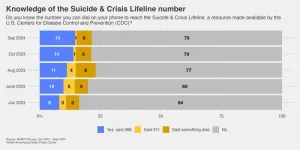
(Press-News.org) PHILADELPHIA – Annenberg Public Policy Center survey data show that public recall of the 988 Suicide & Crisis Lifeline number has grown slowly since the three-digit phone number was introduced in July 2022. Just 15% of U.S. adults are familiar with it, as of September 2024.
Survey respondents who accurately report awareness of the Suicide & Crisis Lifeline number increased significantly from August 2023 (11%) to September 2024 (15%). Those 15% of respondents reported both that they knew the number and, when asked in an open-ended format, said the number was 988. The number who inaccurately reported that the number was 911 (the nationwide emergency phone number) decreased to 1% in September 2024 from 4% in August 2023.
“The help that can be found at the 988 helpline can only save lives if those in need and their loved ones and friends know the number,” said Kathleen Hall Jamieson, director of the Annenberg Public Policy Center of the University of Pennsylvania. “When 988 is as readily recalled as 911, the nation will have cause to celebrate.”
Although the survey found a year-over-year increase, it did not detect an increase in accurate responses between October 2023 and September 2024, a period that included the launch of an eight-month 988 awareness ad campaign by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) in June 2024. The SAMHSA media campaign targets especially vulnerable subsets of the population, which may be too small to impact the overall awareness estimates in our nationally representative, general population sample.
APPC’s Annenberg Science and Public Health knowledge survey
The survey data come from the 21st wave of a nationally representative panel of 1,744 U.S. adults conducted for the Annenberg Public Policy Center by SSRS, an independent market research company. Most have been empaneled since April 2021. To account for attrition, small replenishment samples have been added over time using a random probability sampling design. The most recent replenishment, in September 2024, added 360 respondents to the sample. This wave of the Annenberg Science and Public Health Knowledge (ASAPH) survey was fielded Sept. 13-22 and Sept. 26-30, 2024. The margin of sampling error (MOE) is ± 3.5 percentage points at the 95% confidence level. All figures are rounded to the nearest whole number and may not add to 100%. Combined subcategories may not add to totals in the topline and text due to rounding.
Download the topline and the methods report.
The policy center has been tracking the American public’s knowledge, beliefs, and behaviors regarding vaccination, Covid-19, flu, RSV, and other consequential health issues through this survey panel over the past two-and-a-half years. In addition to Jamieson and Gibson, APPC’s team on the survey includes research analyst Shawn Patterson Jr., Patrick E. Jamieson, director of the Annenberg Health and Risk Communication Institute, and Ken Winneg, managing director of survey research.
The Annenberg Public Policy Center was established in 1993 to educate the public and policy makers about communication’s role in advancing public understanding of political, science, and health issues at the local, state, and federal levels.
END
Fewer than 1 in 5 know the 988 suicide lifeline
2024-11-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Semaglutide eligibility across all current indications for US adults
2024-11-18
About The Study: A total of nearly 137 million adults, representing more than half of all U.S. adults, are eligible for semaglutide therapy. This exceeds the number of adults eligible for statins (approximately 82 million), currently the most prescribed pharmaceuticals among U.S. adults.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Dhruv S. Kazi, MD, MS, email dkazi@bidmc.harvard.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2024.4657)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions ...
Can podcasts create healthier habits?
2024-11-18
Whether it’s ABC Listen’s Health Report or Mamamia’s But Are You Happy, podcasts have fast become a part of our everyday media consumption. In fact, the average person spends more than five hours a week listening to them. But could listening to podcasts lead to healthier habits?
In the first study of its kind, University of South Australia researchers have explored just this, finding that podcasts can significantly improve health knowledge, increase exercise levels, and boost healthy eating.
Reviewing ...
Zerlasiran—A small-interfering RNA targeting lipoprotein(a)
2024-11-18
About The Study: Zerlasiran, a small-interfering RNA targeting hepatic synthesis of apolipoprotein(a), was well-tolerated and reduced time-averaged lipoprotein(a) concentration by more than 80% during 36 weeks of treatment in patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Steven E. Nissen, MD, email nissens@ccf.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.21957)
Editor’s ...
