(Press-News.org) San Diego, California, 7 November 2024 – In a groundbreaking exploration of psychedelic medicine's potential for treating one of psychiatry's most challenging conditions, researchers at University of California, San Diego (UCSD) provided an analysis and further details of a trial published in Nature Medicine (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10427429/) that had shown how psilocybin therapy affects individuals with anorexia nervosa. In the new peer-reviewed Emerging Topic article in Psychedelics the authors of the original trial offer “a granular view of findings based on qualitative data from semi-structured interviews, extensive feedback and interviews from participants, and [their] subjective interpretations of data patterns.” This new Emerging Topic review reveals both promising outcomes and important limitations that could shape future treatment approaches.
The study, published November 7, 2024, in Psychedelics, offers a unique first-hand perspective on how psilocybin treatment impacts patients with anorexia nervosa, a condition that maintains the highest mortality rate among psychiatric illnesses and has historically resisted conventional treatments.
“Our findings suggest that psilocybin may be helpful in supporting meaningful psychological change in a subset of people with anorexia nervosa,” says Dr. Stephanie Knatz Peck, lead author of the study. “What's particularly interesting is that 60% of participants reported a reduction in the importance of physical appearance, while 70% noted quality-of-life improvements and shifts in personal identity.”
Key findings from the trial include:
• 90% of participants ranked their psilocybin session among their top five most meaningful life experiences
• Four out of ten participants showed clinically significant reductions in eating disorder psychopathology
• Treatment effects were most pronounced in shape and weight concerns
• Changes in psychological outlook didn't automatically translate to weight restoration
The research raises intriguing questions about the intersection of psychedelic medicine and eating disorder treatment. Why do some patients respond dramatically while others show minimal improvement? How might genetic variations in serotonin receptors influence treatment outcomes?
“You are able to act in a way that maybe had felt unachievable before if you set the right intention,” reported one participant, while another noted, “Things might not look that different from the outside, but they feel completely different from the inside.”
The study employed a single 25mg dose of psilocybin combined with specialized psychological support before, during, and after administration. While the results show promise, they also highlight the complexity of treating anorexia nervosa, suggesting that psychedelic therapy might work best as part of a comprehensive treatment approach rather than a standalone intervention.
Dr. Walter H. Kaye, senior author and director of the UCSD Eating Disorders Treatment Center, emphasizes the need for larger, well-controlled studies that include brain imaging and genetic analysis to better understand who might benefit most from this novel treatment approach.
The findings open new avenues for research into personalized medicine approaches for eating disorders, while also raising important questions about how to optimize therapeutic protocols for this vulnerable population.
The full Psychedelics peer-reviewed Emerging Topic article, titled “Psychedelic treatment for anorexia nervosa: A first-hand view of how psilocybin treatment did and did not help” is available on 07 November 2024 and it is freely available online at https://url.genomicpress.com/2p8c5kp3.
About Psychedelics - Psychedelics: The Journal of Psychedelic Pharmacology (ISSN: 2997-2671) is a peer-reviewed journal published by Genomic Press, New York. Psychedelics is exclusively dedicated to the latest advancements in the realm of psychedelic substances and their potential therapeutic uses. We embrace the full spectrum of research, from fundamental investigations to cutting-edge clinical studies. Psychedelics welcomes diverse perspectives and contributions, advancing the understanding of psychedelic compounds.
END
First clinical trial reveals promise of psilocybin treatment for anorexia nervosa
UCSD researchers uncover nuanced patient experiences in groundbreaking study exploring psychedelic therapy for treatment-resistant eating disorders
2024-11-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Fabrication of 4-inch wafer-scale heterostructure via PECVD drives AI semiconductor performance innovation!
2024-11-07
As artificial intelligence (AI) technology advances, the demand for higher-performing semiconductors is rapidly growing. The development of new materials and innovative structures to achieve high-performance semiconductors has become crucial. For the first time globally, a 4-inch heterostructure fabrication technology using plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) has been developed. This breakthrough enables the production of low-power, high-performance semiconductors, surpassing the capabilities of traditional silicon-based technology.
The research team led by Senior Researcher Hyeong-U Kim of the Semiconductor Manufacturing Research Center of the ...
Plastic device aids robot-assisted heart surgery
2024-11-07
Robot-assisted heart surgery usually requires an assistant at the operating table to help the surgeon insert the robot arm through a small incision. The assistant has to constantly make sure the surgeon has enough room to operate via the robot arm. For greater independence on the surgeon’s side, an Osaka Metropolitan University-led group has developed a device that can secure the surgical field.
Graduate School of Medicine Professor Toshihiko Shibata and Associate Professor Yosuke Takahashi worked with colleagues and small and ...
