(Press-News.org) CLEVELAND—The standard model for how galaxies formed in the early universe predicted that the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) would see dim signals from small, primitive galaxies. But data are not confirming the popular hypothesis that invisible dark matter helped the earliest stars and galaxies clump together.
Instead, the oldest galaxies are large and bright, in agreement with an alternate theory of gravity, according to new research from Case Western Reserve University published Tuesday November 12 in The Astrophysical Journal. The results challenge astronomers’ understanding of the early universe.
“What the theory of dark matter predicted is not what we see,” said Case Western Reserve astrophysicist Stacy McGaugh, whose paper describes structure formation in the early universe.
McGaugh, professor and director of astronomy at Case Western Reserve, said instead of dark matter, modified gravity might have played a role. He says a theory known as MOND, for Modified Newtonian Dynamics, predicted in 1998 that structure formation in the early universe would have happened very quickly—much faster than the theory of Cold Dark Matter, known as lambda-CDM, predicted.
JWST was designed to answer some of the biggest questions in the universe, such as how and when did stars and galaxies form? Until it was launched in 2021, no telescope was able to see that deeply into the universe and far back in time.
Lambda-CDM predicts that galaxies were formed by gradual accretion of matter from small to larger structures, due to the extra gravity provided by the mass of dark matter.
“Astronomers invented dark matter to explain how you get from a very smooth early universe to big galaxies with lots of empty space between them that we see today,” McGaugh said.
The small pieces assembled in larger and larger structures until galaxies formed. JWST should be able to see these small galaxy precursors as dim light.
“The expectation was that every big galaxy we see in the nearby universe would have started from these itty-bitty pieces,” he said.
But even at higher and higher redshift—looking earlier and earlier into the evolution of the universe—the signals are larger and brighter than expected.
MOND predicted that the mass that becomes a galaxy assembled rapidly and initially expands outward with the rest of the universe. The stronger force of gravity slows, then reverses, the expansion, and the material collapses on itself to form a galaxy. In this theory, there is no dark matter at all.
The large and bright structures seen by JWST very early in the universe were predicted by MOND over a quarter century ago, McGaugh said. He co-authored the paper with former Case Western Reserve postdoctoral researcher Federico Lelli, now at INAF—Arcetri Astrophysical Observatory in Italy, and former graduate student Jay Franck. The fourth coauthor is James Schombert from the University of Oregon.
“The bottom line is, ‘I told you so,’” McGaugh said. “I was raised to think that saying that was rude, but that’s the whole point of the scientific method: Make predictions and then check which come true.” He added that finding a theory compatible with both MOND and General Relativity is still a great challenge.
###
END
WASHINGTON—Vitamin D supplements may lower blood pressure in older people with obesity and taking more than the Institutes of Medicine’s (IOM) recommended daily dose does not provide additional health benefits, according to new research published in the Journal of the Endocrine Society.
The IOM recommends 600 International Units (IU) per day.
Vitamin D deficiency is common worldwide and has been associated with heart disease, immunological diseases, infections and cancer. Studies have linked vitamin D deficiency to a higher risk of hypertension, but evidence for the beneficial effect of vitamin D supplementation on blood pressure outcomes ...
Up to two thirds of the world’s temperate rainforests could fall victim to climate change by the year 2100 according to a new study by researchers at the University of Leeds.
In the first ever worldwide assessment of the impacts of global overheating on these rare ecosystems, scientists used maps of tree cover, forest condition, and climate data to assess how much of the world’s temperate rainforests have already been impacted by human activity and how climate change would push some regions to the brink.
The results of their study which are published today (Tuesday 12 November) ...
The American Pediatric Society (APS) is pleased to announce ninety-eight new members. Founded in 1888, the APS is North America's first and most prestigious academic pediatric organization.
APS members are recognized child health leaders of extraordinary achievement who work together to shape the future of academic pediatrics. Current members nominate new members by recognizing individuals who have distinguished themselves as child health leaders, teachers, scholars, policymakers, and clinicians.
“The Council of the APS is excited to welcome this large group of child health leaders ...
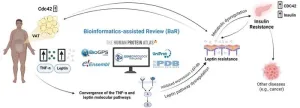
The World Health Organization describes obesity as an epidemic that disrupts metabolic equilibrium, characterized by an excess of adipose tissue and chronic inflammation. This state arises from various factors, including genetic predispositions and lifestyle choices like high caloric intake and physical inactivity. Leptin, primarily produced by adipose tissue, regulates hunger by signaling satiety to the hypothalamus. However, in obesity, leptin's transport to the brain is often blocked, leading to leptin resistance. ...
A new study published in [Journal] highlights the critical role of lysosomes, cellular organelles responsible for waste disposal and recycling, in the development and progression of diabetes. Researchers from [Institution] have uncovered the complex interplay between lysosomal function and the pathogenesis of various diabetes types, including type 1, type 2, gestational diabetes, and cystic fibrosis-related diabetes.
The study, titled “Lysosomal Stress in Pancreatic Endocrine Tissue in the Context of Diabetes Mellitus,” ...
Herbal medicine is difficult to produce on an industrial scale. A team of Kobe University bioengineers manipulated the cellular machinery in a species of yeast so that one such molecule can now be produced in a fermenter at unprecedented concentrations. The achievement also points the way to the microbial production of other plant-derived compounds.
Herbal medicinal products offer many beneficial health effects, but they are often unsuitable for mass production. One example is artepillin C, which has antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anticancer action, but is only available as a bee culture product. The Kobe University bioengineer ...
The cybersecurity refrain when encountering phishing emails invariably advises: “don’t click on that link” and “report that email” — but new research from Drexel University and Arizona State University has revealed a problematic reality: Most major companies do little to support reporting and few take action to shut down phishing sites disguised as their own after they have been reported.
Recently presented at the International Symposium on Research in Attacks, Intrusions and ...
Decoding Deception: The Psychology of Combating Misinformation, a short film produced by Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences with support from the Pulitzer Center, addresses one of the most pressing issues of our time: the quest to stem the swelling tide of misinformation.
Decoding Deception explores potential remedies to this growing societal problem. While social media acts as an accelerant for the rampant spread of misinformation on climate change, public health, and politics, the rise of generative AI risks worsening the problem. Left unchecked, disinformation and misinformation can inflict lasting damage on people, institutions, and society ...
A study links herbivory to phenology in the Arctic. Phenology is the study of the timing of events in the natural world. In recent decades, researchers have investigated how climate change is shifting many natural events. Eric Post and colleagues wanted to understand how a different variable—the presence or absence of herbivores—affects the timing of spring plant growth, or green-up, in Greenland. In an experiment lasting nine years, the authors excluded musk oxen and caribou from some areas, then compared the timing of the spring green-up of 9 tundra plant species in the areas with and without herbivores. Of the plants that showed altered green-up between the conditions, about ...
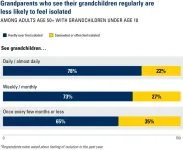
As many Americans prepare to gather with their families for the holidays, a new poll shows the importance of grandchildren in grandparents’ lives.
The poll also suggests that having grandchildren and seeing them regularly may have a link to older adults’ mental health and risk of loneliness.
Although the poll can’t show cause and effect, the findings suggest a need to study the role of grandparenting in older adults’ lives, as part of a broader effort to address social isolation.
At ...