(Press-News.org) A stay in space exerts extreme pressures on the human body. Astronauts’ bodies and brains are impacted by radiation, altered gravity, challenging working conditions, and sleep loss – all of which could compromise cognitive functioning. At the same time, they are required to perform complex tasks, and minor mistakes can have devastating consequences.
Little is known, however, about whether astronauts’ cognitive performance changes while in space. Now, working with 25 astronauts who spent an average of six month on the International Space Station (ISS), researchers in the US have examined changes in a wide range of cognitive performance domains. This dataset makes up the largest sample of cognitive performance data from professional astronauts published to date.
“We show that there is no evidence of any significant cognitive impairment or neurodegenerative decline in astronauts spending six months on the ISS,” said Dr Sheena Dev, a researcher at NASA’s Behavioral Health and Performance Laboratory and first author of the Frontiers in Physiology study. “Living and working in space was not associated with widespread cognitive impairment that would be suggestive of significant brain damage.”
Slower, but no less accurate
Astronauts underwent a series of tests developed to assess a range of cognitive domains using 10 subtests. For each of these tests, the researchers measured speed and accuracy at five time points: pre-mission, early and late flight respectively, as well as at 10 and 30 days after landing.
The results showed that responses to tasks assessing processing speed, working memory, and attention were slower than on Earth, but they were no less accurate. These changes, however, did not persist equally long. “Slowed performance on attention, for example, was only observed early during the mission while slowed performance on processing speed did not return to baseline levels until after the mission ended and crew were back on Earth,” Dev pointed out.
Overall, astronauts’ cognitive performance was stable, and the researchers did not find evidence that would suggest damage to the central nervous system during a six-month space mission.
Data for future space missions
The results showed that some cognitive domains were more susceptible to be impacted than others. “Even on Earth, processing speed, working memory, and attention are cognitive domains that can show temporary changes when an individual is under stress. Other domains, such as memory, are less vulnerable to stressors. For example, if you happen to have a really busy day but couldn’t get much sleep the night before, you might feel like it’s hard to pay attention or that you need more time to complete tasks,” explained Dev.
Astronauts are exposed to these stressors, too, but additional stressors that are unique to space also take their toll. “We found that the most vulnerable domains while astronauts are aboard the ISS are the same as those that are more susceptible to stressors on Earth,” Dev said.
The researchers said that their study can help them understand which changes in cognitive performance might be expected when humans go to extreme environments. What the study didn’t show, however, is why those changes happened, the researchers cautioned. It also didn’t set out to assess whether astronauts’ operational performance suffered. “It could be that even in areas with observed declines, astronauts were still able to compensate and effectively complete their tasks,” Dev said.
Once astronauts start traveling deeper into space – to the moon or Mars, for example – this data from the low Earth orbit can also provide a comparison which can help detect cognitive changes brought about by increased radiation exposure and extended communication delays more quickly, the researchers concluded.
END
Astronauts found to process some tasks slower in space, but no signs of permanent cognitive decline
Researchers found that astronauts’ processing speed, working memory, and attention slowed down, but a few months in space did not result in lasting cognitive impairment
2024-11-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Larger pay increases and better benefits could support teacher retention
2024-11-20
Larger pay increases and better benefits could help keep K-12 teachers in the teacher workforce, finds a new, nationally representative RAND survey.
U.S. teachers reported modest pay increases between the 2022-2023 and 2023-2024 school years, only $2,000 on average and well below their desired increase of $16,000. Black teachers and teachers in states where collective bargaining is prohibited reported they received the smallest pay increases.
“Teachers who received larger pay increases also said they were less likely to intend to leave the profession,” ...
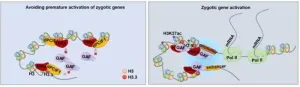
Researchers characterize mechanism for regulating orderly zygotic genome activation in early embryos
2024-11-20
Early development of an embryo is solely supported by maternally deposited RNAs and proteins until its own genome is activated through a process called zygotic genome activation (ZGA).
Recent research by Chinese scientists has revealed novel molecular mechanisms by which HIRA acts in concert with dPCIF1 to establish a totipotent chromatin and facilitate orderly zygotic genome activation in the early embryos of Drosophila.
Results of the study were published in PNAS on Nov. 14 as “HIRA and dPCIF1 coordinately establish totipotent chromatin and control orderly ZGA in Drosophila embryos.”
The ...
