Goblet cells could be the guardians of the gut
2024-11-12
(Press-News.org) In a recent study, researchers at the University of California, San Diego, have provided new insights into the central role of goblet cells—specialized cells that line the gut—in maintaining a healthy and balanced immune environment within the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Led by Dr Fernanda Raya Tonetti, with Dr. Cristina Llorente directing the project and making significant contributions, the study underscores the critical roles of these cells, which act not only as a physical barrier but also as a sophisticated communication link between the gut lining and the immune system.
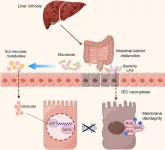
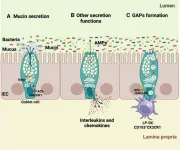
Goblet cells secrete mucus, forming a protective layer that prevents harmful pathogens from reaching the inner gut tissues. However, Dr Llorente points out that these cells serve far beyond mucus production: "Goblet cells are dynamic guardians of gut immunity, engaging in multiple protective actions that include not only pathogen defense but also immune system modulation to ensure a balanced response."
The researchers discuss the role of goblet cells in creating specialized structures known as Goblet Cell-Associated Passages (GAPs), which act as channels through which immune cells can access the contents of the gut lumen. This unique function enables the education of the immune system by sampling benign dietary substances and regular microbiota while monitoring for harmful invaders, maintaining gut tolerance, and preventing unnecessary immunogenic responses.
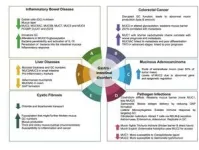
The study also reveals a critical relationship between goblet cells and the gut microbiome—the community of trillions of microbes in the GI tract. This relationship is mutually supportive: beneficial gut bacteria promote healthy goblet cell function, while goblet cells produce the necessary environment for a balanced microbiome. However, disruptions to this balance, such as from infections or dietary changes, can impair goblet cell function, potentially contributing to various GI diseases, including colorectal cancer, inflammatory bowel disease, cystic fibrosis, and liver diseases.
Dr Tonetti states, "This interplay between goblet cells and the gut microbiome is essential to sustaining both a strong immune defense and tolerance."
The findings open promising avenues for therapies that target goblet cell functions and could help develop treatments for GI diseases affecting millions globally. By harnessing goblet cells’ unique protective mechanisms, future therapies could reduce inflammation, support gut barrier integrity, and restore healthy microbiome balance. Dr. Llorente and her team believe these therapies could represent a breakthrough for conditions that are difficult to manage with current treatment options.
See the article:
Raya Tonetti F, Eguileor A, Llorente C. Goblet cells: guardians of gut immunity and their role in gastrointestinal diseases. eGastroenterology 2024;2:e100098. doi:10.1136/egastro-2024-100098
About eGastroenterology
eGastroenterology is a new, open-access, and open peer-reviewed BMJ Journal, which focuses on basic, clinical, translational, and evidence-based medicine research in all areas of gastroenterology (including hepatology, pancreatology, esophagology, and gastrointestinal surgery).
For more information, please visit: egastroenterology.bmj.com and follow us on Twitter (@eGastro_BMJ).
Sign-up to Email Alerts for eGastroenterology: https://emails.bmj.com/k/Bmj/jausu/egastroenterology
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-11-12
The Balkan Network of Science Journalists and the European Federation for Science Journalism are launching a new science journalism guide, this time in Romanian.
From the Field: A Science Journalist's Handbook is the result of a collective effort by more than 20 Romanian journalists and content creators who dedicated their time and expertise to build a 138-page document designed to help journalists navigate the complex world of science reporting.
The guide was coordinated by science ...
2024-11-12
SAN ANTONIO — November 12, 2024 — A Southwest Research Institute-led team combined compositional data of primitive bodies like Kuiper Belt objects, asteroids and comets with new solar data sets to develop a revised solar composition that potentially reconciles spectroscopy and helioseismology measurements for the first time. Helioseismology probes the Sun’s interior by analyzing the waves that travel through it, while spectroscopy reveals the surface composition based on the spectral signature produced by each chemical element.
A paper about this research, which ...
