A new frontier in diabetes research through lysosomal dysfunction and pancreatic tissue
2024-11-12
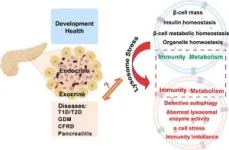
(Press-News.org) A new study published in [Journal] highlights the critical role of lysosomes, cellular organelles responsible for waste disposal and recycling, in the development and progression of diabetes. Researchers from [Institution] have uncovered the complex interplay between lysosomal function and the pathogenesis of various diabetes types, including type 1, type 2, gestational diabetes, and cystic fibrosis-related diabetes.
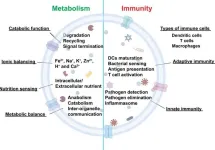
The study, titled “Lysosomal Stress in Pancreatic Endocrine Tissue in the Context of Diabetes Mellitus,” delves into the intricate mechanisms by which lysosomal dysfunction can lead to impaired insulin production, secretion, and glucose regulation. The researchers found that lysosomal stress, characterized by changes in pH, size, membrane permeability, and other factors, can disrupt the normal functioning of pancreatic beta cells, alpha cells, and immune cells.
The study found that lysosomal dysfunction can negatively impact various pancreatic cell types. In beta cells, it can lead to impaired insulin production and secretion. Alpha cells may experience lysosomal stress, contributing to excessive glucagon production, which can raise blood sugar levels. Immune cells can also be affected, with lysosomal dysfunction potentially causing inflammation and the destruction of beta cells in type 1 diabetes. Additionally, lysosomal stress in exocrine pancreatic cells can lead to pancreatitis, a condition that can also contribute to diabetes.
The study also explored the role of lysosomal dysfunction in various diseases, particularly diabetes. The researchers found that lysosomal stress, which occurs when lysosomes are unable to function properly, is associated with the development of diabetes.
These findings suggest that targeting lysosomal function could potentially lead to new therapeutic strategies for diabetes. By understanding the role of lysosomes in these diseases, researchers may be able to develop drugs that can restore normal lysosomal function and improve glycemic control.
See the article:
Hao M, Sebag SC, Qian Q, et al. Lysosomal physiology and pancreatic lysosomal stress in diabetes mellitus. eGastroenterology 2024;2:e100096. doi:10.1136/egastro-2024-100096
About eGastroenterology
eGastroenterology is a new, open-access, and open peer-reviewed BMJ Journal, which focuses on basic, clinical, translational, and evidence-based medicine research in all areas of gastroenterology (including hepatology, pancreatology, esophagology, and gastrointestinal surgery).
For more information, please visit: egastroenterology.bmj.com and follow us on Twitter (@eGastro_BMJ).
Sign-up to Email Alerts for eGastroenterology: https://emails.bmj.com/k/Bmj/jausu/egastroenterology
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-11-12
Herbal medicine is difficult to produce on an industrial scale. A team of Kobe University bioengineers manipulated the cellular machinery in a species of yeast so that one such molecule can now be produced in a fermenter at unprecedented concentrations. The achievement also points the way to the microbial production of other plant-derived compounds.
Herbal medicinal products offer many beneficial health effects, but they are often unsuitable for mass production. One example is artepillin C, which has antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anticancer action, but is only available as a bee culture product. The Kobe University bioengineer ...
2024-11-12
The cybersecurity refrain when encountering phishing emails invariably advises: “don’t click on that link” and “report that email” — but new research from Drexel University and Arizona State University has revealed a problematic reality: Most major companies do little to support reporting and few take action to shut down phishing sites disguised as their own after they have been reported.
Recently presented at the International Symposium on Research in Attacks, Intrusions and ...
2024-11-12
Decoding Deception: The Psychology of Combating Misinformation, a short film produced by Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences with support from the Pulitzer Center, addresses one of the most pressing issues of our time: the quest to stem the swelling tide of misinformation.