AI analysis of urine can predict flare up of lung disease a week in advance
2024-11-20
Researchers have used artificial intelligence (AI) to analyse patient urine samples and predict when symptoms of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) will flare up according to a study published today (Wednesday) in ERJ Open Research [1].
The patients taking part in the study carried out a simple daily dipstick test on their urine and sent their results to researchers using their mobile phones.
Using AI to analyse the results, researchers were able to ‘forecast’ a deterioration in symptoms one week in advance. ...
New DESI results weigh in on gravity
2024-11-20
Gravity has shaped our cosmos. Its attractive influence turned tiny differences in the amount of matter present in the early universe into the sprawling strands of galaxies we see today. A new study using data from the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) has traced how this cosmic structure grew over the past 11 billion years, providing the most precise test to date of gravity at very large scales.
DESI is an international collaboration of more than 900 researchers from over 70 institutions around the world and is managed by the Department of Energy’s ...
New DESI data shed light on gravity’s pull in the universe
2024-11-20
A University of Texas at Dallas physicist and his international colleagues in the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) collaboration are engaged in a multiyear data-gathering mission to try to answer one of the most puzzling observations in astrophysics: Why does the expansion of the universe appear to be accelerating?
Competing theories have attempted to explain this observation. One is that dark energy is somehow pushing galaxies apart. A second theory posits that gravity, the attractive force that in local environments like the solar system draws objects together, works differently at large cosmological scales and needs to be modified to explain cosmic ...
Boosting WA startups: Report calls for investment in talent, diversity and innovation
2024-11-20
A new report from the Bankwest Curtin Economics Centre reveals Western Australia’s startup and innovation ecosystem requires targeted reforms and investment to unlock its full potential, calling for improvements in talent development, gender diversity and access to capital and infrastructure to support a more diversified economy.
The report, titled ‘Dare to Venture: Startups and the innovation ecosystem in Western Australia’, highlights WA’s strengths in mining, ...
New AEM study highlights feasibility of cranial accelerometry device for prehospital detection of large-vessel occlusion stroke
2024-11-20
Des Plaines, IL – A new study exploring the use of cranial accelerometry (CA) headsets for the prehospital detection of large-vessel occlusion (LVO) strokes has been published in a recent issue of Academic Emergency Medicine (AEM), the peer-reviewed journal of the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine (SAEM).
LVO strokes, which represent one-third of acute ischemic stroke (AIS) cases in the United States, are responsible for two-thirds of poststroke dependence and 90% of poststroke mortality. The introduction of endovascular thrombectomy (EVT) over the past decade has significantly advanced the management of LVO strokes, emphasizing ...
High cardiorespiratory fitness linked to lower risk of dementia
2024-11-20
High cardiorespiratory fitness is associated with better cognitive performance and lower risk of dementia long term, including in people with a genetic predisposition to dementia, show the findings of a study published online in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
Cardiorespiratory fitness (CRF) is the capacity of the circulatory and respiratory systems to supply oxygen to muscles and declines increasingly with age as skeletal muscle is lost. CRF declines by around 3% to 6% per decade when people are in their 20s and 30s, but this accelerates to more than 20% per decade by the time people reach their 70s. Low CRF is a strong predictor of cardiovascular ...
Oral microbiome varies with life stress and mental health symptoms in pregnant women
2024-11-20
The number and type of microbes present in the saliva of pregnant women differ according to whether they are experiencing life stress and symptoms of anxiety, depression and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), finds a study published in the open access journal BMJ Mental Health.
Although several studies have shown links between the diversity of microbes in the gastrointestinal tract and stress, anxiety and depression in pregnant women and new mothers, no previous study has looked at the association between the type and number of microorganisms in the mouth and throat—oral microbiome—and ...
NFL’s Arizona Cardinals provide 12 schools with CPR resources to improve cardiac emergency outcomes
2024-11-20
PHOENIX, November 19, 2024 — The American Heart Association and the Arizona Cardinals gathered representatives from 12 local schools for cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and automated external defibrillator (AED) training on Nov. 18 at Pima Elementary School in Scottsdale. According to American Heart Association data, Nearly 9 out of 10 people who experience cardiac arrest outside of a hospital die, in part because they do not receive immediate CPR more than half of the time. CPR, especially if performed immediately, can double or triple a person’s chance of survival.
“Early ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] Astronauts found to process some tasks slower in space, but no signs of permanent cognitive declineResearchers found that astronauts’ processing speed, working memory, and attention slowed down, but a few months in space did not result in lasting cognitive impairment