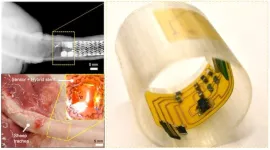
(Press-News.org) Xiaoguang Dong, assistant professor of mechanical engineering, is leading a team of researchers that has developed a system of artificial cilia capable of monitoring mucus conditions in human airways to better detect infection, airway obstruction, or the severity of diseases like Cystic Fibrosis (CF), Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases (COPD) and lung cancer.
The research was published in the November 4 issue of PNAS in the article, “Sensory Artificial Cilia for In Situ Monitoring of Airway Physiological Properties.”
In their paper, the researchers noted that continuously monitoring human airway conditions is crucial for timely interventions, especially when airway stents are implanted to alleviate central airway obstruction in lung cancer and other diseases. In particular, mucus conditions offer important biomarkers for indicating inflammation and stent patency but remain challenging to monitor. Current methods—reliant on computational tomography imaging and bronchoscope inspection—pose risks due to radiation and lack the ability to provide continuous real-time feedback outside of hospitals.
Mimicking the sensing ability of biological cilia, Dong and his team developed novel technology for detecting mucus conditions, including viscosity and layer thickness, which are crucial biomarkers for disease severity.
“The sensing mechanism for mucus viscosity leverages external magnetic fields to actuate a magnetic artificial cilium and sense its shape using a flexible strain-gauge,” the researchers wrote. “Additionally, we report an artificial cilium with capacitance sensing for mucus layer thickness, offering unique self-calibration, adjustable sensitivity, and range, all enabled by external magnetic fields generated by a wearable magnetic actuation system.”
The researchers tested the method by deploying the sensors independently or in conjunction with an airway stent within an artificial trachea and sheep trachea. Sensing signals are transferred wirelessly to a smart phone or the cloud for further data analysis and disease diagnosis.
“The proposed sensing mechanisms and devices pave the way for real-time monitoring of mucus conditions, facilitating early disease detection and providing stent patency alerts, thereby allowing timely interventions and personalized care,” according to the study.
This work was done in collaboration with Vanderbilt University Medical Center faculty members Fabien Maldonado, professor of medicine and thoracic surgery; Caitlin Demarest, assistant professor Thoracic Surgery; and Caglar Oskay, chair of the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering and Cornelius Vanderbilt Professor of Engineering. Yusheng Wang, the study’s first author, is a third-year Ph.D. student in the Department of Mechanical Engineering.
Earlier this year, Dong was awarded an R21 Trailblazer Award by the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB) of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to pursue a project about “Wirelessly Actuated Ciliary Stent for Minimally Invasive Treatment of Cilia Dysfunction.”
The Trailblazer R21 Award supports new and early-stage investigators pursuing research programs that are of high interest to NIBIB, at the interface of life sciences with engineering and the physical sciences.
END
Researchers develop robotic sensory cilia that monitor internal biomarkers to detect and assess airway diseases
2024-11-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Could crowdsourcing hold the key to early wildfire detection?
2024-11-07
The 2023 blaze in Lahaina, Hawaii, which claimed more than 100 lives and burned 6,500 acres of land across Maui, is a tragic example of how rapid wildfire spread can make effective response efforts impossible, resulting in the loss of life and property.
What if technology could help people detect wildfires earlier? The solution could already be in your pocket: a mobile phone.
USC computer science researchers have developed a new crowdsourcing system that dramatically slashes wildfire mapping time from hours to seconds using a network of low-cost mobile phones mounted on properties in high fire threat areas. In computer simulations, the system, FireLoc, detected blazes igniting ...
Reconstruction of historical seasonal influenza patterns and individual lifetime infection histories in humans based on antibody profiles
2024-11-07
Reconstruction of historical seasonal influenza patterns and individual lifetime infection histories in humans based on antibody profiles
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002864
Article Title: Reconstructed influenza A/H3N2 infection histories reveal variation in incidence and antibody dynamics over the life course
Author Countries: United Kingdom, China, United States
Funding: see manuscript END ...
