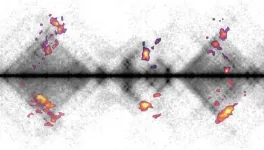
(Press-News.org) New research from the Kind Group at the Hubrecht Institute sheds light on how cells repair damaged DNA. For the first time, the team has mapped the activity of repair proteins in individual human cells. The study demonstrates how these proteins collaborate in so-called "hubs" to repair DNA damage. This knowledge offers opportunities to improve cancer therapies and other treatments where DNA repair is essential. The researchers published their findings in Nature Communications on November 21.
DNA is the molecule that carries our genetic information. It can be damaged by normal cellular processes as well as external factors such as UV radiation and chemicals. Such damage can lead to breaks in the DNA strand. If DNA damage is not properly repaired, mutations can occur, which may result in diseases like cancer. Cells use repair systems to fix this damage, with specialized proteins locating and binding to the damaged regions.
Zooming in on individual cells
The body has various mechanisms to repair DNA, but the process can differ from cell to cell. This makes it important to study DNA repair in individual cells. “Finding breaks in DNA is an enormous challenge,” explains first author Kim de Luca. “We don’t know exactly where the damage occurs or why some areas are harder to repair. Our approach allowed us to answer these questions.”
Using advanced techniques, the researchers mapped where repair proteins attach to DNA. “Previous studies looked at an average picture of multiple cells,” De Luca explains. “By studying individual cells, we discovered unique and sometimes rare ways in which DNA damage is repaired.”
A ‘DNA repair café’
The findings also revealed that DNA can be repaired by cooperation between repair proteins. These proteins organize themselves into “hubs,” where multiple damaged DNA regions come together. These hubs are similar to "repair cafés," where people gather to fix broken items. “Such a central place makes the process more efficient,” says De Luca. “A hub can involve as many as six different breaks that are being repaired in a coordinated way.”
Toward more effective treatments
The results of this study could contribute to better treatments for diseases involving DNA damage, such as cancer and genetic disorders. By understanding more about how cells repair DNA breaks, researchers can target specific DNA repair mechanisms. “With precise knowledge of DNA repair, we can design new treatments that are both more effective and less harmful,” says De Luca.
About Job Kind
Jop Kind is group leader at the Hubrecht Institute, professor by special appointment of Single Cell Epigenomics at the Radboud University Nijmegen and Investigator at Oncode Institute. His group is interested in elucidating the role of chromatin and nuclear architecture in gene-regulation and DNA-repair. The Kind group develops new techniques, such as the recently developed DamID and m6ATracer techniques. These techniques enable them to study genome architecture and protein-DNA interactions in high resolution in single cells. The Kind group uses these techniques to study the role of genome architecture and chromatin context in temporal and spatial control of gene expression in development and disease.
About the Hubrecht Institute
The Hubrecht Institute is a research institute focused on developmental and stem cell biology. Because of the dynamic character of the research, the institute as a variable number of research group, around 20, that do fundamental, multidisciplinary research on healthy and diseased cells, tissues and organisms. The Hubrecht Institute is a research institute of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences (KNAW), situated on Utrecht Science Park. Since 2008, the institute is affiliated with the UMC Utrecht, advancing the translation of research to the clinic. The Hubrecht Institute has a partnership with the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL). For more information, visit www.hubrecht.eu.
END
DNA repair: A look inside the cell’s ‘repair café’
2024-11-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Astronomers take the first close-up picture of a star outside our galaxy
2024-11-21
“For the first time, we have succeeded in taking a zoomed-in image of a dying star in a galaxy outside our own Milky Way,” says Keiichi Ohnaka, an astrophysicist from Universidad Andrés Bello in Chile. Located a staggering 160 000 light-years from us, the star WOH G64 was imaged thanks to the impressive sharpness offered by the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope Interferometer (ESO’s VLTI). The new observations reveal a star puffing out gas and dust, in the last stages before it becomes a supernova.
“We discovered an ...
Here’s something Americans agree on: Sports build character
2024-11-21
COLUMBUS, Ohio – In a polarized nation, there is one thing that nearly all Americans agree on, according to a recent study: Sports are good for us.
Researchers from The Ohio State University and Ithaca College found that more than 9 out of 10 Americans agreed that sports build character and improved one’s health, while 84% agreed playing sports makes one popular in school and 85% said it makes one more well-known in the community.
According to 67% of those surveyed, playing sports even leads to better grades in school.
While these beliefs may seem harmless, ...
