(Press-News.org) A new study presents “Evo” – a machine learning model capable of decoding and designing DNA, RNA, and protein sequences, from molecular to genome scale, with unparalleled accuracy. Evo’s ability to predict, generate, and engineer entire genomic sequences could change the way synthetic biology is done. “The ability to predict the effects of mutations across all layers of regulation in the cell and to design DNA sequences to manipulate cell function would have tremendous diagnostic and therapeutic implications for disease,” writes Christina Theodoris in a related Perspective. With a vocabulary of just four nucleotides, DNA encodes all the genetic information essential for life. Variations in the genomic sequence reflect adaptations selected for specific biological functions. These variations drive evolution by enabling organisms to adapt to new or changing environments. Advances in DNA sequencing technologies have allowed for genomic variations to be mapped at the whole-genome scale. These data, combined with novel machine learning algorithms, could enable the creation of a comprehensive model that can understand DNA, RNA, and protein functions and their interactions. But, while some researchers inspired by the success of large language models (LLMs) have attempted to model DNA as a "language" by applying similar techniques, current generative models tend to focus narrowly on individual molecules or DNA segments. Alongside computational limitations, this has constrained the scope of these models in capturing broader genomic interactions necessary for understanding complex biological processes.
Here, Eric Nguyen and colleagues present Evo – a large-scale genomic foundation model, equipped with 7 billion parameters and designed to generate DNA sequences up to whole-genome scale. Built on the StripedHyena architecture, Evo was trained on a dataset of 2.7 million evolutionary diverse microbial genomes. According to Nguyen et al., Evo excels in both predictive and generative biological tasks, achieving high accuracy in zero-shot evaluations for predicting mutation impacts on bacterial proteins and RNA, as well as in modeling gene regulation. Evo also grasps the intricate coevolution between coding and noncoding sequences, supporting the design of complex biological systems like CRISPR-Cas complexes and transposable elements. At the genomic scale, Evo can generate sequences over 1 megabase in length, a capability vastly surpassing prior models. “Future models may learn from diverse human and other eukaryotic genomes, using larger context lengths to capture distant genomic interactions over larger genomic scales,” writes Theodoris in the Perspective.
END
Presenting Evo – a model for decoding and designing genetic sequences
Summary author: Walter Beckwith
2024-11-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Global plastic waste set to double by 2050, but new study offers blueprint for significant reductions
2024-11-14
Without intervention, global plastic waste could double by 2050, a new machine learning study predicts. However, according to simulations by the study’s authors, a mix of policy interventions could cut plastic waste by more than 90% and it could cut plastics-related emissions by a third. With UN treaty negotiations underway, these findings provide a crucial blueprint for tackling the plastic crisis. Plastic production has increased relentlessly for decades, leading to surging plastic waste generation and environmental mismanagement. As plastic ...
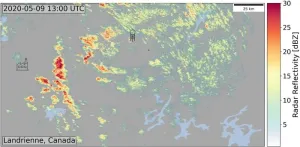
Industrial snow: Factories trigger local snowfall by freezing clouds
2024-11-14
Anthropogenic aerosols, tiny solid and liquid air pollution particles, have masked a fraction of global warming caused by anthropogenic greenhouse gases. Climate researchers have known for decades that anthropogenic aerosols perturb liquid clouds by enabling the formation of a larger number of cloud droplets, making clouds brighter. A new landmark study led by the University of Tartu suggests that anthropogenic aerosols may also influence clouds by converting cloud droplets to ice at temperatures below zero degrees Celsius.
Powerplant Snow
Using satellite observations, climate researchers discovered unique plumes of ice clouds and reduced cloud cover downwind of industrial hot spots ...
Backyard birds learn from their new neighbors when moving house
2024-11-14
Scientists have found a trigger for social learning in wild animals. An experiment on great tits has pinpointed a single factor—immigration—that can cause birds to pay close attention to others, leading them to rapidly adopt useful behaviors. The study is the first to provide experimental support of a long-held assumption that immigrants should strategically use social learning. The study, conducted by scientists from the Max Planck Institute of Animal Behavior (MPI-AB) and the Cluster of Excellence Collective Behaviour at the University of Konstanz in Germany, is published November 14 in PLOS Biology.
Many animals that live in groups learn from one another, but few ...
New study in Science finds that just four global policies could eliminate more than 90% of plastic waste and 30% of linked carbon emissions by 2050
2024-11-14
Berkeley, CA/Santa Barabara, CA (14 November 2024) — A new study released in Science today determines that just four policies can reduce mismanaged plastic waste — plastic that isn’t recycled or properly disposed of and ends up as pollution — by 91% and plastic-related greenhouse gasses by one-third. The policies are: mandate new products be made with 40% post-consumer recycled plastic; cap new plastic production at 2020 levels; invest significantly in plastic waste management — such as landfills and waste collection services; and implement a small fee on plastic packaging. ...
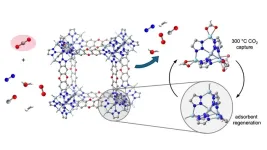
Breakthrough in capturing 'hot' CO2 from industrial exhaust
2024-11-14
Industrial plants, such as those that make cement or steel, emit copious amounts of carbon dioxide, a potent greenhouse gas, but the exhaust is too hot for state-of-the-art carbon removal technology. Lots of energy and water are needed to cool the exhaust streams, a requirement that has limited adoption of CO2 capture in some of the most polluting industries.