UVM scientists find space-for-time substitutions exaggerate urban bird–habitat ecological relationships
2024-11-07
As bird populations dwindle across the globe, a new study from University of Vermont researchers suggests some species may be more flexible to habitat changes than previously understood, creating new opportunities for supporting populations through city planting efforts. The team’s findings were published in the Journal of Animal Ecology today.
While studies have found bird populations are on the decline—Canada and the United States have lost nearly three billion birds over the last half century—measuring ...
Molecular Frontiers Symposium in Hong Kong “Frontiers of New Knowledge in Science”
2024-11-07
Event Date: 15 November 2024 to 17 November 2024
Time: 9:00am - 6:30pm
Venue: Main Hall, Shaw Auditorium, HKUST
INTRODUCTION
The Molecular Frontiers Symposium, organized by the globally renowned Molecular Frontiers Foundation - founded by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences - is recognized as one of the most influential scientific organizations worldwide.
For the first time in the organization’s history, the Foundation's annual flagship symposium will be held in Greater China, hosted at The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology.
With the theme "Frontiers of New Knowledge in Science", the Symposium ...
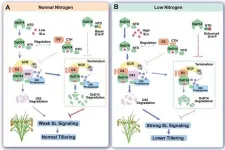
Scientists reveal strigolactone perception mechanism and role in tillering responses to nitrogen
2024-11-07
“How is plant growth controlled?” and “What is the basis of variation in stress tolerance in plants?” were among the 125 most challenging scientific questions, according to the journal Science in 2016.
Strigolactone (SL) is an important plant hormone that plays essential roles in regulating branch number, a key growth and development trait for plants. Recently, scientists from the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) have uncovered the mechanism behind SL perception and its key role in the tillering response to nitrogen.
The “gas and brake” mechanism of SL perception allows “smart and flexible” regulation of the duration ...
Increasing trend of overweight and obesity among Japanese patients with incident end-stage kidney disease
2024-11-07
Niigata, Japan - A new nationwide study from Japan spanning a 14 year study period has revealed an increasing trend of overweight and obesity in patients with the incident end-stage kidney disease (ESKD). Although, underweight individuals remain prevalent in this patient population, the study highlights that excessive weight and obesity in patients with the incident ESKD is a shared global challenge. Consequently, the study suggests the need for public health strategies to address the global obesity epidemic as well as underweight individuals in incident ESKD populations.
“The global ...
An extra five minutes of exercise per day could help to lower blood pressure
2024-11-07
Adding small amounts of exercise into daily routine, such as climbing stairs or cycling to the shops, could help to reduce blood pressure, with just five additional minutes a day estimated to yield improvements, finds a new study from researchers at UCL and the University of Sydney.
The study, supported by the British Heart Foundation (BHF) and published in Circulation, analysed health data from 14,761 volunteers who wore activity trackers to explore the relationship between daily movement and blood pressure.
The researchers split daily activity into six behaviours1:
Sleep
Sedentary behaviour (such as sitting)
Slow walking (cadence ...
Five minutes of exercise a day could lower blood pressure
2024-11-07
New research suggests that adding a small amount of physical activity – such as uphill walking or stair-climbing – into your day may help to lower blood pressure.
The study, published in Circulation, was carried out by experts from the ProPASS (Prospective Physical Activity, Sitting and Sleep) Consortium, an international academic collaboration led by the University of Sydney and University College London (UCL).
Just five minutes of activity a day was estimated to potentially reduce blood pressure, while replacing ...
Social media likes and comments linked to young men’s obsession with perfect pecs and a six-pack
2024-11-06
Social media platforms like TikTok and Instagram are fuelling unrealistic, unhealthy obsessions with a lean and muscular physique among many young men, according to a new Australian study.
Men who place higher importance on receiving likes and positive comments on their posts are significantly more likely to experience symptoms of what is termed “muscle dysmorphia” (MD) – a belief that their bodies are small and weak, even though many of them have a good physique.
In an online survey of almost 100 men, aged between 18-34, all admitted to viewing celebrity, fashion, and fitness content on social media sites, but the link with MD was only significant when it came to ...
$2.1M aids researchers in building chemical sensors to safeguard troops
2024-11-06
The U.S. Army has awarded a team of researchers led by Judith Su, University of Arizona associate professor of biomedical engineering and optical sciences, $2.1 million to build a handheld version of her record-breaking FLOWER sensing device for active military personnel.
The device picks up target compounds at zeptomolar (10 to the power of negative 21) concentrations, an astonishingly minuscule amount of 600 particles per liter. FLOWER is useful for drug testing and a wide variety of other applications, such as health diagnostics.
The military ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
Psilocybin trends in states that decriminalized use
New data signals high demand in aesthetic surgery in southern, rural U.S. despite access issues
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
[Press-News.org] First clinical trial reveals promise of psilocybin treatment for anorexia nervosaUCSD researchers uncover nuanced patient experiences in groundbreaking study exploring psychedelic therapy for treatment-resistant eating disorders