2024-11-12
Background and Aims
Necroptosis is critical for regulating intestinal epithelial cells (IECs). Butyric acid (BA), produced during intestinal microbial metabolism, protects the intestinal epithelial barrier. However, whether necroptosis occurs in IECs during liver cirrhosis and whether sodium butyrate (NaB) can regulate necroptosis have not yet been reported. In this study, we aimed to investigate whether IECs undergo necroptosis in cirrhosis and whether NaB can regulate necroptosis and the related regulatory mechanisms.
Methods
Serum levels of RIPK3, MLKL, and Zonulin, as well as fecal BA levels, were measured and correlated in 48 patients with liver cirrhosis ...
2024-11-12
The story of Arctic greening has overlooked some main characters. At center stage are climate change and warming temperatures. Meanwhile, large grazing wildlife, such as caribou and muskoxen, also play a key role in the timing and abundance of Arctic plants, according to a study from the University of California, Davis.
The study, published today in the journal PNAS Nexus, highlights the importance of large herbivores to the Arctic ecosystem, linking grazing with plant phenology and abundance in the Arctic tundra.
Phenology is the study of the timing and cyclical patterns in nature, such as when birds migrate, or when a plant first sprouts or blooms. ...
2024-11-12
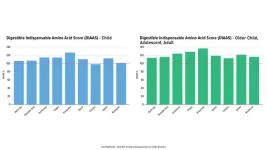
A recent study led by researchers from the University of Illinois, including Dr. Hans Stein, confirms that a wide range of pork cuts, Italian hams, and sausages offer excellent protein quality. The study, published in JSFA Reports,1 utilized the Digestible Indispensable Amino Acid Score (DIAAS) method to measure protein quality, finding that all tested pork products, except one, achieved a DIAAS greater than 100, qualifying them as "excellent" protein sources for children, adolescents, and adults.
The researchers ...
2024-11-12
CLEVELAND—The standard model for how galaxies formed in the early universe predicted that the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) would see dim signals from small, primitive galaxies. But data are not confirming the popular hypothesis that invisible dark matter helped the earliest stars and galaxies clump together.
Instead, the oldest galaxies are large and bright, in agreement with an alternate theory of gravity, according to new research from Case Western Reserve University published Tuesday November 12 in The Astrophysical Journal. The results challenge astronomers’ understanding of the early universe.
“What the theory of dark matter predicted is not what we ...
2024-11-12
WASHINGTON—Vitamin D supplements may lower blood pressure in older people with obesity and taking more than the Institutes of Medicine’s (IOM) recommended daily dose does not provide additional health benefits, according to new research published in the Journal of the Endocrine Society.
The IOM recommends 600 International Units (IU) per day.
Vitamin D deficiency is common worldwide and has been associated with heart disease, immunological diseases, infections and cancer. Studies have linked vitamin D deficiency to a higher risk of hypertension, but evidence for the beneficial effect of vitamin D supplementation on blood pressure outcomes ...
2024-11-12
Up to two thirds of the world’s temperate rainforests could fall victim to climate change by the year 2100 according to a new study by researchers at the University of Leeds.
In the first ever worldwide assessment of the impacts of global overheating on these rare ecosystems, scientists used maps of tree cover, forest condition, and climate data to assess how much of the world’s temperate rainforests have already been impacted by human activity and how climate change would push some regions to the brink.
The results of their study which are published today (Tuesday 12 November) ...
2024-11-12
The American Pediatric Society (APS) is pleased to announce ninety-eight new members. Founded in 1888, the APS is North America's first and most prestigious academic pediatric organization.
APS members are recognized child health leaders of extraordinary achievement who work together to shape the future of academic pediatrics. Current members nominate new members by recognizing individuals who have distinguished themselves as child health leaders, teachers, scholars, policymakers, and clinicians.
“The Council of the APS is excited to welcome this large group of child health leaders ...
2024-11-12
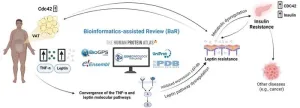
The World Health Organization describes obesity as an epidemic that disrupts metabolic equilibrium, characterized by an excess of adipose tissue and chronic inflammation. This state arises from various factors, including genetic predispositions and lifestyle choices like high caloric intake and physical inactivity. Leptin, primarily produced by adipose tissue, regulates hunger by signaling satiety to the hypothalamus. However, in obesity, leptin's transport to the brain is often blocked, leading to leptin resistance. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Goblet cells could be the guardians of the gut