(Press-News.org)
“The classification of patients according to their level of frailty allows us to adjust prevention programs and focus our limited resources on the right action for the right person.”
BUFFALO, NY- November 12, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science), on October 24, 2024, Volume 16, Issue 20, titled, "Development and validation of an electronic frailty index in a national health maintenance organization."
The study, led by researchers Fabienne Hershkowitz Sikron, Rony Schenker, Yishay Koom, Galit Segal, Orit Shahar, Idit Wolf, Bawkat Mazengya, Maor Lewis, Irit Laxer and Dov Albukrek from Meuhedet Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) in collaboration with colleagues from the Joint-Eshel Organization and the Israeli Ministry of Health, introduces the Meuhedet Electronic Frailty Index (MEFI)—a digital tool designed to assess frailty in older people and identify those most at risk for serious health outcomes, such as hospitalization or death.
As people live longer, identifying those at higher risk for health complications is essential to maintaining quality of life in older age. Frailty, a condition marked by increased vulnerability to adverse health outcomes, has emerged as a crucial predictor of health deterioration in older people. While frailty assessment tools exist, this study adapts and validates an Electronic Frailty Index (EFI) tailored specifically to Israeli data and healthcare infrastructure, enabling more targeted and culturally relevant assessments.
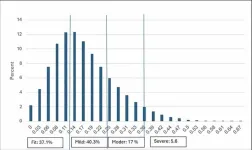
The MEFI was developed using data from 120,986 individuals aged 65 and older, comprising different indicators, including physical, social, and cognitive deficits. The index classifies individuals as "fit," "mildly frail," "moderately frail," or "severely frail" and is integrated into Israel’s electronic health records system.
Researchers found that patients with higher MEFI scores faced significantly increased risks of hospitalization or mortality within one year, with risk levels rising fourfold for the most frail compared to those classified as fit. According to the authors, “The findings also showed that the MEFI version we created is valid in predicting mortality or hospitalization and had better predictive accuracy compared to CCI,” underscoring its reliability in assessing health risks. This integration enables Meuhedet HMO to implement proactive and preventive care measures across its network.
Beyond predicting hospitalization and mortality, the MEFI’s alignment with Israel’s National Social Security benefit system reinforces its validity and practical use. As the authors note, “As a health maintenance organization, our mandate is to help our patients live longer and better. Using the MEFI as part of routine primary care may help us achieve this goal.” By focusing on early intervention for those most at risk, MEFI could significantly impact health maintenance costs and enable clinicians to allocate resources more effectively.
This new EFI version positions Israel at the forefront of frailty research, and its success could pave the way for other countries with similar healthcare systems to adopt or adapt the approach. Future steps include integrating MEFI as a routine part of primary care in Israel to ensure timely intervention and support as patients age.
In summary, MEFI is a powerful tool that empowers Israel’s healthcare system to identify and support older adults most in need, marking a significant advancement in caring for an aging population.
Read the full paper: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.206141
Corresponding author: Fabienne Hershkowitz Sikron - fabian_hershkowitz@meuhedet.co.il
Keywords: frailty, older people, electronic frailty index, electronic health record, health maintenance organization
Click here to sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article.
About Aging:
The journal Aging aims to promote 1) treatment of age-related diseases by slowing down aging, 2) validation of anti-aging drugs by treating age-related diseases, and 3) prevention of cancer by inhibiting aging. (Cancer and COVID-19 are age-related diseases.)
Aging is indexed by PubMed/Medline (abbreviated as “Aging (Albany NY)”), PubMed Central, Web of Science: Science Citation Index Expanded (abbreviated as “Aging‐US” and listed in the Cell Biology and Geriatrics & Gerontology categories), Scopus (abbreviated as “Aging” and listed in the Cell Biology and Aging categories), Biological Abstracts, BIOSIS Previews, EMBASE, META (Chan Zuckerberg Initiative) (2018-2022), and Dimensions (Digital Science).
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
Facebook
X
Instagram
YouTube
LinkedIn
Reddit
Pinterest
Spotify, and available wherever you listen to podcasts
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker St., Suite 1
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
END
A research team led by UCLA Health Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center investigators has shown that that combining pembrolizumab, an immunotherapy drug, with standard chemotherapy can improve treatment outcomes for patients with small cell bladder cancer and small cell/neuroendocrine prostate cancer.
