(Press-News.org) Breast cancer is a major health concern worldwide, and early detection is crucial for effective treatment. Traditional imaging methods, such as mammography, have limitations, especially for women with dense breast tissue. Photoacoustic imaging, which combines light and sound to create detailed images of breast tissue, offers a promising alternative. However, recent research has highlighted a significant challenge: skin tone bias.
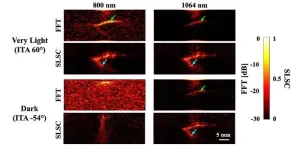
A team of researchers from Johns Hopkins University recently investigated how skin tone affects the visibility of breast cancer targets in photoacoustic imaging. As reported in Biophotonics Discovery, the study focused on three image reconstruction methods: fast Fourier transform (FFT)-based reconstruction, delay-and-sum (DAS) beamforming, and short-lag spatial coherence (SLSC) beamforming. The study used simulations with different wavelengths (757, 800, and 1064 nm), target sizes (0.5 to 3 mm), and skin tones (ranging from very light to dark).
The results revealed that traditional methods like FFT and DAS struggle to visualize small targets under darker skin tones, especially at 757 and 800 nm wavelengths. Targets smaller than 3 mm were particularly hard to detect, with lower signal-to-noise ratios (SNR) and contrast-to-noise ratios (gCNR). However, the 1064 nm wavelength showed significant improvements, especially when combined with SLSC beamforming. This combination enhanced the visibility of targets across all skin tones, providing clearer images with higher SNR and gCNR values.
“This work was motivated by a previously poor understanding of photoacoustic imaging performance under combined variations of small target sizes and darker skin tones,” says senior and corresponding author Muyinatu Bell. “Our results are enlightening, as we now have a better understanding of advanced photoacoustic imaging techniques and associated wavelengths necessary to detect small targets.”
The results of this study are promising for the future of breast cancer diagnosis. By addressing the skin tone bias, photoacoustic imaging can become a more reliable tool for early detection, benefiting women of all skin tones. The study underscores the importance of considering skin tone in the development of next-generation imaging systems, ensuring equitable healthcare for all.
For details, see the original Gold Open Access article by R. D. Rasquinha, M. R. Gubbi, and M. A. L. Bell, “Impact of skin tone on target size detectability in photoacoustic breast imaging,” Biophotonics Discovery 2(1), 012502 (2024), doi: 10.1117/1.BIOS.2.1.01250.
END
Researchers shed light on skin tone bias in breast cancer imaging
New imaging technique reduces skin tone bias in breast cancer detection, improving visibility across diverse skin tones
2024-11-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study finds humidity diminishes daytime cooling gains in urban green spaces
2024-11-14
Urban green spaces provide shade for city dwellers facing rising temperatures brought on by climate change, but how much relief from the heat island effect do they provide when humidity is factored in?
The temperature and humidity effect cancel each other out during daylight hours, but green spaces provide a net reduction in humid heat at night, according to a new study in Nature Cities, co-authored by Yale School of the Environment doctoral student Yichen Yang and Xuhui Lee, Sara Shallenberger Brown Professor of Climate Science.
"When it comes to urban ...
Tennessee RiverLine secures $500,000 Appalachian Regional Commission Grant for river experience planning and design standards
2024-11-14
The Tennessee RiverLine, an initiative of University of Tennessee Extension, has been awarded a $500,000 Area Development grant from the Appalachian Regional Commission (ARC) and Tennessee Department of Economic and Community Development to support the development of comprehensive Planning and Design Standards. These standards will help accelerate the creation of new river experience amenities along the 652-mile stretch of the Tennessee River, benefitting residents and visitors throughout the region.
The 18-month project will be led by a professional ...
AI tool ‘sees’ cancer gene signatures in biopsy images
2024-11-14
To determine the type and severity of a cancer, pathologists typically analyze thin slices of a tumor biopsy under a microscope. But to figure out what genomic changes are driving the tumor’s growth — information that can guide how it is treated — scientists must perform genetic sequencing of the RNA isolated from the tumor, a process that can take weeks and costs thousands of dollars.
Now, Stanford Medicine researchers have developed an artificial intelligence-powered computational program that can predict the activity of thousands of genes within tumor cells based only on standard microscopy images of the biopsy. The tool, described online in Nature Communications Nov. 14, ...
Answer ALS releases world's largest ALS patient-based iPSC and bio data repository
2024-11-14
Answer ALS Releases World's Largest ALS Patient-Based iPSC and Bio Data Repository
Unprecedented resource, created with Cedars-Sinai, to accelerate ALS research and drive development of targeted therapies globally
NEW ORLEANS, [November 14, 2024] — In a landmark continuing collaboration, Answer ALS and Cedars-Sinai have announced the completed availability of the largest amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) patient-based induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) and bio data repository. The repository encompasses biological and clinical data from nearly 1,000 ALS patients, offering an unprecedented resource for global ...
2024 Joseph A. Johnson Award Goes to Johns Hopkins University Assistant Professor Danielle Speller
2024-11-14
WASHINGTON, Nov. 14, 2024 – AIP and the National Society of Black Physicists congratulate Danielle Speller as the winner of the 2024 Joseph A. Johnson Award for Excellence. Jessica Esquivel is also being recognized with an Honorable Mention.
