(Press-News.org) Minuscule particles of plastic are not only bad for the environment. A study led from Umeå University, Sweden, has shown that the so-called nanoplastics which enter the body also can impair the effect of antibiotic treatment. The results also indicate that the nanoplastics may lead to the development of antibiotic resistance. Even the indoor air in our homes contains high levels of nanoplastics from, among other things, nylon, which is particularly problematic.
"The results are alarming considering how common nanoplastics are and because effective antibiotics for many can be the difference between life and death," says Lukas Kenner, professor at the Department of Molecular Biology at Umeå University and one of the researchers who led the study.
Nanoplastics are plastic particles that are smaller than a thousandth of a millimetre. Due to their smallness, they can float freely in the air and have the ability to enter the body.
In the study, led not only by researchers in Umeå, but also by scientists based in Germany and Hungary, the authors have focused on how some of the most common nanoplastics interact with tetracycline, which is a common broad-spectrum antibiotic. It turned out that there was significant accumulation of the antibiotics on the surfaces of the nanoplastic particles. You could say that the nanoplastics absorb antibiotics.
The nanoplastics in question come from common types of plastics such as polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene and nylon. They are commonly found in packaging and textiles. Indoor air contains about five times as much nanoplastics as outdoor air, partly due to particles released from textiles.
One risk that the researchers point out is that the binding to nanoplastics can lead to the antibiotics "hitchhiking" with the nanoplastic in the bloodstream and being transported to other places in the body than they are intended for. This can both reduce the targeted effect of the antibiotics and risk enabling the emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. When antibiotics accumulate in unintended areas, sub-lethal doses can spur bacterial mutations, selecting for antibiotic-resistant strains.
The researchers used advanced computer models to analyze how the nanoplastics bind to tetracycline. It turned out that the bond was particularly strong to nylon – one of the substances that is most abundant in nanoplastics in indoor air.
"Although more research is needed to shed light on the connections and possible measures, we can conclude from our results that nanoplastics are a health risk that should be taken more seriously," says Lukas Kenner.
The study, which is published in the scientific journal Scientific Reports, has been led by Lukas Kenner at Umeå University, Barbara Kirchner at the University of Bonn in Germany and Oldamur Hollóczki at the University of Debrecen, Hungary. The sub-study on the binding of nanoplastics to antibiotics has been led by Nikola Zlatkov Kolev at the Department of Molecular Biology at Umeå University. Lukas Kenner has recently taken up the position of visiting professor at the Department of Molecular Biology at Umeå University and continues his research on nanoplastics and health effects.
END
Nanoplastics can impair the effect of antibiotics
2024-11-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Be humble: Pitt studies reveal how to increase perceived trustworthiness of scientists
2024-11-18
How can scientists across climate science, medical and psychological topics foster the public’s trust in them and their science? Show that they are intellectually humble.
Those are some of the findings of two intellectually humble University of Pittsburgh scientists and their co-authors, using five separate studies totaling 2,034 participants in research published Nov. 18 in Nature Human Behaviour.
“Research has shown that having intellectual humility — which is an awareness that one’s knowledge or beliefs might be incomplete or wrong — is associated with engaging in more effortful and less biased information processing,” said Jonah Koetke, ...
Promising daily tablet increases growth in children with dwarfism
2024-11-18
A promising daily tablet is effective at increasing height and improving proportional limb growth in children with achondroplasia, the most common form of dwarfism, according to a new study. And the findings could spare these children from needing to have a daily injection to boost growth.
The phase II study, led by Murdoch Children’s Research Institute (MCRI) and published in the New England Journal of Medicine, found the drug infigratinib, an investigational product, was safe and effective in treating children with achondroplasia aged 3-11 ...
How 70% of the Mediterranean Sea was lost 5.5 million years ago
2024-11-18
Mediterranean Sea dropped during the Messinian Salinity Crisis – a major geological event that transformed the Mediterranean into a gigantic salt basin between 5.97 and 5.33 million years ago2.
Until now, the process by which a million cubic kilometres of salt accumulated in the Mediterranean basin over such a short period of time remained unknown. Thanks to analysis of the chlorine isotopes3 contained in salt extracted from the Mediterranean seabed, scientists have been able to identify the ...
