(Press-News.org) In 79 CE, the active volcanic system in southern Italy known as Somma-Vesuvius erupted, burying the small Roman town of Pompeii and everyone in it. The “Pompeii eruption” covered everything in a layer of ash that preserved many of the bodies. Now, ancient DNA collected from the famed body casts alters the history that’s been written since the once forgotten town’s rediscovery in the 1700s. As reported on November 7, 2024, in Current Biology, the DNA evidence shows that individuals’ sexes and family relationships don’t match traditional interpretations that had been formulated largely from modern-day assumptions.
“The scientific data we provide do not always align with common assumptions,” says David Reich of Harvard University. “For instance, one notable example is the discovery that an adult wearing a golden bracelet and holding a child, traditionally interpreted as a mother and child, were an unrelated adult male and child. Similarly, a pair of individuals thought to be sisters, or mother and daughter, were found to include at least one genetic male. These findings challenge traditional gender and familial assumptions.”
The study team including Alissa Mittnik, also at Harvard University, and David Caramelli of the Universita di Firenze in Italy had heard the stories of Pompeii. They realized that ancient DNA and strontium isotopes used to date samples could help them understand better the diversity and origins of Pompeii’s residents. They extracted DNA from highly fragmented skeletal remains mixed with the plaster casts, focusing on 14 of 86 casts that are undergoing restoration.
The researchers’ goal was to learn as much as possible from the DNA evidence about these 14 victims. Their approach allowed them to accurately determine the genetic relationships, sex, and ancestry of those 14 individuals. What they found out was largely in contrast to long-held assumptions based solely on the physical appearance and positioning of the casts.
The genetic data offered insight into the Pompeiians’ ancestry, revealing that the Pompeiians had diverse genomic backgrounds. They primarily descended from recent immigrants from the eastern Mediterranean. The finding highlights the cosmopolitan nature of the Roman Empire, according to the researchers.
“Our findings have significant implications for the interpretation of archaeological data and the understanding of ancient societies,” Mittnik says. “They highlight the importance of integrating genetic data with archaeological and historical information to avoid misinterpretations based on modern assumptions. This study also underscores the diverse and cosmopolitan nature of Pompeii’s population, reflecting broader patterns of mobility and cultural exchange in the Roman Empire.”
The findings highlight the need for a multidisciplinary approach including genetic analysis to fully understand the past of Pompeii and beyond, the researchers say.
“This study illustrates how unreliable narratives based on limited evidence can be, often reflecting the worldview of the researchers at the time,” Caramelli says.
###
Current Biology, Pilli et al. “Ancient DNA challenges prevailing interpretations of the Pompeii plaster casts” https://www.cell.com/current-biology/fulltext/S0960-9822(24)01361-7
Current Biology (@CurrentBiology), published by Cell Press, is a bimonthly journal that features papers across all areas of biology. Current Biology strives to foster communication across fields of biology, both by publishing important findings of general interest and through highly accessible front matter for non-specialists. Visit http://www.cell.com/current-biology. To receive Cell Press media alerts, contact press@cell.com.
END
Scientists have known for decades that the classic symptoms of schizophrenia, such as jumping to conclusions or difficulty adjusting to new information, can be attributed to poor communication between the cerebral cortex and the thalamus, known as the brain’s central switchboard. By measuring brain cell activity between these two regions as volunteers completed ambiguous tasks, a team of Tufts University School of Medicine and Vanderbilt University School of Medicine researchers found a way to use someone’s sensitivity to uncertainty as a diagnostic tool.
In a study published November 7 in the journal ...
Annual emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2) from private aviation increased by 46% between 2019 and 2023, according to an analysis published in Communications Earth & Environment. The results also show that some individuals who regularly use private aviation may produce almost 500 times more CO2 in a year than the average individual, and that there were significant emissions peaks around certain international events, including COP 28 and the 2022 FIFA World Cup.
