(Press-News.org) Anthropogenic aerosols, tiny solid and liquid air pollution particles, have masked a fraction of global warming caused by anthropogenic greenhouse gases. Climate researchers have known for decades that anthropogenic aerosols perturb liquid clouds by enabling the formation of a larger number of cloud droplets, making clouds brighter. A new landmark study led by the University of Tartu suggests that anthropogenic aerosols may also influence clouds by converting cloud droplets to ice at temperatures below zero degrees Celsius.
Powerplant Snow
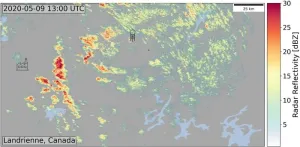
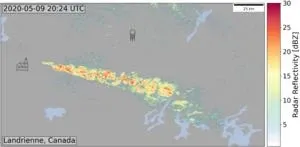
Using satellite observations, climate researchers discovered unique plumes of ice clouds and reduced cloud cover downwind of industrial hot spots in North America, Europe and Asia. Moreover, ground-based precipitation radar data revealed plumes of snowfall in the same areas where reduced cloud cover was observed in satellite images. Combining satellite and ground-based radar observations, researchers traced the physical processes from the formation of ice to snowfall to reduced cloud cover downwind of industrial hot spots. The lead author of the study, Assoc Prof V. Toll from the University of Tartu, highlighted that collaboration among researchers with diverse expertise was essential for developing the physical understanding of the identified anthropogenic snowfall events.
Supercooled Water
Water freezes at zero degrees Celsius, right? In fact, cloud droplets can stay liquid down to temperatures as low as about -40 degrees Celsius, known as the supercooling of water. This is because suitable aerosol particles are needed to convert cloud droplets to ice at temperatures between zero and -40 degrees Celsius. The study suggests that industries such as metallurgical and cement factories, coal-fired power plants, and oil refineries emit aerosol particles that cause freezing of supercooled liquid clouds, leading to snowfall. However, it is important to note that heat and water vapour emitted by industries may also play a role in the freezing of supercooled liquid clouds.
The discovered plumes of reduced cloud cover are local phenomena, and it remains unclear if anthropogenic aerosols induce ice formation in clouds at larger spatial scales. Further research is needed to understand the ability of various types of anthropogenic aerosols to initiate the formation of ice.
END
Industrial snow: Factories trigger local snowfall by freezing clouds
2024-11-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Backyard birds learn from their new neighbors when moving house
2024-11-14
Scientists have found a trigger for social learning in wild animals. An experiment on great tits has pinpointed a single factor—immigration—that can cause birds to pay close attention to others, leading them to rapidly adopt useful behaviors. The study is the first to provide experimental support of a long-held assumption that immigrants should strategically use social learning. The study, conducted by scientists from the Max Planck Institute of Animal Behavior (MPI-AB) and the Cluster of Excellence Collective Behaviour at the University of Konstanz in Germany, is published November 14 in PLOS Biology.
Many animals that live in groups learn from one another, but few ...
New study in Science finds that just four global policies could eliminate more than 90% of plastic waste and 30% of linked carbon emissions by 2050
2024-11-14
Berkeley, CA/Santa Barabara, CA (14 November 2024) — A new study released in Science today determines that just four policies can reduce mismanaged plastic waste — plastic that isn’t recycled or properly disposed of and ends up as pollution — by 91% and plastic-related greenhouse gasses by one-third. The policies are: mandate new products be made with 40% post-consumer recycled plastic; cap new plastic production at 2020 levels; invest significantly in plastic waste management — such as landfills and waste collection services; and implement a small fee on plastic packaging. ...
Breakthrough in capturing 'hot' CO2 from industrial exhaust
2024-11-14
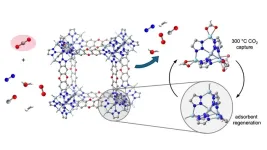
Industrial plants, such as those that make cement or steel, emit copious amounts of carbon dioxide, a potent greenhouse gas, but the exhaust is too hot for state-of-the-art carbon removal technology. Lots of energy and water are needed to cool the exhaust streams, a requirement that has limited adoption of CO2 capture in some of the most polluting industries.
Now, chemists at the University of California, Berkeley, have discovered that a porous material can act like a sponge to capture CO2 at temperatures close to those of many industrial exhaust streams. ...