Engineering nature’s blueprint: Dendron-based assemblies for chlorophyll’s materials
2024-11-21
Researchers often look to photosynthesis—a process that turns sunlight into chemical energy in plants and bacteria—as a model for innovation. Photosynthesis is in turn linked to chlorophyll pigments, tiny green molecules that play a key role in harvesting light. Naturally, these chlorophyll molecules are organized into precise structures to optimize light absorption in plants and bacteria, and efficiently capture sunlight for energy. Inspired by this natural structure, scientists have explored ways to synthetically assemble chlorophyll-based ...
Study reveals how cell types shape human brain networks
2024-11-21
Rutgers researchers at the Brain Health Institute (BHI) and Center for Advanced Human Brain Imaging Research (CAHBIR) have uncovered how different types of brain cells work together to form large-scale functional networks in the human brain – interconnected systems that support everything from sensory processing to complex decision-making – paving the way for new insights into brain health and disease.
By pinpointing these cellular foundations, the study, published in Nature Neuroscience, offers a deeper understanding of the cellular foundations of cognition and mental health.
The brain’s functional properties arise from the varied ...
New genetic explanation for heart condition revealed
2024-11-21
A potentially life-changing heart condition, dilated cardiomyopathy, can be caused by the cumulative influence of hundreds or thousands of genes and not just by a single “aberrant” genetic variant, as was previously thought, finds a new study led by researchers at UCL (University College London), Imperial College London and the MRC Laboratory of Medical Sciences.
Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a condition in which the heart becomes progressively enlarged and weakened, reducing its ability to pump blood efficiently. It is estimated to affect up to 260,000 people in the UK (one in every 250 individuals) and is the leading cause of heart transplantation.
Previously, ...
Poor mental health linked to browsing negative content online
2024-11-21
People with poorer mental health are more prone to browsing negative content online, which further exacerbates their symptoms, finds a study led by UCL researchers.
The relationship between mental health and web-browsing is causal and bi-directional, according to the Wellcome-funded study published in Nature Human Behaviour.
The researchers have developed a plug-in tool* that adds ‘content labels’ to webpages—similar to nutrition labels on food—designed to help users make healthier and more informed decisions about the ...
People with migraine at high risk of depression during pandemic
2024-11-21
Toronto, ON – A recent longitudinal study from the University of Toronto reveals the mental health consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic on older adults living with migraine.
Using a sample of more than 2,000 older adults with migraine from the Canadian Longitudinal Study on Aging, researchers examined changes in depression status among this population during the pandemic. More than 1 in 7 older adults with migraine experienced depression for the first time during the COVID-19 pandemic, while approximately 1 in 2 with a previous history of depression experienced a recurrence during this period.
“People ...
Climate-driven hazards increases risk for millions of coastal residents, study finds
2024-11-21
A new study published in Nature Climate Change estimates that a 1-meter sea level rise by 2100 would affect over 14 million people and $1 trillion worth of property along the Southeast Atlantic coast, from Norfolk, Virginia, to Miami, Florida.
The study assesses the cumulative impact of multiple climate-driven coastal hazards, including sea level rise, flooding, beach erosion, sinking land, and rising groundwater, all of which are expected to worsen significantly by the end of the 21st century.
The scale of these interconnected ...
Females sleep less, awaken more frequently than males
2024-11-21
Females sleep less, wake up more often and get less restorative sleep than males, according to a new animal study by CU Boulder researchers.
The findings, published in the journal Scientific Reports, shed new light on what may underlie sleep differences in men and women and could have broad implications for biomedical research, which for decades has focused primarily on males.
“In humans, men and women exhibit distinct sleep patterns, often attributed to lifestyle factors and caregiving roles,” said senior author Rachel Rowe, assistant professor of integrative physiology. “Our results suggest that biological ...
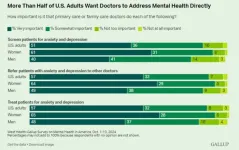
Most Americans want primary care providers to address mental health
2024-11-21
WASHINGTON, D.C. — Nov. 21, 2024 — A majority of Americans (70%) say they would prefer to be asked about both their physical and mental health during medical appointments with their primary care providers (PCPs). The finding from the new West Health-Gallup Survey on Mental Health in America comes as more than one in five U.S. adults, or 59.3 million people, were living with a mental illness in 2022, and little more than half of them (50.6%) received treatment within the prior year.
According to the survey, majorities of men (65%) and women (76%) are eager to discuss both their mental and physical health with their primary ...