Private aviation is highly energy-intensive, emitting significantly more CO2 per passenger than commercial flights, but is used by approximately 0.003% ...
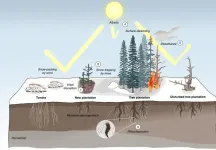
Tree planting has been widely touted as a cost-effective way of reducing global warming, due to trees’ ability to store large quantities of carbon from the atmosphere. But, writing in the journal Nature Geoscience, an international group of scientists argue that tree planting at high latitudes will accelerate, rather than decelerate, global warming.
As the climate continues to warm, trees can be planted further and further north, and large-scale tree-planting projects in the Arctic have been championed by governments and ...
Genes contain instructions for making proteins, and a central dogma of biology is that this information flows from DNA to RNA to proteins. But only two percent of the human genome actually encodes proteins; the function of the remaining 98 percent remains largely unknown.
One pressing problem in human genetics is to understand what these regions of the genome do—if anything at all. Historically, some have even referred to these regions as “junk.”
Now, a new study in Cell finds that some noncoding RNAs are not, in fact, junk—they are functional and play an important role in our cells, including in cancer and human development. Using CRISPR technology that ...
About The Study: In this longitudinal cohort study of multiple aspects of child neurodevelopment between ages 6 and 24 months, negligible associations between prenatal exposure to SARS-CoV-2 infection and child outcomes were observed. Follow-up research is warranted to determine whether these predominantly null effects persist into later childhood.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Gerald F. Giesbrecht, PhD, email ggiesbre@ucalgary.ca.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.43697)
Editor’s ...
About The Study: Results from this study highlight a lower genetic detection rate for Black patients than for white patients with inherited retinal diseases. This supports a concern that the current development of inherited retinal disease therapeutics is highly dependent on the ability to identify the genetic cause of disease.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, K. Thiran Jayasundera, M.D., email thiran@med.umich.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2024.4696)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including ...
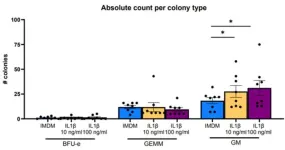
When thinking about the immune system, most people think about B and T cells and how they can be trained to recognize pathogens, preventing re-infections. Besides this “adaptive” immune system, we also have an “innate” immune system which acts as first line defense against e.g. bacteria and viruses. The textbook view is that the innate immune system is non-specific so that it’s response always follows the same pattern, even for recurring infections. However, research published today in Stem Cell Reports provides evidence ...
“It’s necessary to consider the full life cycle of plastics, starting from the extraction of fossil fuel and the primary plastic polymer production” says lead article writer Patricia Villarrubia-Gómez at Stockholm Resilience Centre.
Plastics are not as safe and inert as previously thought. The new research article written by an international team of researchers uses the planetary boundaries framework to structure the rapidly mounting evidence of the effects of plastics on the environment, health and human wellbeing.
500 million tons of plastics are now produced yearly but only nine percent get recycled globally. Plastics are everywhere: ...
The risks of adverse effects and complications from treatment for prostate cancer are substantial and continue for years after treatment ends. The largest comprehensive analysis reporting long-term risks from such treatment relative to the risks faced by a control group of untreated men has just been published in the journal JAMA Oncology.
In the 12 years following treatment, men whose initial treatment was a prostatectomy (removal of all or part of the prostate) had a risk of urinary or sexual complications ...
Before 2024 ends, Congress will decide whether to keep or change rules about telehealth, or let them expire. And even though the decision will focus on Medicare’s payment for virtual patient care, it will likely impact telehealth access for people with other kinds of health insurance too.
Now, a new University of Michigan study suggests that policymakers can rest easier about one of the top worries about telehealth: that virtual care will drive up the use of tests and scans that patients don’t need, wasting money and resources.
In fact, the study shows that low-value care didn’t rise faster at primary care practices that used telehealth the most, compared with those ...