(Press-News.org) A new study published in Nature Climate Change estimates that a 1-meter sea level rise by 2100 would affect over 14 million people and $1 trillion worth of property along the Southeast Atlantic coast, from Norfolk, Virginia, to Miami, Florida.
The study assesses the cumulative impact of multiple climate-driven coastal hazards, including sea level rise, flooding, beach erosion, sinking land, and rising groundwater, all of which are expected to worsen significantly by the end of the 21st century.
The scale of these interconnected hazards is much greater than anticipated, said study co-author Manoochehr Shirzaei from Virginia Tech’s Department of Geosciences.
“The risk of flooding, compounded by sinking land and beach loss, could displace millions and damage critical infrastructure unless robust adaptation strategies are implemented,” said Shirzaei.
Key findings
Shallow groundwater hazards: By 2100, 70 percent of the coastal population will be exposed to shallow or emerging groundwater, a far more significant exposure than daily flooding. The research projects that this groundwater hazard will affect approximately $1 trillion in property value, creating new challenges for infrastructure such as roads, buildings, septic systems, and utilities.
Storm-driven flooding: Coastal storms and hurricanes will amplify the risk of flooding over land. With 1 meter of sea level rise, overland flooding will affect up to 50 percent of residents in the region, impacting $770 billion in property value.
Beach erosion and loss: The Southeast Atlantic region, known for its barrier islands and coastal ecosystems, could lose up to 80 percent of its sandy beaches with just 1 meter of sea level rise.
Land subsidence: In addition to sea level rise, many areas along the Southeast Atlantic coast are experiencing sinking land, called subsidence, which exacerbates the effects of rising seas.
Socioeconomic exposure: A significant portion of the population and property in the Southeast Atlantic will be exposed to multiple coastal hazards, which will disproportionately affect lower-income communities. As much as half the population in flood-prone areas will be exposed to risks from both groundwater and storm-driven flooding.
The study stresses the necessity of a holistic approach to coastal resilience that addresses the full spectrum of climate-related hazards.
“We need to rethink how we plan and build for the future, especially in highly vulnerable coastal regions,” said Shirzaei. “By including a wider range of climate hazards in resilience strategies, we can better protect our communities from the compounded effects of sea level rise and extreme weather.”
The study, led by Patrick Barnard of U.S. Geological Survey, was conducted using cutting-edge geospatial data and modeling tools developed in collaboration with academic institutions and government agencies. The researchers employed the Coastal Storm Modeling System and other state-of-the-art models to project potential coastal hazard impacts, providing a crucial resource for informed decision-making.
DOI: 10.1038/s41558-024-02180-2
END
Climate-driven hazards increases risk for millions of coastal residents, study finds
2024-11-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Females sleep less, awaken more frequently than males
2024-11-21
Females sleep less, wake up more often and get less restorative sleep than males, according to a new animal study by CU Boulder researchers.
The findings, published in the journal Scientific Reports, shed new light on what may underlie sleep differences in men and women and could have broad implications for biomedical research, which for decades has focused primarily on males.
“In humans, men and women exhibit distinct sleep patterns, often attributed to lifestyle factors and caregiving roles,” said senior author Rachel Rowe, assistant professor of integrative physiology. “Our results suggest that biological ...
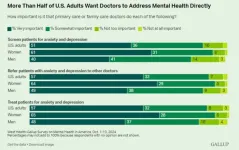
Most Americans want primary care providers to address mental health
2024-11-21
WASHINGTON, D.C. — Nov. 21, 2024 — A majority of Americans (70%) say they would prefer to be asked about both their physical and mental health during medical appointments with their primary care providers (PCPs). The finding from the new West Health-Gallup Survey on Mental Health in America comes as more than one in five U.S. adults, or 59.3 million people, were living with a mental illness in 2022, and little more than half of them (50.6%) received treatment within the prior year.
According to the survey, majorities of men (65%) and women (76%) are eager to discuss both their mental and physical health with their primary ...
Millions of Americans hurt by others’ drinking, drug use: study
2024-11-21
by Amy Norton
PISCATAWAY, NJ – The risks of alcohol and other drug consumption to the user are well known, but many Americans--nearly 160 million--say they’ve been harmed by someone else’s substance use, according to a new study in the Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs.