Anti-obesity drugs, lifestyle interventions show cardiovascular benefits beyond weight loss
2024-11-18
Popular anti-obesity drugs continue to show cardiovascular benefits beyond weight loss, according to several new papers published in JACC, the flagship journal of the American College of Cardiology, that are being simultaneously presented at the American Heart Association’s 2024 Scientific Sessions. JACC is publishing two secondary analyses on the impact of GLP-1 medications in improving cardiac structure and function in heart failure patients and cardiovascular outcomes in those who previously had cardiac bypass surgery, ...
Oral muvalaplin for lowering of lipoprotein(a)
2024-11-18
About The Study: Muvalaplin, an oral small molecule lipoprotein(a) inhibitor, reduced lipoprotein(a) measured using intact lipoprotein(a) and apolipoprotein(a)-based assays and was well tolerated. The effect of muvalaplin on cardiovascular events requires further investigation.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Stephen J. Nicholls, MBBS, PhD, email stephen.nicholls@monash.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.24017)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including ...
Revealing the hidden costs of what we eat
2024-11-18
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — Shifting our diets to be more sustainable can be a powerful way for each of us to address both climate change and global food insecurity, however making such adjustments at the large scales necessary to make a difference globally can be a delicate matter.
“Changes in food demand in one part of the world can have cascading environmental and human welfare implications for people around the world),” said Joe DeCesaro, data analyst at UC Santa Barbara’s National Center for Ecological Analysis & Synthesis (NCEAS).
Despite the seemingly daunting complexity of the global food system, to ensure a healthy population ...
New therapies at Kennedy Krieger offer effective treatment for managing Tourette syndrome
2024-11-18
BALTIMORE, November 18, 2024— Researchers at Kennedy Krieger Institute have made significant strides in improving the lives of patients with Tourette syndrome. Their recent publication highlights how behavioral therapies—an approach that teaches patients how to manage certain tics using behavioral strategies—are proving to be the most effective treatment.
Tourette syndrome (TS), a neurodevelopmental disorder affecting up to 1% of the population, is characterized by motor and vocal tics, which are sudden, repetitive movements or sounds that can significantly ...
American soil losing more nutrients for crops due to heavier rainstorms, study shows
2024-11-18
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Phosphorus, a nutrient in soil essential for sustaining most forms of life, is increasingly disappearing from land as it is washed into waterways throughout the United States, according to a new study led by researchers at Penn State.
The study, published today (Nov. 18) in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, analyzed data from 430 rivers across the U.S. and found that phosphorus loss from agricultural lands has increased over the past four decades, despite efforts to reduce it. This loss of phosphorus ...
With new imaging approach, ADA Forsyth scientists closely analyze microbial adhesive interactions
2024-11-18
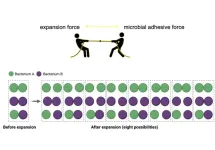
Cambridge, Mass., 11/18/2024 – Scientists have identified many types of bacteria in the mouth, but many problems remain in understanding how they work with one another. One of the problems is that microbes assemble themselves into densely packed multi-species biofilms. Their density and complexity pose acute difficulties for visualizing individual cells and analyzing their interactions at single-cell level.
ADA Forsyth scientists have developed a new imaging approach that makes it possible to analyze the spatial connections between bacteria, including the strength of adhesive forces that hold them together. Adhesion is of fundamental importance in ...
Global antibiotic consumption has increased by more than 21 percent since 2016
2024-11-18
Washington, DC / Bangalore, India — A new study highlights recent, but fluctuating, growth in global human antibiotic consumption, one of the main drivers of growing antimicrobial resistance (AMR). AMR results in infections that no longer respond to antibiotics (and other antimicrobial medicines) and often leads to longer hospital stays, higher treatment costs, and higher mortality rates. AMR is estimated to be associated with nearly five million global deaths annually.
Researchers affiliated with the One Health Trust (OHT), the Population Council, GlaxoSmithKline, the University of Zurich, the University of Brussels, ...