(Press-News.org) Tsukuba, Japan—Students often appear for high-stakes tests that hold significant weight in determining their futures. One such examination, the Common Test for University Admissions, currently allows examinees using braille an extended examination time of 1.5 times the standard duration. However, with the recent increase in complex questions and questions involving charts and diagrams in such tests, it is necessary to review whether the current accommodations remain adequate.
The researchers assessed the validity of the current time extension for examination questions containing complex tables by measuring the time required to read the text and complex tables. The results showed that 70% of the examinees completed the braille text reading task within 1.5 times the standard duration and 100% completed it within double the duration. However, none of the examinees finished the braille table reading task within 1.5 or even double the extended time. Furthermore, the table reading task revealed considerable individual differences in reading speed, with no correlation observed between this task and braille text reading. This suggests that people who read braille sentences quickly cannot necessarily read braille tables at the same pace.
These findings demonstrate that the current time extension for examinees using braille is insufficient when examination questions include complex tables. This prompts a consideration of how to properly assess the abilities of such examinees and raises the broader question of how to evaluate the skills of each individual regardless of disability status. This research indicates the need to reconsider the current examination framework itself.
###
This work was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (grant number 20H00822).
Original Paper
Title of original paper:
Investigating the Validity Issue of Extended Time for Students with Blindness in Tests Involving Complex Tables
Journal:
Journal of Visual Impairment & Blindness
DOI:
10.1177/0145482X241286001
Correspondence
Associate Professor MIYAUCHI, Hisae
Institute of Human Sciences, University of Tsukuba
Related Link
Institute of Human Sciences
END
Current test accommodations for students with blindness do not fully address their needs
2024-11-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Wide-incident-angle wideband radio-wave absorbers boost 5G and beyond 5G applications
2024-11-08
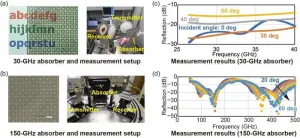
5G wireless communication services have rapidly expanded worldwide, leveraging millimeter-wave (mmW) frequencies in the 24 GHz to 71 GHz range (referred to as frequency range 2, or FR2). Looking ahead, Beyond 5G and 6G services, projected to offer ultra-fast connectivity exceeding 100 Gbit/s, are expected to be introduced in the 2030s. Frequencies in the 150-GHz to 300-GHz range are being considered as potential candidates for these future networks. However, critical components such as radio-wave absorbers, essential for packaging and modularization, still need to be developed. These absorbers play a key role in reducing ...
A graph transformer with boundary-aware attention for semantic segmentation
2024-11-08
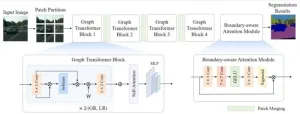
The transformer-based semantic segmentation approaches, which divide the image into different regions by sliding windows and model the relation inside each window, have achieved outstanding success. However, since the relation modeling between windows was not the primary emphasis of previous work, it was not fully utilized.
To solve the problems, a research team led by Zizhang Wu published their new research on 15 October 2024 in Frontiers of Computer Science co-published by Higher Education Press and Springer ...
C-Path announces key leadership appointments in neurodegenerative disease research
2024-11-08
TUCSON, Ariz., November 7, 2024 — Critical Path Institute® (C-Path) today announced key leadership appointments: Diane Stephenson, Ph.D., has been promoted to Vice President of Neurology, and Nadine Tatton, Ph.D., has been welcomed as the new Executive Director of C-Path’s Critical Path for Alzheimer’s Disease (CPAD) Consortium.
With over 30 years of specialized research in neuroscience and drug development and having served as the Executive Director of the Critical Path for Parkinson’s Consortium (CPP) for nearly 15 years, Dr. Stephenson has been an extraordinary partner in advancing our understanding ...
First-of-its-kind analysis of U.S. national data reveals significant disparities in individual well-being as measured by lifespan, education, and income
2024-11-08
First-of-its-kind analysis of US national data reveals significant disparities in individual well-being as measured by lifespan, education, and income.
White males make up largest share of the group with lowest well-being while American Indian and Alaska Native individuals, and Black males, face the most significant challenges to overall well-being.
Populations at the lowest levels of well-being across the US are especially concentrated in the Deep South, Appalachia, and the Rust Belt.
The ...
Exercise programs help cut new mums’ ‘baby blues’ severity and major depression risk
2024-11-08
Exercise-only programmes help cut the severity of the ‘baby blues’ and the risk of major clinical depression in new mums, finds a pooled data analysis of the available evidence, published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
But at least 80 weekly minutes of moderate intensity exercise, such as brisk walking, water aerobics, stationary cycling, and resistance training with bands, weights, or body weight are needed to achieve the effects, the findings show.
Maternal depression and anxiety are relatively common after giving birth and associated with reduced self-care and compromised infant caregiving and bonding, ...
Gut microbiome changes linked to onset of clinically evident rheumatoid arthritis
2024-11-08
Changes in the make-up of the gut microbiome are linked to the onset of clinically evident rheumatoid arthritis in those at risk of the disease because of genetic, environmental, or immunological factors, suggests research published online in the Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
It’s not clear if this instability is a cause or consequence of disease development, emphasise the researchers, but the findings might nevertheless help to identify those at risk as well as paving the way for preventive and personalised treatment strategies, they suggest.
Previously published research consistently shows an unfavourable imbalance in ...
Signals from the gut could transform rheumatoid arthritis treatment
2024-11-08
Changes in the gut microbiome before rheumatoid arthritis is developed could provide a window of opportunity for preventative treatments, new research suggests.
Bacteria associated with inflammation is found in the gut in higher amounts roughly ten months before patients develop clinical rheumatoid arthritis, a longitudinal study by Leeds researchers has found.
Affecting more than half a million people in the UK, rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic disease that causes swelling, pain and stiffness in the ...
Pioneering research reveals some of the world’s least polluting populations are at much greater risk of flooding fuelled by climate change
2024-11-08
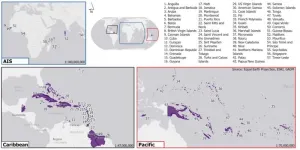
A new study has exposed for the first time how inhabitants of the smallest countries globally, contributing least to climate change, already bear the brunt of its devastating consequences and the burden is likely to worsen.
The research, led by the University of Bristol, showed on average nearly one in five people (20%) in Small Island Developing States (SIDS) – totalling some 8.5million – are now exposed to coastal and inland flooding. For three of the 57 countries concentrated in the Pacific, Caribbean, Indian Ocean, ...
UK’s health data should be recognized as critical national infrastructure, says independent review
2024-11-08
An independent review, Uniting the UK’s Health Data: A Huge Opportunity for Society, published today (8 November 2024), has found that complexities and inefficiencies are impeding the use of the UK’s rich sources of health data to improve people’s health and lives. Researchers and analysts frequently have to wait many months – or even years – to securely access health data to improve care and for vital research into diseases like dementia, cancer and heart disease.
Led by Professor ...
A 36-gene predictive score of anti-cancer drug resistance anticipates cancer therapy outcomes
2024-11-07
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – In 1937, President Franklin Roosevelt signed the National Cancer Act, launching a nationwide effort to combat the disease. Eighty-seven years later, despite significant progress, cancer treatment often falls short, with 50 to 80 percent of patients not responding to treatment and more than 600,000 cancer deaths annually in the United States.
What if clinicians could predict the success of any cancer treatment, ensuring each patient receives the most effective care?
The challenge lies in the diverse nature of the disease. There are hundreds of different types of cancers, characterized by the specific type of cell from which they originate. Even patients ...