomes of all manner of competitions, including sports, games and social hierarchies in both humans and animals.
This dimension, which they call "depth of competition," can be integrated into a variety of important and lucrative fields. It could, for instance, help project winners of match-ups in sports, forecast consumer preferences, rank universities and evaluate hiring practices.
But it also ...
New PFAs testing method created at UMass Amherst
2024-11-06
AMHERST, Mass. — University of Massachusetts Amherst researchers have discovered a new way to detect per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in water. This marks an important step forward in creating testing devices that are simpler, more cost-effective, faster and generally more accessible than existing methods.
PFAS, the so-called forever chemicals, have been recognized as a concerning pollutant.
These chemicals persist in the environment because they resist breaking down and pose significant health threats. Exposure to these chemicals is linked to various cancers ...
Asteroid grains shed light on the outer solar system’s origins
2024-11-06
Tiny grains from a distant asteroid are revealing clues to the magnetic forces that shaped the far reaches of the solar system over 4.6 billion years ago.
Scientists at MIT and elsewhere have analyzed particles of the asteroid Ryugu, which were collected by the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) Hayabusa2 mission and brought back to Earth in 2020. Scientists believe Ryugu formed on the outskirts of the early solar system before migrating in toward the asteroid belt, eventually settling into an orbit between Earth and Mars.
The team analyzed Ryugu’s particles for signs of any ancient magnetic field that might have been present ...
Grant supports finding brain-inspired ways to develop low-energy computing
2024-11-06
The human brain is an astonishing organ, as any neuroscientist can attest. And its ability to collect, store, analyze and use information is intriguing to physicists, engineers and computer scientists, too.
Benjamin Jungfleisch, associate professor of physics at the University of Delaware, is among them.
Jungfleisch, who joined UD’s faculty in 2018, is an expert in magnon spintronics. He uses lasers to explore the dynamics of magnetic nanostructures — tiny magnets that can be used to ...
People engaging in self-harm find support on Reddit. But is that community helping them?
2024-11-06
A new study from the University of Georgia suggests people posting in Reddit’s r/selfharm community are likely seeking support for negative emotions.
While sharing traumatic events online can be cathartic, the researchers caution that subreddits can’t provide the same type of mental health help and support face-to-face interactions and professional help can.
“We don’t know the accuracy of the information that’s being shared in these communities about nonsuicidal self-injury,” ...
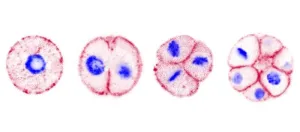
The egg or the chicken? An ancient unicellular says egg!
2024-11-06
Chromosphaera perkinsii is a single-celled species discovered in 2017 in marine sediments around Hawaii. The first signs of its presence on Earth have been dated at over a billion years, well before the appearance of the first animals. A team from the University of Geneva (UNIGE) has observed that this species forms multicellular structures that bear striking similarities to animal embryos. These observations suggest that the genetic programmes responsible for embryonic development were already present before the emergence of animal life, ...
Coping and resilience aids parents of disabled children, study says
2024-11-06
OXFORD, Miss. – For parents of children with disabilities, finding time to focus on themselves may be difficult. However, a new study finds that the right coping strategies and resilience can significantly help manage the challenges of raising children with special needs.
That is the key finding from research published in the International Journal of Developmental Disabilities that studied families with neurodevelopmentally disabled children in Ghana to see what helps parents cultivate healthy, happy lives for themselves and their children.
“Our main interest ...
Lupus Research Alliance announces inaugural recipients of Translational Bridge Award
2024-11-06
New York, NY. November 6, 2024. The Lupus Research Alliance (LRA) is excited to announce the first-ever recipients of the Translational Bridge Award (TBA), established this year to accelerate the translation of groundbreaking research into potential treatments and diagnostics for lupus. The award aims to propel high-potential projects from LRA-funded foundational discoveries with strong commercialization potential or an opportunity for clinical evaluation. Five exceptional researchers have been awarded the 2024 Translational Bridge Award to tackle pressing ...