Small cell carcinomas can arise in various tissues—including the bladder, prostate, lung, ovaries and breast—and are known for their rapid progression, tendency to relapse after initial treatment and poor overall survival ...
WASHINGTON, Nov. 12, 2024 – Indoor badminton courts are often used for high-stakes tournaments, but even an enclosed court can affect the path of a birdie.
The airflow from a court’s heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) system and cross ventilation plays a significant role in badminton. The lightweight feathered birdie passed between the players can be affected by low wind speed in the stadium. This is known as wind drift and has been at the center of multiple tournament controversies. While shutting ...
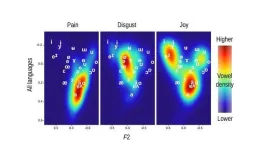
WASHINGTON, Nov. 12, 2024 – There are an estimated 7,000 languages spoken worldwide, each offering unique ways to express human emotion. But do certain emotions show regularities in their vocal expression across languages?
In JASA, published on behalf of the Acoustical Society of America by AIP Publishing, an interdisciplinary team of linguists and bioacousticians led by Maïa Ponsonnet, Katarzyna Pisanski, and Christophe Coupé explored this by comparing expressive interjections (like “wow!”) ...
About The Study: In this cohort study of 1.2 million individuals ages 20 to 79 in South Korea, the risk of mortality with low income was most prominent among individuals with type 2 diabetes ages 20 to 39. These findings highlight the need for socioeconomic support to reduce income-related health disparities in younger individuals.
Corresponding authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Sin Gon Kim, MD, PhD (k50367@korea.ac.kr) and Nam Hoon Kim, MD, PhD (pourlife@korea.ac.kr).
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: ...
About The Study: The frequency of discipline for physician-spread misinformation observed in this cross-sectional study was quite low despite increased salience and medical board warnings since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic about the dangers of physicians spreading falsehoods. These findings suggest a serious disconnect between regulatory guidance and enforcement and call into question the suitability of licensure regulation for combatting physician-spread misinformation.
Corresponding author: To contact the corresponding author, Richard S. Saver, J.D., ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Suicide remains a pressing public health concern. An estimated 703,000 people die by suicide each year worldwide, according to The World Health Organization. In 2022, there were 49,449 suicides in the United States.
A new study found that brief cognitive behavioral therapy for suicide prevention – when delivered remotely via video telehealth – reduces suicide attempts and suicidal ideation.
Researchers at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and College of Medicine led the study that is published online in the journal JAMA Network Open.
The randomized clinical ...
Researchers from the Mattiroli group have found that the way DNA is packaged in cells can directly impact how fast DNA itself is copied during cell division. They discovered that DNA packaging sends signals through an unusual pathway, affecting the cell’s ability to divide and grow. This opens up new doors to study how the copying of the DNA and its packaging are linked. These findings, published in Molecular Cell, may help scientists to find therapies and medicines for diseases such as cancer in the future.
Chromatin as a guide
Every day, our cells divide. Each time they need to copy both their DNA and the structure in which the DNA is packed. This packaging, ...
Seawater electrolysis has long been seen as a promising pathway for sustainable hydrogen production but has faced significant limitations due to chloride ion (Cl⁻) corrosion, which can degrade a catalyst's performance.
Now scientists from the Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, along with their collaborators, have developed an efficient electrocatalyst called Co-N/S-HCS that demonstrates remarkable activity and stability in ...
LOS ANGELES — Researchers at City of Hope®, one of the largest and most advanced cancer research and treatment organizations in the United States, ranked among the nation’s top 5 cancer centers by U.S. News & World Report and a national leader in providing cancer patients with best-in-class, integrated supportive care programs, now understand why taking an investigational white button mushroom supplement shows promise in slowing and even preventing prostate cancer from spreading among men who joined ...
November 12, 2024—(BRONX, NY)— Marina Konopleva, M.D., Ph.D., director of the Leukemia Program and co-director of the Blood Cancer Institute at the National Cancer Institute-designated Montefiore Einstein Comprehensive Cancer Center (MECCC), has joined forces with Break Through Cancer, a collaborative medical research foundation that supports teams of scientists as they advance treatments for some of the world’s deadliest cancers. Dr. Konopleva will play a pivotal role in the Eradicating Minimal Residual Disease (MRD) in Acute ...