(Press-News.org) How can scientists across climate science, medical and psychological topics foster the public’s trust in them and their science? Show that they are intellectually humble.
Those are some of the findings of two intellectually humble University of Pittsburgh scientists and their co-authors, using five separate studies totaling 2,034 participants in research published Nov. 18 in Nature Human Behaviour.
“Research has shown that having intellectual humility — which is an awareness that one’s knowledge or beliefs might be incomplete or wrong — is associated with engaging in more effortful and less biased information processing,” said Jonah Koetke, the principal author and a graduate student under co-author Karina Schumann, associate professor of psychology. “In this work, we wanted to flip the perspective and examine whether members of the public believe that scientists who are intellectually humble also produce more rigorous and trustworthy research.
“Because it is so critical to the scientific process — for example, being aware of the limits of our knowledge, communicating the limitations of results, being willing to update beliefs — members of the public might be more likely to trust scientists who exhibit intellectual humility.”
The article, also co-authored by Shauna Bowes of Vanderbilt University and Nina Vaupotič of the University of Vienna, cited statistics showing how Americans reporting a great deal of confidence in scientists decreased by 10% from 2020 to 2021 (the last measured year at the time of the writing), to 29% overall. For hot-button topics, the confidence dips even lower — as evidenced by differing public perceptions amid the pandemic over lockdowns, social distancing, vaccines and more — despite the presence of evidence-based science affirming their effectiveness.
“These are anxiety-provoking times for people, and they feel uncertain about who to trust and which recommendations to follow,” Schumann said. “We wanted to know what can help people feel more confident putting their faith in scientists working to find solutions to some of the complex global challenges we are facing.”
This dilemma stood at the heart of their study: What are the factors “that legitimately promote or hinder trust” in science and scientists? The researchers measured perceived trustworthiness as having the qualities of expertise, benevolence (seeing scientists as people who pursue wellbeing for all), and integrity. They also measured how much people trusted the scientists’ research by asking about their willingness to learn more about the research and follow the scientists’ recommendations.
The researchers theorized that intellectual humility would be a key characteristic of scientists that guides how members of the public perceive them.
“When scientists fail to behave in ways that reflect intellectual humility, it might be especially detrimental and jarring, as it goes against both the fundamental norms of science and people’s expectations for how a responsible scientist should act,” the co-authors reasoned.
So they set out to research whether perceptions of scientists’ intellectual humility would influence people’s trust in scientists and their research.
Study 1: They asked 298 online participants from across the U.S. to think of scientists and rate them on their perceived intellectual humility. Participants also offered ratings of the perceived trustworthiness of scientists and of their belief in polarizing science topics such as climate change, vaccinations and genetically modified foods. In the end, the study showed correlational evidence that the more participants believed scientists were intellectually humble, the more they trusted scientists and believed in evidence-based science.
Study 2: To better isolate the effects of intellectual humility on trust, they next tested their hypothesis by assigning 317 participants to read one of three “articles” about an ostensible scientist identified as a woman researching new treatments for long COVID-19 symptoms. The three “articles” described the scientist in ways that conveyed either low intellectual humility or high intellectual humility, or did not discuss characteristics related to intellectual humility (control condition). They found large effects on trust in the predicted direction, with participants reporting lower trust toward the scientist described as having low intellectual humility compared to the other two conditions. Participants in the low intellectual humility condition also reported less belief in the scientist’s research on the new treatment.
Study 3: Because questions surrounding gender perception were left unanswered in Study 2, the co-authors sought to examine the effect of a scientist’s gender identity on the public’s reactions to intellectual humility. They randomly assigned 369 participants to read an article about an ostensible psychological scientist studying why people should talk across political divides. They used the same three “article” designs as Study 2, but varied whether each described either a female or male scientist. Replicating Study 3, they again found large effects of intellectual humility on trust, as well as small-to-medium effects on belief in the research and whether participants would follow the scientist’s recommendations. The described gender of the scientist had no influence on the benefits of high vs. low intellectual humility on these outcomes.
