(Press-News.org) Cannabis use causes cellular damage that increases the risk of highly cancerous tumours, according to a new paper published in the scientific journal Addiction Biology. The paper describes cannabis as a “genotoxic” substance because it damages a cell's genetic information, which can lead to DNA mutations, accelerated aging, and cancer. To make matters worse, this genotoxicity may be transmitted via damaged egg and sperm to the cannabis user’s offspring, making the risk of cannabis use trans-generational.
In a recent publication in Addiction Biology researchers from The University of Western Australia have made a link between established knowledge that cannabis use damages cellular energy production by inhibiting mitochondria and new cancer research published in Science1,2 showing that mitochondrial dysfunction drives chromosomal damage, which shows up as increased rates of cancer, accelerated aging, and birth defects.
The Science studies were not conducted in the context of cannabis use; however, they provide mechanistic insights into some observations about cannabis use that were not previously well understood, such as that cannabis causes both mitochondrial and genetic damage. Taken together, the article in Addiction Biology put older historical research about cannabis into context and suggests that cannabis-related genotoxic damage may be all around us — even if we largely don't see it.
Co-author Dr. Stuart Reece comments: “The link we’ve described between cannabis use and genotoxicity has far-reaching consequences. This new research shows how genetic damage from cannabis use can be passed down the generations. This should reframe the discussion surrounding cannabis legalization from a personal choice to one that potentially involves multiple subsequent generations.”
1 Melody Di Bona et al., Micronuclear collapse from oxidative damage. Science 385, eadj8691 (2024). DOI:10.1126/science.adj8691
2Sara Martin et al., A p62-dependent rheostat dictates micronuclei catastrophe and chromosome rearrangements. Science 385, eadj7446 (2024). DOI:10.1126/science.adj7446
-- Ends –
For editors:
This Open Access paper is available on the Wiley Online Library (https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/adb.70003) or you may request a copy from Jean O’Reilly, jean@addictionjournal.org.
To speak with lead author Dr. Stuart Reece, please contact him at The University of Western Australia by telephone (617 3844 4000) or e-mail (stuart.reece@uwa.edu.au).
Full citation for article: Reece AS and Hulse GK. Key Insights into Cannabis-Cancer Pathobiology and Genotoxicity. Addiction Biology. 2024. DOI: 10.1111/adb.70003.
Primary funding: None.
Declaration of interests: None to declare.
END
Cannabis use can cause chromosomal damage, increasing cancer risk and harming offspring
2024-11-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Survey finds many Americans apply misguided and counterproductive advice to combat holiday weight gain
2024-11-14
Orlando, Fla - For those striving to maintain a healthy lifestyle, holiday celebrations can feel like a minefield of dietary pitfalls, bound to derail the progress you’ve made through diet and exercise the rest of the year. In fact, a new national survey by Orlando Health finds nearly two in five (39%) Americans worry about how much they eat over the holidays. The good news is that dietitians say there’s no need to feel guilty about a few holiday treats.
“Holidays come around once a year, and indulging in a few traditional foods and favorite recipes that may have a little extra ...
New study reveals half a century of change on Britain’s iconic limestone pavements
2024-11-14
Fifty years of change on iconic limestone pavements has revealed mixed fortunes for one of the most distinctive landscapes in the UK.
The landscapes - which will be familiar to visitors to the Yorkshire Dales and fans of Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows film – have, in many places, seen reductions of specialist species and more common less desirable species become more abundant.
However, it is not all bad news as the picture is very mixed across the UK’s areas of limestone pavement with some areas increasing in plant biodiversity.
The ...
Green flight paths could unlock sustainable aviation, new research suggests
2024-11-14
‘Green flight paths’ between key global locations could help to fast-track fully decarbonised aviation, according to research led by an international team based at Heriot-Watt University in the United Kingdom and the American University of Sharjah in the United Arab Emirates.
The research, published in the in the Royal Society of Chemistry’s top international journal, Energy and Environmental Science, recommends that a small number of long-haul flights with high passenger volumes, ...