Keeping the lights on and the pantry stocked: Ensuring water for energy and food production
2024-11-18
A new study, focused on a remote region of the Peruvian Andes where the waters of the Amazon originate, carries lessons for hydropower operators and farming communities worldwide: collaborating on sustainable land management is the best decision they can make for the long-term viability of their businesses and livelihoods. It also opens opportunities for restoration of degraded ecosystems. Research from the Stanford-based Natural Capital Project (NatCap) in Communications - Earth & the Environment integrates hydropower operations with ...
Parkinson’s Paradox: When more dopamine means more tremor
2024-11-18
Researchers from the Champalimaud Foundation shed light on the puzzling relationship between dopamine and rest tremor in Parkinson’s disease, finding that preserved dopamine in certain brain regions may actually contribute to tremor symptoms, challenging common beliefs.
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a progressive neurological disorder known for its characteristic motor symptoms: tremor, rigidity, and slowness of movement. Among these, rest tremor—a shaking that occurs when muscles are relaxed—is one of the most recognisable yet least understood.
A new study from the Champalimaud ...
Study identifies strategy for AI cost-efficiency in health care settings
2024-11-18
New York, NY [November 18, 2024]—A study by researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai has identified strategies for using large language models (LLMs), a type of artificial intelligence (AI), in health systems while maintaining cost efficiency and performance.
The findings, published in the November 18 online issue of npj Digital Medicine [DOI: 10.1038/s41746-024-01315-1], provide insights into how health systems can leverage advanced AI tools to automate tasks efficiently, saving time and reducing operational costs while ensuring these models remain ...
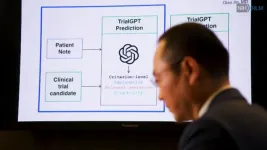
NIH-developed AI algorithm successfully matches potential volunteers to clinical trials release
2024-11-18
Researchers from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) have developed an artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm to help speed up the process of matching potential volunteers to relevant clinical research trials listed on ClinicalTrials.gov. A study published in Nature Communications found that the AI algorithm, called TrialGPT, could successfully identify relevant clinical trials for which a person is eligible and provide a summary that clearly explains how that person meets the criteria for study enrollment. The researchers ...
Greg Liu is in his element using chemistry to tackle the plastics problem
2024-11-18
As an undergraduate student at Zhejiang University in eastern China, Greg Liu went with some of his classmates on a university-sponsored trip to tour a host of chemical industries within the area.
The tour gave students pursuing degrees in chemical engineering an opportunity to learn more about the manufacturing and production processes of chemicals within China at the time. Liu realized that day exactly what he wanted to do for a career – find ways to alleviate or stop the industry from polluting the environment.
“I realized that this was not going to be the sustainable way of our future. Pollution ...
Cocoa or green tea could protect you from the negative effects of fatty foods during mental stress - study
2024-11-18
University of Birmingham News Release
STRICTLY EMBARGOED UNTIL Monday 18th November 2024 8.00am UK/ 3.00am EST
Cocoa or green tea could protect you from the negative effects of fatty foods during mental stress - study
New research has found that a flavanol-rich cocoa drink can protect the body’s vasculature against stress even after eating high-fat food.
Food choices made during periods of stress can influence the effect of stress on cardiovascular health. For example, recent research from the University of Birmingham found that high-fat foods can negatively affect vascular function and oxygen delivery to the brain, meanwhile flavanol compounds found in abundance in cocoa ...
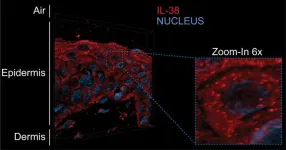
A new model to explore the epidermal renewal
2024-11-18
The mechanisms underlying skin renewal are still poorly understood. Interleukin-38 (IL-38), a protein involved in regulating inflammatory responses, could be a game changer. A team from the University of Geneva (UNIGE) has observed it for the first time in the form of condensates in keratinocytes, the cells of the epidermis. The presence of IL-38 in these aggregates is enhanced close to the skin’s surface exposed to atmospheric oxygen. This process could be linked to the initiation of programmed ...