Study 4: To ensure that the benefits of perceived intellectual humility generalized to scientists of color, the co-authors next tested if participants were affected by the racial identity of the scientist. Some 371 participants were randomly assigned to read an “article” about an ostensible climate scientist testing the benefits of plant-rich diets for reducing global carbon emissions. In this new scientific context, the authors replicated the effects from the prior studies and also discovered a small-to-medium effect on participants’ desire to obtain further information about switching to a plant-rich diet — 36% people opted in to receive this information when the scientist was high in intellectual humility compared to 21% when the scientist was low in intellectual humility. Notably, as with gender, the described race of the scientist didn’t show an effect.
Study 5: In the final study, the authors set out to test an important question that remained: How can a scientist express they are intellectually humble when communicating their research to the public? The authors randomly assigned 679 participants in a census-matched sample to read one of four “interviews” with an ostensible scientist discussing the psychological benefits of taking a social-media break (not considered as polarizing as the previous study topics). These interviews included approaches like describing the methodological limitations of the research or giving credit to their graduate students. However, although the approaches were generally effective at increasing perceptions of intellectual humility, none of the communication strategies successfully increased perceptions of scientists’ trustworthiness and several even backfired by shaking people’s trust in the research. The authors humbly noted that they still don’t how scientists can communicate intellectual humility in ways that also builds trust.
“We still have a lot to learn about specific strategies scientists can use to display their intellectual humility in their public communications,” Koetke said. “This will be the focus of future work.”
For now, the research team came away feeling that the general public values intellectual humility.
“As a scientist, I felt incredibly encouraged by our findings,” Schumann said. “They suggest that the public understands that science isn’t about having all the answers; it's about asking the right questions, admitting what we don’t yet understand, and learning as we go. Although we still have much to discover about how scientists can authentically convey intellectual humility, we now know people sense that a lack of intellectual humility undermines the very aspects of science that make it valuable and rigorous. This is a great place to build from.”
END
Be humble: Pitt studies reveal how to increase perceived trustworthiness of scientists
2024-11-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Promising daily tablet increases growth in children with dwarfism
2024-11-18
A promising daily tablet is effective at increasing height and improving proportional limb growth in children with achondroplasia, the most common form of dwarfism, according to a new study. And the findings could spare these children from needing to have a daily injection to boost growth.
The phase II study, led by Murdoch Children’s Research Institute (MCRI) and published in the New England Journal of Medicine, found the drug infigratinib, an investigational product, was safe and effective in treating children with achondroplasia aged 3-11 ...
How 70% of the Mediterranean Sea was lost 5.5 million years ago
2024-11-18
Mediterranean Sea dropped during the Messinian Salinity Crisis – a major geological event that transformed the Mediterranean into a gigantic salt basin between 5.97 and 5.33 million years ago2.
Until now, the process by which a million cubic kilometres of salt accumulated in the Mediterranean basin over such a short period of time remained unknown. Thanks to analysis of the chlorine isotopes3 contained in salt extracted from the Mediterranean seabed, scientists have been able to identify the ...
Keeping the lights on and the pantry stocked: Ensuring water for energy and food production
2024-11-18
A new study, focused on a remote region of the Peruvian Andes where the waters of the Amazon originate, carries lessons for hydropower operators and farming communities worldwide: collaborating on sustainable land management is the best decision they can make for the long-term viability of their businesses and livelihoods. It also opens opportunities for restoration of degraded ecosystems. Research from the Stanford-based Natural Capital Project (NatCap) in Communications - Earth & the Environment integrates hydropower operations with ...
Parkinson’s Paradox: When more dopamine means more tremor
2024-11-18
Researchers from the Champalimaud Foundation shed light on the puzzling relationship between dopamine and rest tremor in Parkinson’s disease, finding that preserved dopamine in certain brain regions may actually contribute to tremor symptoms, challenging common beliefs.