In a national survey of U.S. adults, researchers found that 34% said they’d ever suffered “secondhand harm” from someone else’s alcohol use--ranging from marriage and family problems to financial fall-out to being assaulted or injured in a drunk-driving accident. Meanwhile, 14% said they’d been harmed ...
Plasma-derived atomic hydrogen advances low-temperature CO2 methanation at high yield
2024-11-21
Plasma-derived atomic hydrogen (PDAH) enables low-temperature carbon dioxide methanation reaction through the Eley−Rideal-type reaction channel, improving methane yield at low temperatures, as shown by scientists at Science Tokyo. The findings underscore the potential of PDAH in advancing sustainable carbon dioxide recycling methods and optimizing other catalytic hydrogenation reactions, providing a promising avenue for improved efficiency in various energy and environmental technologies.
Despite declining reserves and significant carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions contributing to ...
Photon qubits challenge AI, enabling more accurate quantum computing without error-correction techniques
2024-11-21
The just-announced Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to University of Washington Professor David Baker, Google DeepMind CEO Hershavis, and Principal Investigator John Jumper for their work using AI to predict the structure of proteins, enabling the discovery of new drugs and new materials. In an era where AI and data are driving the scientific revolution, quantum computing technology is emerging as another game-changer in the development of new drugs and new materials.
Dr. Hyang-Tag Lim's ...
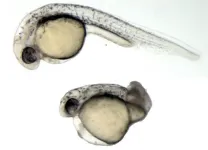
Single gene causes embryo notochord deformity in zebrafish
2024-11-21
Can a single protein-encoding gene determine whether a vertebrate embryo develops normally? Yes, according to Osaka Metropolitan University researchers, who found that suppression of Pcdh8 is essential for the notochord to elongate properly in zebrafish.
Graduate School of Medicine Dr. Masatake Kai and Professor Makoto Kondo focused on this paraxial protocadherin (PAPC), which is excluded when dividing cells migrate and form the notochord in the embryo.
In the experiments with zebrafish embryo, when this PAPC is not ...
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet - Nov 2024
2024-11-21
NOVEMBER TIP SHEET - SYLVESTER COMPREHENSIVE CANCER CENTER
CANCER RESEARCH
Sylvester Researchers to Share Insights at ASH 2024 Annual Meeting
Dozens of physician-scientists and other investigators from Sylvester Cancer will share their insights at ASH 2024, the American Society of Hematology’s 66th-annual meeting in San Diego, Dec. 7-10. Sylvester researchers will be involved in more than 130 presentations, including oral, poster and special sessions. Additionally, Sylvester Director Stephen D. Nimer, MD, will receive the 2024 ASH Mentor Award for his exemplary work in mentoring trainees and colleagues.
BREAST CANCER
The Cancer Journey: Asking For and Accepting Help
Journalist ...
AI speaks volumes when it comes to detecting Parkinson’s disease
2024-11-21
Algorithms that can detect subtle changes in a person’s voice are emerging as a potential new diagnostic tool for Parkinson’s disease, according to researchers from Iraq and Australia.
Speech impairments are often the first indicators of the fastest-growing neurological disease in the world, affecting more than 8.5 million people, but traditional diagnostic methods are often complex and slow, delaying early detection.
Researchers from Middle Technical University (MTU) in Baghdad and the University of South Australia (UniSA) have recently published a conference paper reviewing ...
Signals of inflammation during pregnancy linked to aging and memory changes 50 years later
2024-11-21
Findings from a Mass General Brigham-led study that has followed participants since before birth may offer clues about the origins of Alzheimer’s disease.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
Stress-related immune activity during the late second to early third trimester of pregnancy can have long-term sex-dependent effects on offspring memory circuitry, function, and decline that potentially increase vulnerability for memory disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease, after menopause.
Sex differences in immune function begin in fetal development ...
Two million ex-smokers currently vape in England
2024-11-21
About one in five people who have stopped smoking for more than a year in England currently vape, equivalent to 2.2 million people, according to a new study led by UCL (University College London) researchers.
The study, published in the journal BMC Medicine and funded by Cancer Research UK, found that this increased prevalence was largely driven by greater use of e-cigarettes in attempts to quit smoking.
However, the researchers also found a rise in vaping uptake among people who had already stopped smoking, with an estimated one in 10 ex-smokers who vape having quit smoking prior to 2011, when e-cigarettes ...