Around the world, the historic geomagnetic superstorm of late spring 2024 inspired millions of non-scientists around the world—many armed with highly sensitive smartphone cameras—to take a fantastic, unprecedented number of images of the aurora it produced.
In Japan, this widespread popular uptake of what is now quite advanced imaging technology (even if it is kept in everyone’s pocket) proved to be a tremendous boon for atmospheric physicists and other scientists specializing in “space weather.” It allowed them to discover why the Northern Lights over Japan appeared as a mysterious magenta color this time instead of the typical red that is observed when aurorae are visible over that country.
The researchers describe both their findings and what could be a model for the organization of future “citizen-science” operations in the journal Scientific Reports on October 28.
In early May this year, one of the most extreme geomagnetic storms in the history of recording such events hit the Earth’s atmosphere. This great ‘storm’ in space, composed of ionized particles, is what produces the aurora borealis, or Northern Lights, in the northern hemisphere and the aurora australis, or Southern Lights, in the southern hemisphere.
This time, however, the storm was so strong—the ninth most severe storm in the 110-year history of Japan’s Kakioka Magnetic Observatory, one of the oldest geomagnetic stations in the world—that the polar lights could be photographed at much lower latitudes than normal.
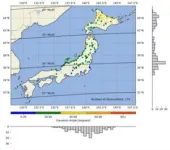
In Japan, space weather researchers took advantage of ordinary people taking pictures of the aurora with their smartphones to organize one of the densest citizen science observation efforts anywhere, despite being a low-latitude country where the aurora was somewhat fainter than in places like Canada or northern Europe.
The different colors of an aurora come from the emission of light from different atoms and molecules in the atmosphere when they are bombarded by the particles from space. The dramatic green hue seen in many photographs of the polar lights comes of atomic oxygen (single atoms of oxygen rather than molecular oxygen, or two oxygen atoms bound together) at the lower altitudes within the atmosphere that are visible to people. (The human eye is also just very sensitive to this color). At even lower altitudes, where atomic oxygen is less common, blue is more visible, and this comes from the greater presence of nitrogen.
At the very highest altitudes in the atmosphere, however, there is a lower concentration of atoms of any kind. The fewer collisions there result in a perception by humans of the excited atomic oxygen atoms as the color red. This is why the upper parts of the aurora curtains can appear as green fading into a scarlet hue.
At low latitudes as in Japan, normally there is no green at all, only red because only the upper part of the aurora can be seen above the horizon.
“Yet this time, weirdly, the images revealed a very clear and dominant magenta hue to the aurora ‘curtains’ over Japan, not red,” said Ryuho Kataoka, the lead author of the study and a specialist in extreme space weather.
To solve the mystery, the researchers quickly took to social media to encourage people to observe and report their sightings of the auroras, as well as to input data into a questionnaire asking about observation locations, time, elevation angles and other details, allowing researchers to analyze the auroras' characteristics in unprecedented detail.
The effort resulted in an impressive 775 grassroots submissions, which the researchers then combined with satellite observations and advanced modeling techniques to explore the conditions that had led to the magenta aurora.
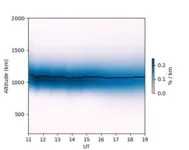
The elevation data from these citizen scientists proved to be particularly useful. The researchers used elevation angles to calculate the position of the aurora over time, and found that it was often a surprisingly high altitude of roughly 1000 km above sea level—which should thus drive a red appearance. But on top of this, the time and season of year meant the atmosphere was more “preheated” ahead of the aurora, in turn driving an upwelling of ionized molecular nitrogen—what is usually responsible for a blue hue.
“Blue plus red makes us see magenta,” added Professor Kataoka. “And the magenta was made all the more visible and vibrant by the sheer volume of solar activity, even though, ironically, the preheating would also have worked to reduce the peak brightness of the aurora.”
Better understanding of magnetic storms goes beyond explaining why humans see the pretty colors of aurorae; these storms can have profound, negative impacts on satellite operations, GPS systems, power grids and even the safety of passengers and crews aboard high-altitude flights.
And so ahead of the next magnetic storm, the researchers want to take an even more coordinated approach to citizen science and spread their efforts further afield. This particular study was limited to Japan and used only the Japanese language, representing something of a proof of concept.
But by using automated translation of their questionnaires and social media posts into local languages around the world, the researchers feel that they will be able to produce a global replication of this effort, with the ultimate aim of analyzing different phases of magnetic storms, to better protect humanity from the dangers posed by extreme space weather.
###
About National Institute of Polar Research (NIPR)
The NIPR engages in comprehensive research via observation stations in Arctic and Antarctica. As a member of the Research Organization of Information and Systems (ROIS), the NIPR provides researchers throughout Japan with infrastructure support for Arctic and Antarctic observations, plans and implements Japan's Antarctic observation projects, and conducts Arctic researches of various scientific fields such as the atmosphere, ice sheets, the ecosystem, the upper atmosphere, the aurora and the Earth's magnetic field. In addition to the research projects, the NIPR also organizes the Japanese Antarctic Research Expedition and manages samples and data obtained during such expeditions and projects. As a core institution in researches of the polar regions, the NIPR also offers graduate students with a global perspective on originality through its doctoral program. For more information about the NIPR, please visit: https://www.nipr.ac.jp/english/
About the Research Organization of Information and Systems (ROIS)
ROIS is a parent organization of four national institutes (National Institute of Polar Research, National Institute of Informatics, the Institute of Statistical Mathematics and National Institute of Genetics) and the Joint Support-Center for Data Science Research. It is ROIS's mission to promote integrated, cutting-edge research that goes beyond the barriers of these institutions, in addition to facilitating their research activities, as members of inter-university research institutes.
END