Community partners key to success of vaccine clinic focused on neurodevelopmental conditions
2024-11-14
A new paper shows how partnering with the community can lead to more inclusive health care, especially for individuals with autism and other neurodevelopmental disabilities. The article, published this week in Pediatrics, details the success of a unique COVID-19 and flu vaccine clinic at the UC Davis MIND Institute.
The clinic team includes developmental-behavioral pediatricians, child life specialists, nurses, psychologists, social workers and staff trained to help families navigate health care. The goal is not only to administer vaccines, but to help patients build skills needed to successfully complete medical procedures for the rest of their lives.
Listening to ...
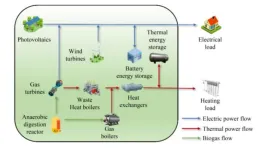
Low-carbon collaborative dual-layer optimization for energy station considering joint electricity and heat demand response
2024-11-14
In a significant step towards achieving the "Carbon Peaking and Carbon Neutrality" goals, researchers at the Chinese Academy of Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing Institute of Technology, in collaboration with Hohai University, have developed a groundbreaking dual-layer optimization strategy for park-level integrated energy systems (PIES). This strategy, which integrates electricity and heat demand response, significantly boosts the economic efficiency and low-carbon operation ...
McMaster University researchers uncover potential treatment for rare genetic disorders
2024-11-14
Hamilton, ON, Nov. 14, 2024, In a groundbreaking study, researchers at McMaster University have identified a potential treatment for Sandhoff and Tay-Sachs diseases—two rare, often fatal lysosomal storage disorders that cause progressive damage to nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord.
After years of investigating the diseases’ underlying mechanisms, the research team has identified an existing FDA-approved drug that could significantly improve quality of life for affected patients and their families.
“Sandhoff and Tay-Sachs are devastating diseases,” ...
The return of protectionism: The impact of the Sino-US trade war
2024-11-14
Since 2018, Sino-US economic and trade relations have become increasingly tense. Between 2018 and 2019, the US imposed seven rounds of tariffs on China, to which China responded with retaliatory measures. The simple average tariff rates on US imports from China rose from 4.07% in January 2018 to 24.43% in December 2019, while the simple average tariff rates on Chinese imports from the US increased from 9.32% in January 2018 to 22.53% in December 2019 (see figure 1).
Consequently, the share of Chinese goods in US imports declined significantly — ...
UTokyo and NARO develop new vertical seed distribution trait for soybean breeding
2024-11-14
We have probably all seen a soybean plant, about 1 meter high with leaves and pods compactly arranged on a main stem with a few short side branches. The wild relative of the domesticated soybean is a long vine with pods widely distributed on many side branches. Plant breeding by farmers thousands of years ago is to thank for this dramatic change.
As human population increases and protein demand doubles, modern plant breeders must further optimize soybean plant architecture and per plant yield for modern farming systems. Conventional ...
Research into UK’s use of plastic packaging finds households ‘wishcycle’ rather than recycle – risking vast contamination
2024-11-14
Lancaster University researchers investigating consumer attitudes and behaviours around plastic food packaging have found UK households are ‘wishcycling’ rather than recycling – and say it’s a problem that everyone - government, food producers, waste management and residents – has to solve.
Wishcycling – the act of putting packaging in recycling bins and hoping for the best, rather than knowing it’s recyclable – is something households are doing due to confusing product labels and differing recycling facilities around the country, experts warn.
The academics behind Lancaster ...
Vaccine shows promise against aggressive breast cancer
2024-11-14
A small clinical trial shows promising results for patients with triple-negative breast cancer who received an investigational vaccine designed to prevent recurrence of tumors. Conducted at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis with a therapy designed by WashU Medicine researchers, the trial is the first to report results for this type of vaccine — known as a neoantigen DNA vaccine — for breast cancer patients.
The study, which found the vaccine to be well-tolerated and to stimulate ...