(Press-News.org) Anyone who has ever tried to get rid of a few extra kilos knows the frustration: the weight drops initially, only to be back within a matter of weeks – the yo-yo effect has struck. Researchers at ETH Zurich have now been able to show that this is all down to epigenetics.
Epigenetics is the part of genetics that’s based not on the sequence of genetic building blocks but on small yet characteristic chemical markers on these building blocks. The sequence of building blocks has evolved over a long period of time; we all inherit them from our parents. Epigenetic markers, on the other hand, are more dynamic: environmental factors, our eating habits and the condition of our body – such as obesity – can change them over the course of the lifetime. But they can remain stable for many years, sometimes decades, and during this time, they play a key role in determining which genes are active in our cells and which are not. “Epigenetics tells a cell what kind of cell it is and what it should do,” says Laura Hinte, a doctoral student in the group led by Ferdinand von Meyenn, Professor of Nutrition and Metabolic Epigenetics.
An epigenetic memory of obesity
The researchers led by the two and their colleague Daniel Castellano Castillo, a former postdoc in von Meyenn’s group, looked for the molecular causes of the yo-yo effect in mice. They analysed fat cells from overweight mice and those that had shed their excess weight through dieting. Their investigations revealed that obesity leads to characteristic epigenetic changes in the nucleus of fat cells. What’s special about these changes is that they remain even after a diet. “The fat cells remember the overweight state and can return to this state more easily,” von Meyenn says. The scientists were able to show that mice with these epigenetic markers regained weight more quickly when they again had access to a high-fat diet. “That means we’ve found a molecular basis for the yo-yo effect.”
They also found evidence for this mechanism in humans. The ETH Zurich researchers analysed fat tissue biopsies from formerly overweight people who had undergone stomach reduction or gastric bypass surgery. The tissue samples came from various studies carried out at Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm and at hospitals in Leipzig, Dresden and Karlsruhe. In these samples, the researchers analysed gene expression rather than epigenetic markers. However, the results are consistent with those of the mice. The researchers report on their work in the latest issue of the journal Nature.
Prevention is the key
Something the researchers haven’t investigated is how long fat cells can remember obesity. “Fat cells are long-lived cells. On average, they live for ten years before our body replaces them with new cells,” Hinte says.
It’s not currently possible to change the relevant epigenetic marks in the cell nucleus with drugs and thus erase the epigenetic memory. “Maybe that’s something we’ll be able to do in the future,” Hinte says. “But for the time being, we have to live with this memory effect.” Von Meyenn adds: “It’s precisely because of this memory effect that it’s so important to avoid being overweight in the first place. Because that’s the simplest way to combat the yo-yo phenomenon.” The researchers are directing this message primarily at children and young people and their parents.
With their work, the ETH researchers have shown for the first time that fat cells possess an epigenetic memory of obesity. However, they don’t assume that fat cells are the only cells with such a memory. “Other body cells might also play a part in the yo-yo effect,” von Meyenn says. It’s quite conceivable that cells in the brain, blood vessels or other organs also remember obesity and contribute to the effect. Whether this is actually the case is what the researchers want to find out next.
END
Cause of the yo-yo effect deciphered
2024-11-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Suicide rates for young male cancer survivors triple in recent years
2024-11-18
LOS ANGELES — New research published in JAMA Network Open from USC Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center, part of Keck Medicine of USC, suggests that among all cancer survivors, male adolescents and young adults (AYA) have the highest rate of death by suicide.
The study also reports that the number of suicide deaths in the AYA male cancer survivor group (ages 15-39) increased three-fold during the 21-year-study period. In 2021, one in 65 deaths among the group was attributed to suicide. Suicide deaths have also increased for other cancer ...
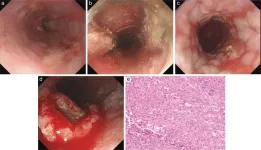
Achalasia and esophageal cancer: A case report and literature review
2024-11-18
Achalasia is primarily caused by the degeneration of the myenteric plexus in the esophageal wall, leading to impaired relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) and loss of esophageal peristalsis. Although the exact etiology is not fully understood, it is believed to involve autoimmune mechanisms and viral infections. Key pathological features include the absence of peristalsis, LES hypertonicity, and symptoms such as dysphagia and regurgitation. In this condition, the esophagus fails to contract and move food toward the stomach, while the LES ...