Decoding Deception explores potential remedies to this growing societal problem. While social media acts as an accelerant for the rampant spread of misinformation on climate change, public health, and politics, the rise of generative AI risks worsening the problem. Left unchecked, disinformation and misinformation can inflict lasting damage on people, institutions, and society ...
2024-11-12
A study links herbivory to phenology in the Arctic. Phenology is the study of the timing of events in the natural world. In recent decades, researchers have investigated how climate change is shifting many natural events. Eric Post and colleagues wanted to understand how a different variable—the presence or absence of herbivores—affects the timing of spring plant growth, or green-up, in Greenland. In an experiment lasting nine years, the authors excluded musk oxen and caribou from some areas, then compared the timing of the spring green-up of 9 tundra plant species in the areas with and without herbivores. Of the plants that showed altered green-up between the conditions, about ...
2024-11-12
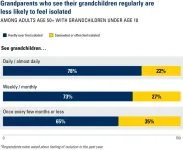
As many Americans prepare to gather with their families for the holidays, a new poll shows the importance of grandchildren in grandparents’ lives.
The poll also suggests that having grandchildren and seeing them regularly may have a link to older adults’ mental health and risk of loneliness.
Although the poll can’t show cause and effect, the findings suggest a need to study the role of grandparenting in older adults’ lives, as part of a broader effort to address social isolation.
At ...
2024-11-12
In the race to develop robust perception systems for robots, one persistent challenge has been operating in bad weather and harsh conditions. For example, traditional, light-based vision sensors such as cameras or LiDAR (Light Detection And Ranging) fail in heavy smoke and fog.
However, nature has shown that vision doesn't have to be constrained by light’s limitations — many organisms have evolved ways to perceive their environment without relying on light. Bats navigate using the echoes of sound waves, while sharks hunt by sensing electrical fields from their prey's movements.
Radio waves, whose wavelengths are orders of magnitude ...
2024-11-12
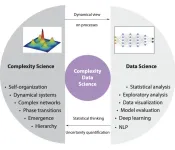
A Perspective suggests that “digital twins” are not simply tools for science but are an example of the integration of complexity science and data science into a new scientific field. A “digital twin” is a digital representation of a real-world object or system. The idea emerged from manufacturing but has been adopted by science, especially by the fields of medicine, immunology, and epidemiology. Digital twins are typically frequently or continuously updated and improved with real data from the real object the digital twin mirrors, allowing ...
2024-11-12
Researchers at the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG) reveal that metabolic enzymes known for their roles in energy production and nucleotide synthesis are taking on unexpected "second jobs" within the nucleus, orchestrating critical functions like cell division and DNA repair.
The discovery, reported across two separate research papers out today in Nature Communications, not only challenges longstanding biological paradigms in cellular biology but also opens new avenues for cancer therapies, particularly against aggressive tumours like triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).
For decades, biology textbooks have neatly compartmentalised ...
2024-11-12
Next-generation metagenomic sequencing test developed at UCSF proves its effectiveness in quickly diagnosing almost any kind of pathogen.
A genomic test developed at UC San Francisco to rapidly detect almost any kind of pathogen – virus, bacteria, fungus or parasite – has proved successful after a decade of use.
The test has the potential to vastly improve care for neurological infections that cause diseases like meningitis and encephalitis, as well as speed up the detection of new viral pandemic threats. It uses a powerful genomic sequencing ...
2024-11-12
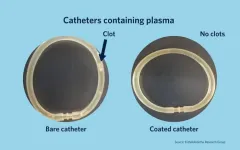
University of B.C. researchers have developed a groundbreaking coating that could make medical devices safer for millions of patients, reducing the risks associated with blood clots and dangerous bleeding.
The new material, designed to mimic the natural behavior of blood vessels, could allow for safer use of blood-contacting devices like catheters, stents, blood-oxygenation machines and dialysis machines—especially in cases where blood clots are a significant concern.
“This discovery could be a transformative step in the development of safer medical devices,” said Dr. Jayachandran Kizhakkedathu, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A new frontier in diabetes research through lysosomal dysfunction and pancreatic tissue