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a progressive neurological disorder known for its characteristic motor symptoms: tremor, rigidity, and slowness of movement. Among these, rest tremor—a shaking that occurs when muscles are relaxed—is one of the most recognisable yet least understood.
A new study from the Champalimaud ...
Study identifies strategy for AI cost-efficiency in health care settings
2024-11-18
New York, NY [November 18, 2024]—A study by researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai has identified strategies for using large language models (LLMs), a type of artificial intelligence (AI), in health systems while maintaining cost efficiency and performance.
The findings, published in the November 18 online issue of npj Digital Medicine [DOI: 10.1038/s41746-024-01315-1], provide insights into how health systems can leverage advanced AI tools to automate tasks efficiently, saving time and reducing operational costs while ensuring these models remain ...
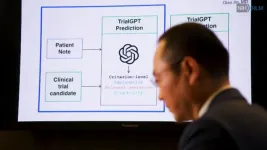
NIH-developed AI algorithm successfully matches potential volunteers to clinical trials release
2024-11-18
Researchers from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) have developed an artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm to help speed up the process of matching potential volunteers to relevant clinical research trials listed on ClinicalTrials.gov. A study published in Nature Communications found that the AI algorithm, called TrialGPT, could successfully identify relevant clinical trials for which a person is eligible and provide a summary that clearly explains how that person meets the criteria for study enrollment. The researchers ...
Greg Liu is in his element using chemistry to tackle the plastics problem
2024-11-18
As an undergraduate student at Zhejiang University in eastern China, Greg Liu went with some of his classmates on a university-sponsored trip to tour a host of chemical industries within the area.
The tour gave students pursuing degrees in chemical engineering an opportunity to learn more about the manufacturing and production processes of chemicals within China at the time. Liu realized that day exactly what he wanted to do for a career – find ways to alleviate or stop the industry from polluting the environment.
“I realized that this was not going to be the sustainable way of our future. Pollution ...
Cocoa or green tea could protect you from the negative effects of fatty foods during mental stress - study
2024-11-18
University of Birmingham News Release
STRICTLY EMBARGOED UNTIL Monday 18th November 2024 8.00am UK/ 3.00am EST
Cocoa or green tea could protect you from the negative effects of fatty foods during mental stress - study
New research has found that a flavanol-rich cocoa drink can protect the body’s vasculature against stress even after eating high-fat food.
Food choices made during periods of stress can influence the effect of stress on cardiovascular health. For example, recent research from the University of Birmingham found that high-fat foods can negatively affect vascular function and oxygen delivery to the brain, meanwhile flavanol compounds found in abundance in cocoa ...
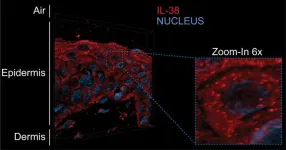
A new model to explore the epidermal renewal
2024-11-18
The mechanisms underlying skin renewal are still poorly understood. Interleukin-38 (IL-38), a protein involved in regulating inflammatory responses, could be a game changer. A team from the University of Geneva (UNIGE) has observed it for the first time in the form of condensates in keratinocytes, the cells of the epidermis. The presence of IL-38 in these aggregates is enhanced close to the skin’s surface exposed to atmospheric oxygen. This process could be linked to the initiation of programmed ...
Study reveals significant global disparities in cancer care across different countries
2024-11-18
A recent analysis reveals striking disparities in the cost and availability of cancer drugs across different regions of the globe, with significant gaps between high- and low-income countries. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
The analysis, which drew on relevant published studies and reviews related to cancer and the availability of cancer treatments, predicts that there will be an estimated 28.4 million new cancer cases worldwide in 2040 alone. In the coming years, cancer incidence is expected to increase most significantly in low-income countries. Cancer mortality ...