The Johnson Award, now in its fifth year, is given jointly by AIP and NSBP to recognize early-career scientists who demonstrate scientific ingenuity and impactful mentorship and service—the core values of NSBP founder Joseph A. Johnson.
“Dr. Speller not only ...
Slow editing of protein blueprints leads to cell death
2024-11-14
FRANKFURT. Genes contain the essential building instructions for life, guiding cells on which amino acids to assemble in what sequence to produce specific proteins. The human genome codes for about 20,000 such instructions. “Nevertheless, our cells can produce several hundred thousand different proteins,” explains Prof. Ivan Đikić from the Institute of Biochemistry II at Goethe University Frankfurt.
This diversity is enabled by a process known as “splicing.” When a cell requires a protein, it generates a copy of the relevant instructions in the cell nucleus. During splicing, this transcript undergoes modification: a cellular editing complex, the spliceosome, ...
Industrial air pollution triggers ice formation in clouds, reducing cloud cover and boosting snowfall
2024-11-14
Pollution from industrial hotspots can trigger ice formation in supercooled clouds, altering their reflective properties and increasing regional snowfall, according to a new study. The findings shed light on poorly understood impacts of anthropogenic aerosols on climate and could help improve climate modeling and mitigation strategies. The impact of human-generated aerosols (tiny air pollution particles) on climate, particularly in counteracting greenhouse gas-induced warming, remains uncertain. These aerosols, in addition to influencing cloud formation as cloud condensation nuclei (CCN), may also act as ice-nucleating particles (INPs), crucial for ice formation in supercooled ...
Emerging alternatives to reduce animal testing show promise
2024-11-14
In a Policy Forum, Chad Nelson and colleagues highlight the efforts of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in advancing alternative methods to reduce animal testing for regulatory use. Animal studies have been crucial for advancing disease understanding, developing therapies, and assessing the safety and effectiveness of consumer products. However, reducing animal use and developing effective alternatives is an ongoing priority. Although advances in biology, engineering, and artificial intelligence offer new opportunities to improve product safety assessments, these technologies require extensive development to meet regulatory ...
Presenting Evo – a model for decoding and designing genetic sequences
2024-11-14
A new study presents “Evo” – a machine learning model capable of decoding and designing DNA, RNA, and protein sequences, from molecular to genome scale, with unparalleled accuracy. Evo’s ability to predict, generate, and engineer entire genomic sequences could change the way synthetic biology is done. “The ability to predict the effects of mutations across all layers of regulation in the cell and to design DNA sequences to manipulate cell function would have tremendous diagnostic and therapeutic implications for disease,” writes Christina Theodoris ...
Global plastic waste set to double by 2050, but new study offers blueprint for significant reductions
2024-11-14
Without intervention, global plastic waste could double by 2050, a new machine learning study predicts. However, according to simulations by the study’s authors, a mix of policy interventions could cut plastic waste by more than 90% and it could cut plastics-related emissions by a third. With UN treaty negotiations underway, these findings provide a crucial blueprint for tackling the plastic crisis. Plastic production has increased relentlessly for decades, leading to surging plastic waste generation and environmental mismanagement. As plastic ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New book captures hidden toll of immigration enforcement on families
New record: Laser cuts bone deeper than before
Heart attack deaths rose between 2011 and 2022 among adults younger than age 55
Will melting glaciers slow climate change? A prevailing theory is on shaky ground
New treatment may dramatically improve survival for those with deadly brain cancer
Here we grow: chondrocytes’ behavior reveals novel targets for bone growth disorders
Leaping puddles create new rules for water physics
Scientists identify key protein that stops malaria parasite growth
Wildfire smoke linked to rise in violent assaults, new 11-year study finds
New technology could use sunlight to break down ‘forever chemicals’
Green hydrogen without forever chemicals and iridium
Billion-DKK grant for research in green transformation of the built environment
For solar power to truly provide affordable energy access, we need to deploy it better
Middle-aged men are most vulnerable to faster aging due to ‘forever chemicals’
Starving cancer: Nutrient deprivation effects on synovial sarcoma
Speaking from the heart: Study identifies key concerns of parenting with an early-onset cardiovascular condition
From the Late Bronze Age to today - Old Irish Goat carries 3,000 years of Irish history
Emerging class of antibiotics to tackle global tuberculosis crisis
Researchers create distortion-resistant energy materials to improve lithium-ion batteries
Scientists create the most detailed molecular map to date of the developing Down syndrome brain
Nutrient uptake gets to the root of roots
Aspirin not a quick fix for preventing bowel cancer
HPV vaccination provides “sustained protection” against cervical cancer
Many post-authorization studies fail to comply with public disclosure rules
GLP-1 drugs combined with healthy lifestyle habits linked with reduced cardiovascular risk among diabetes patients
Solved: New analysis of Apollo Moon samples finally settles debate about lunar magnetic field
University of Birmingham to host national computing center
Play nicely: Children who are not friends connect better through play when given a goal
Surviving the extreme temperatures of the climate crisis calls for a revolution in home and building design
The wild can be ‘death trap’ for rescued animals
[Press-News.org] Researchers shed light on skin tone bias in breast cancer imagingNew imaging technique reduces skin tone bias in breast cancer detection, improving visibility across diverse skin tones