Authoritative review makes connections between electron density topology, future of materials modeling and how we understand mechanisms of phenomena in familiar devices at the atomistic level
2024-11-18
2024 marks an important milestone with the publication of a comprehensive review in Chemical Reviews on electron density-based methods. The review, authored by an international team, was spearheaded by leading researchers from Institute of Science Tokyo (Sergei Manzhos and Manabu Ihara of the Ihara-Manzhos lab) and included collaborators from Canada (Paul Ayers of McMaster University and Cherif Matta of Mount Saint Vincent University), China (Samantha Jenkins of Hunan Normal University), and the USA (Michele Pavanello from Rutgers University). The project also saw significant contributions from young researchers, Daniel Koch from ...
Understanding neonatal infectious diseases in low- and middle-income countries: New insights from a 30-year study
2024-11-18
Researchers from Peking University have conducted an in-depth study on the epidemic status, secular trends, and risk factors of 15 common neonatal infectious diseases across low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) from 1990 to 2019. The study, published in Health Data Science, provides a comprehensive overview of the changes in incidence and mortality rates, identifying key trends and potential areas for targeted public health interventions to improve neonatal health outcomes.
Neonatal infectious diseases remain a significant cause of morbidity and mortality in LMICs, where newborns are particularly vulnerable to infections due to underdeveloped immune systems ...
This year’s dazzling aurora produced a spectacular display… of citizen science
2024-11-18
Citizen scientists in Japan enabled researchers to learn why May 2024’s aurora appeared a magenta color over the country. This effort in extending research beyond academies and laboratories has greater consequence for humanity than explaining pretty lights
Around the world, the historic geomagnetic superstorm of late spring 2024 inspired millions of non-scientists around the world—many armed with highly sensitive smartphone cameras—to take a fantastic, unprecedented number of images of the aurora it produced.
In ...
New oral drug to calm abdominal pain
2024-11-18
University of Queensland researchers have developed a new class of oral painkillers to suppress chronic abdominal pain that is based on the peptide hormone oxytocin that drives childbirth contractions.
Associate Professor Markus Muttenthaler from UQ’s Institute for Molecular Bioscience led a team that has changed the chemical structure of oxytocin to make it gut-stable after earlier work revealed the hormone could treat abdominal pain.
Dr Muttenthaler said there was an urgent need for new ...
New framework champions equity in AI for health care
2024-11-18
(Toronto, November 18, 2024) A recent study published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research introduced the EDAI framework, a comprehensive guideline designed to embed equity, diversity, and inclusion (EDI) principles throughout the artificial intelligence (AI) lifecycle. Led by Dr Samira Abbasgholizadeh-Rahimi, PhD, the Canada Research Chair (Tier II) in AI and Advanced Digital Primary Health Care, the research addresses a significant gap in current AI development and implementation practices in health and oral health care, which often overlook critical EDI factors. With EDAI, AI ...
We finally know where black holes get their magnetic fields: Their parents
2024-11-18
Black holes are one of the most enigmatic stellar objects. While best known for swallowing up their surroundings into a gravity pit from which nothing can escape, they can also shoot off powerful jets of charged particles, leading to explosive bursts of gamma rays that can release more energy in mere seconds than our sun will emit in its entire lifetime. For such a spectacular event to occur, a black hole needs to carry a powerful magnetic field. Where this magnetism comes from, however, has been a long-standing ...
Multiple sclerosis drug may help with poor working memory
2024-11-18
Fampridine is currently used to improve walking ability in multiple sclerosis. A new study shows that it could also help individuals with reduced working memory, as seen in mental health conditions like schizophrenia or depression.
Remembering a code for long enough to type it in; holding a conversation and reacting appropriately to what is being said: in everyday situations like these, we use our working memory. It allows a memory to be actively retained for a few seconds. Certain conditions, such as schizophrenia ...
The MIT Press releases workshop report on the future of open access publishing and policy
2024-11-18
Cambridge, MA (November 18, 2024) – Today the MIT Press is releasing a workshop report on what additional information is needed to ensure that open access publication benefits research, entitled "Access to Science & Scholarship 2024: Building an Evidence Base to Support the Future of Open Research Policy." The report is the outcome of a workshop funded by the National Science Foundation and held at the D.C. headquarters of the American Association for the Advancement of Science on September 20, 2024.
The implementation of open access has resulted in consolidation of the publishing industry, an explosion in unreviewed articles, and new costs that may be hard ...