New discovery enables gene therapy for muscular dystrophies, other disorders
2024-11-14
Gene therapy can effectively treat various diseases, but for some debilitating conditions like muscular dystrophies there is a big problem: size. The genes that are dysfunctional in muscular dystrophies are often extremely large, and current delivery methods can’t courier such substantial genetic loads into the body. A new technology, dubbed “StitchR,” surmounts this obstacle by delivering two halves of a gene separately; once in a cell, both DNA segments generate messenger RNAs (mRNAs) that join seamlessly together to restore expression of a protein that is missing or inactive in disease.
Published in ...
Anti-anxiety and hallucination-like effects of psychedelics mediated by distinct neural circuits
2024-11-14
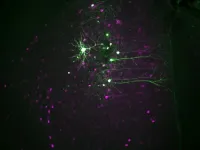
New research suggests that it could be possible to separate treatment from hallucinations when developing new drugs based on psychedelics. The anti-anxiety andhallucination-inducing qualities of psychedelic drugs work through different neural circuits, according to research using a mouse model. The work is published Nov. 15 in Science.
The research shows that decoupling the beneficial effects of psychedelics from their hallucinogenic effects isn’t just a matter of chemical compound design. It’s a matter of targeted neural circuitry.
“In the past, we did this using chemistry by making new compounds, but here we focused on identifying the circuits responsible ...
How do microbiomes influence the study of life?
2024-11-14
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Microorganisms — bacteria, viruses and other tiny life forms — may drive biological variation in visible life as much, if not more, than genetic mutations, creating new lineages and even new species of animals and plants, according to Seth Bordenstein, director of Penn State’s One Health Microbiome Center, professor of biology and entomology, and the Dorothy Foehr Huck and J. Lloyd Huck Endowed Chair in Microbiome Sciences. Bordenstein and 21 other scientists from around the world published a paper in the leading journal Science, summarizing research that they said drives a deeper understanding of biological ...
Plant roots change their growth pattern during ‘puberty’
2024-11-14
Ghent, November 15, 2024 – Understanding how roots grow can help us develop plants that, for example, are more resistant to drought. Research by Prof. Bert De Rybel’s team (VIB-UGent), in collaboration with the VIB Screening Core and Ghent University, uncovers how roots go through a puberty phase, which could have important implications for developing climate-resilient agriculture. Their work appears in Science.
Plant puberty
Plants, like all living organisms, transition through various developmental stages, starting as a seed, becoming a shoot, and eventually a full-grown, fertile plant. They even go through a sort of ‘puberty’ ...
Study outlines key role of national and EU policy to control emissions from German hydrogen economy
2024-11-14
Hydrogen is set to play an important role in a future low-carbon economy. However, the hydrogen value chain comes with a set of emissions challenges that need to be addressed for hydrogen deployment to help achieve climate goals. A study prepared by the Research Institute for Sustainability – Helmholtz Centre Potsdam (RIFS) with support from Environmental Defense Fund Europe evaluates the potential impact of climate-warming emissions in Germany’s future hydrogen economy and provides recommendations for German and EU policymakers on how to avoid them.
There are hopes that hydrogen can become a carbon neutral alternative to fossil ...
Beloved Disney classics convey an idealized image of fatherhood
2024-11-14
For decades, Disney animations have shaped perceptions of family relationships and gender roles. Although much focus has traditionally been on princesses and female characters, a new study shifts attention to fatherhood and the evolving ideals of masculinity.
"In the history of Disney films, female characters and princess imagery have been widely analyzed, yet the role of masculinity has been explored far less. My research aims to deepen our understanding of the male ideals Disney has constructed and how they reflect ...
Sensitive ceramics for soft robotics
2024-11-14
Most people think of coffee cups, bathroom tiles or flower pots when they hear the word "ceramic". Not so Frank Clemens. For the research group leader in Empa's Laboratory for High-Performance Ceramics, ceramics can conduct electricity, be intelligent, and even feel. Together with his team, Clemens is developing soft sensor materials based on ceramics. Such sensors can "feel" temperature, strain, pressure or humidity, for instance, which makes them interesting for use in medicine, but also in the field of soft robotics.
Soft ceramics – how is that supposed to work? Materials ...