Now, chemists at the University of California, Berkeley, have discovered that a porous material can act like a sponge to capture CO2 at temperatures close to those of many industrial exhaust streams. ...
New discovery enables gene therapy for muscular dystrophies, other disorders
2024-11-14
Gene therapy can effectively treat various diseases, but for some debilitating conditions like muscular dystrophies there is a big problem: size. The genes that are dysfunctional in muscular dystrophies are often extremely large, and current delivery methods can’t courier such substantial genetic loads into the body. A new technology, dubbed “StitchR,” surmounts this obstacle by delivering two halves of a gene separately; once in a cell, both DNA segments generate messenger RNAs (mRNAs) that join seamlessly together to restore expression of a protein that is missing or inactive in disease.
Published in ...
Anti-anxiety and hallucination-like effects of psychedelics mediated by distinct neural circuits
2024-11-14
New research suggests that it could be possible to separate treatment from hallucinations when developing new drugs based on psychedelics. The anti-anxiety andhallucination-inducing qualities of psychedelic drugs work through different neural circuits, according to research using a mouse model. The work is published Nov. 15 in Science.
The research shows that decoupling the beneficial effects of psychedelics from their hallucinogenic effects isn’t just a matter of chemical compound design. It’s a matter of targeted neural circuitry.
“In the past, we did this using chemistry by making new compounds, but here we focused on identifying the circuits responsible ...
How do microbiomes influence the study of life?
2024-11-14
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Microorganisms — bacteria, viruses and other tiny life forms — may drive biological variation in visible life as much, if not more, than genetic mutations, creating new lineages and even new species of animals and plants, according to Seth Bordenstein, director of Penn State’s One Health Microbiome Center, professor of biology and entomology, and the Dorothy Foehr Huck and J. Lloyd Huck Endowed Chair in Microbiome Sciences. Bordenstein and 21 other scientists from around the world published a paper in the leading journal Science, summarizing research that they said drives a deeper understanding of biological ...
Plant roots change their growth pattern during ‘puberty’
2024-11-14
Ghent, November 15, 2024 – Understanding how roots grow can help us develop plants that, for example, are more resistant to drought. Research by Prof. Bert De Rybel’s team (VIB-UGent), in collaboration with the VIB Screening Core and Ghent University, uncovers how roots go through a puberty phase, which could have important implications for developing climate-resilient agriculture. Their work appears in Science.
Plant puberty
Plants, like all living organisms, transition through various developmental stages, starting as a seed, becoming a shoot, and eventually a full-grown, fertile plant. They even go through a sort of ‘puberty’ ...
Study outlines key role of national and EU policy to control emissions from German hydrogen economy
2024-11-14
Hydrogen is set to play an important role in a future low-carbon economy. However, the hydrogen value chain comes with a set of emissions challenges that need to be addressed for hydrogen deployment to help achieve climate goals. A study prepared by the Research Institute for Sustainability – Helmholtz Centre Potsdam (RIFS) with support from Environmental Defense Fund Europe evaluates the potential impact of climate-warming emissions in Germany’s future hydrogen economy and provides recommendations for German and EU policymakers on how to avoid them.
There are hopes that hydrogen can become a carbon neutral alternative to fossil ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Middle-aged men are most vulnerable to faster aging due to ‘forever chemicals’
Starving cancer: Nutrient deprivation effects on synovial sarcoma
Speaking from the heart: Study identifies key concerns of parenting with an early-onset cardiovascular condition
From the Late Bronze Age to today - Old Irish Goat carries 3,000 years of Irish history
Emerging class of antibiotics to tackle global tuberculosis crisis
Researchers create distortion-resistant energy materials to improve lithium-ion batteries
Scientists create the most detailed molecular map to date of the developing Down syndrome brain
Nutrient uptake gets to the root of roots
Aspirin not a quick fix for preventing bowel cancer
HPV vaccination provides “sustained protection” against cervical cancer
Many post-authorization studies fail to comply with public disclosure rules
GLP-1 drugs combined with healthy lifestyle habits linked with reduced cardiovascular risk among diabetes patients
Solved: New analysis of Apollo Moon samples finally settles debate about lunar magnetic field
University of Birmingham to host national computing center
Play nicely: Children who are not friends connect better through play when given a goal
Surviving the extreme temperatures of the climate crisis calls for a revolution in home and building design
The wild can be ‘death trap’ for rescued animals
New research: Nighttime road traffic noise stresses the heart and blood vessels
Meningococcal B vaccination does not reduce gonorrhoea, trial results show
AAO-HNSF awarded grant to advance age-friendly care in otolaryngology through national initiative
Eight years running: Newsweek names Mayo Clinic ‘World’s Best Hospital’
Coffee waste turned into clean air solution: researchers develop sustainable catalyst to remove toxic hydrogen sulfide
Scientists uncover how engineered biochar and microbes work together to boost plant-based cleanup of cadmium-polluted soils
Engineered biochar could unlock more effective and scalable solutions for soil and water pollution
Differing immune responses in infants may explain increased severity of RSV over SARS-CoV-2
The invisible hand of climate change: How extreme heat dictates who is born
Surprising culprit leads to chronic rejection of transplanted lungs, hearts
Study explains how ketogenic diets prevent seizures
New approach to qualifying nuclear reactor components rolling out this year
U.S. medical care is improving, but cost and health differ depending on disease
[Press-News.org] Presenting Evo – a model for decoding and designing genetic sequencesSummary author: Walter Beckwith