New study traces impact of COVID-19 pandemic on global movement and evolution of seasonal flu
2024-11-07
UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL 19:00 GMT / 14:00 US EASTERN TIME THURSDAY 7 NOVEMBER 2024
Increased capabilities for genomic surveillance have offered new insights into global viral evolution;
Seasonal flu showed a ‘remarkable’ bounce back to pre-pandemic levels once international air travel resumed;
Regions with fewer COVID-19 restrictions were associated with sustained flu virus transmission.
Seasonal influenza epidemics impose substantial burdens on healthcare systems and cause >5 million hospitalizations of adults each year. The current approach to influenza vaccine development requires comprehensive surveillance ...
Presenting a Janus channel of membranes for complete oil-and-water separation
2024-11-07
Named after the two-faced Roman god Janus to reflect its dual-purpose design, researchers present a novel membrane system – a Janus channel of membranes (JCM) – capable of simultaneously separating oil and water from complex emulsions. The system addresses a critical challenge for sustainable water and oil reclamation across various industries. Separating oil and water from complex mixtures is essential for many scientific and industrial applications, such as wastewater treatment and biological sorting. Membrane ...
COVID-19 restrictions altered global dispersal of influenza viruses
2024-11-07
Although travel restrictions and social measures during the COVID-19 pandemic led to a dramatic global drop in seasonal influenza cases, certain influenza lineages in specific regions kept the virus circulating and evolving, according to a new study. This was true in tropical areas with fewer travel restrictions, for example, including South and West Asia. The spread of seasonal influenza is closely tied to social behavior, particularly air travel, and to the periodic evolution of new virus strains that evade immunity from prior infections or vaccinations. In 2020, nonpharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) introduced to combat COVID-19 – such as ...
Disconnecting hepatic vagus nerve restores balance to liver and brain circadian clocks, reducing overeating in mice
2024-11-07
Disruptions between the brain’s master circadian clock and the liver’s internal clock, communicated via the hepatic afferent vagal nerve (HVAN), can lead to unhealthy eating patterns and increased weight gain, according to a new study in mice. The findings identify the neural link as a potential therapeutic target for obesity and metabolic dysfunction related to circadian disruption. In mammals, circadian rhythms are controlled by the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) – a small part of the brain’s hypothalamus that regulates the body’s circadian rhythms. This cycle triggers a feedback loop involving key clock genes that keep ...
Mechanosensory origins of “wet dog shakes” – a tactic used by many hairy mammals – uncovered in mice
2024-11-07
“Wet dog shakes” – a common reflex behavior shared among many hairy mammals and designed to expel water and irritants from their coats – happens when particular mechanoreceptors are activated, researchers studying mice report. Many furry mammals engage in rapid body twists known as "wet dog shakes" to effectively remove water from their fur, as well as to eliminate irritants like tangles or parasites, particularly in areas on the neck and back that are largely unreachable by self-grooming or licking. However, despite the commonality of this behavior ...
New study links liver-brain communication to daily eating patterns
2024-11-07
PHILADELPHIA— People who work the nightshift or odd hours and eat at irregular times are more prone to weight gain and diabetes, likely due to eating patterns not timed with natural daylight and when people typically eat. But is it possible to stave off the ill effects of eating at these “unusual” times despite it not being biologically preferable? A new study from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania says ‘yes’, and sheds light on how the body knows when to eat. The study, published today in Science, explains how researchers discovered a connection between the liver's internal clock and feeding centers in the ...
Defense or growth – How plants allocate resources
2024-11-07
The more a plant species invests in defense, the less potential it has for growth, according to a new study. Research made possible by open science provides new insights into plant adaptation and interspecies variation.
Pathogens can significantly weaken the fitness of their hosts, sometimes even causing host mortality. Yet considerable variation is found between species in their investment in disease defense. Evolutionary theory predicts that allocation costs regulate this investment, but testing this hypothesis ...
Study identifies hip implant materials with the lowest risk of needing revision
2024-11-07
Hip implants with a delta ceramic or oxidised zirconium head and highly crosslinked polyethylene liner or cup had the lowest risk of revision during the 15 years after surgery, a new study led by the University of Bristol has found. The research could help hospitals, surgeons and patients to choose what hip implant to use for replacement surgery.
The aim of the study was to establish hip implant materials at risk of revision to help orthopaedic surgeons, and patients, and to improve shared decision making ...